Molecular Analysis of the Two-Component CusS/CusR Regulon for Copper Resistance: Cloning, Phylogenetics, and Structural Modeling
Molecular Analysis of the Two-Component CusS/CusR Regulon for Copper Resistance: Cloning, Phylogenetics, and Structural Modeling
Soumble Zulfiqar* and Abdul Rauf Shakoori
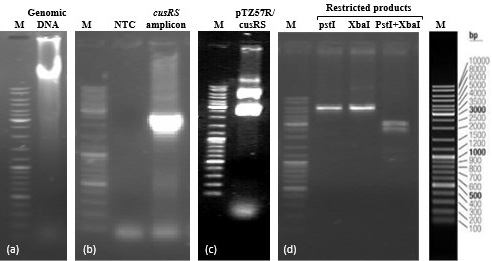
Clonig of cusRS. (a) Genomic DNA of K. pneumoniae KW (b) cusRS amplicon (2.316 kb) (c) recombinant plasmid pTZ57R/cusRS (d) Restriction products of single and double digestion of the recombinant plasmid. Lanes M represent DNA marker (Fermentas cat # SM0331).
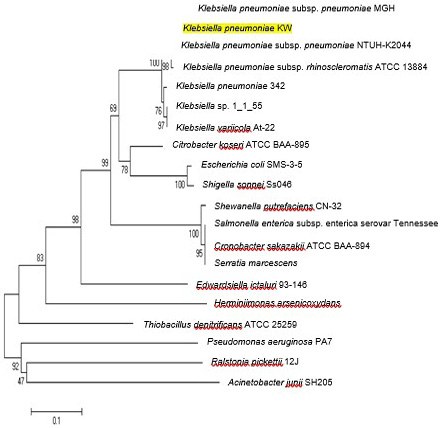
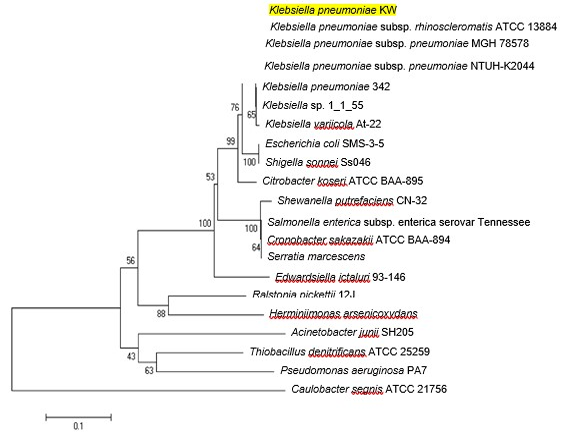
Neighbor joining trees showing relationship of CusS protein of K. pneumoniae KW among various bacterial strains. Bootstrap values expressed as a percentage of 1000 replications are given at branching points. In each tree, bar represents substitutions per residue position.
Neighbor joining trees showing relationship of CusR protein of K. pneumoniae KW among various bacterial strains. Bootstrap values expressed as a percentage of 1000 replications are given at branching points. In each tree, bar represents substitutions per residue position.
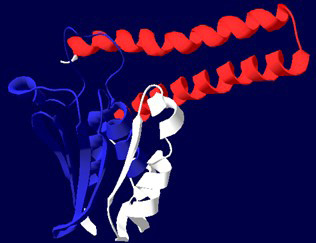
Ribbon diagram of CusS. His KA domain is shown in red colour and HATPase_C domain is blue.
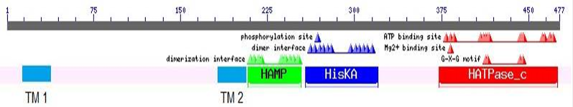
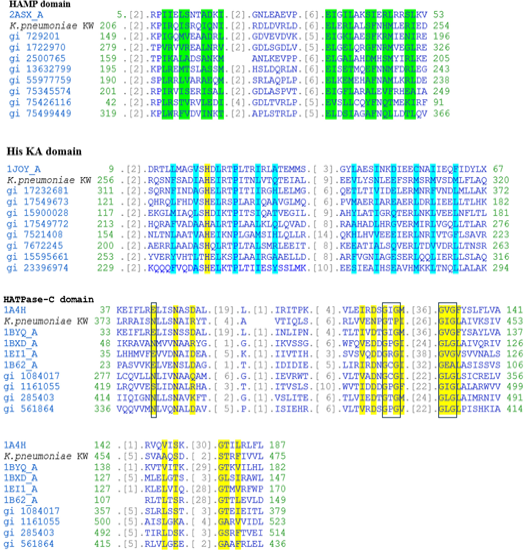
Multiple alignment of the three domains in CusS of K. pneumoniae KW along with related domain sequences found in CDD. In HAMP domain, residues involved in dimerization interface are highlighted with green colour. In His KA domain, phosphoacceptor site and residues involved in dimerization are highlighted with yellow and blue colours, respectively. In HATPase-C domain, residues involved in ATP binding are highlighted with yellow colour while Mg binding site and GXG motives are boxed with blue and black boundaries, respectively.
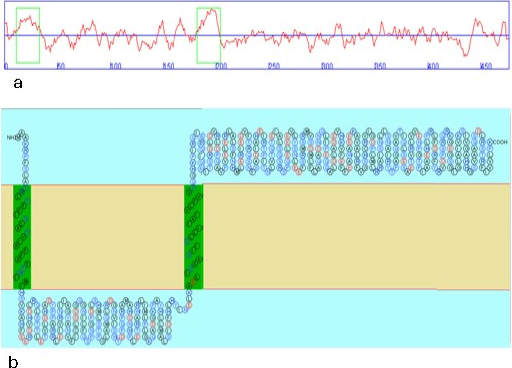
Topology of CusS. Hydropathic graph (a) reveals two trans membrane regions. Topological model (b) shows amino acid residues constituting the two trans membrane regions (shown in green boxes).
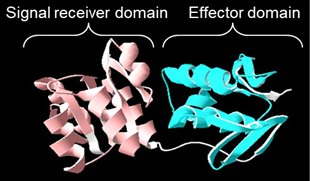
Ribbon diagram of response regulator CusR. CusR is composed of two domains. Signal receiver domain is shown in pink colour and effector domain is shown in blue colour.
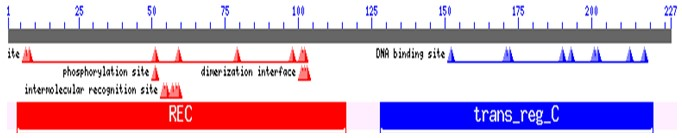
Structural organization of CusR. This protein is composed of Signal receiver domain (REC) followed by effector domain (trans-reg-C).
Musltiple alignment trans_reg_C domain in CusR of K. pneumoniae KW along with related protein sequences found in CDD. In REC domain, residues contributing active site are highlighted with yellow colour while phosphorylation site, dimerization interface and intermolecular recognition site are boxed with black, orange and red boundaries, respectively. In trans_reg_C domain, residues involved in DNA binding are highlighted with green colour.