Lemon Juice and Microwave Assisted Modification of Date Seed Husk for Arsenic Biosorption
Lemon Juice and Microwave Assisted Modification of Date Seed Husk for Arsenic Biosorption
Tahira Moeen Khan*, Irum Riaz, Shahida Hameed and Bushra Khan
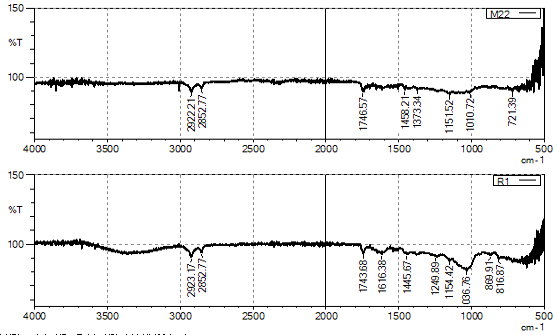
Overlay FTIR spectra of RDS and LMDS.
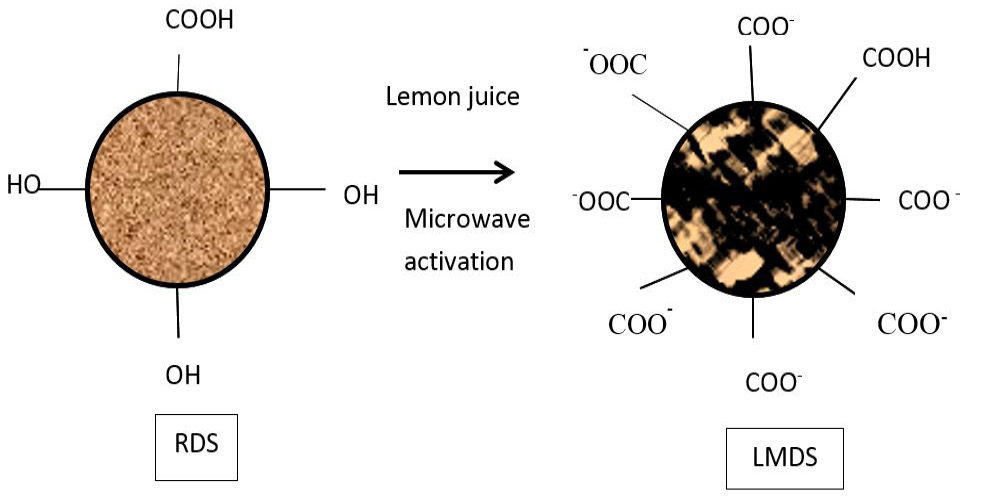
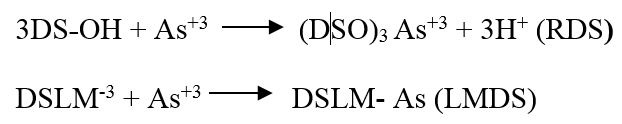
Surface modification of RDS with lemon juice and microwave radiation.
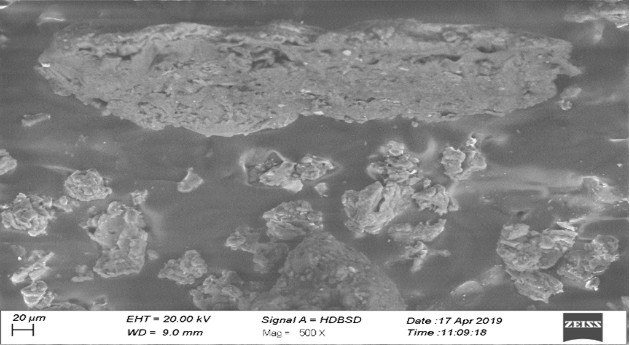
SEM image of RDS.
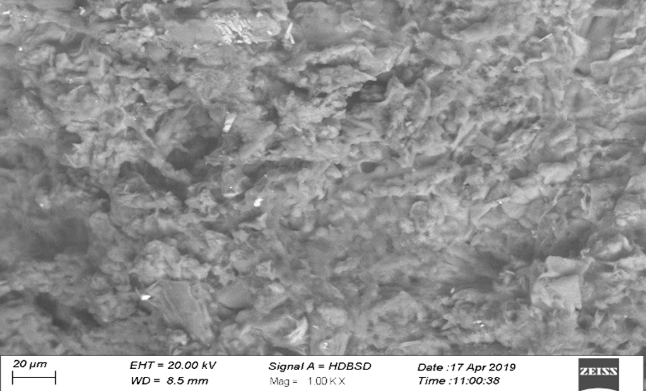
SEM image of LMDS.
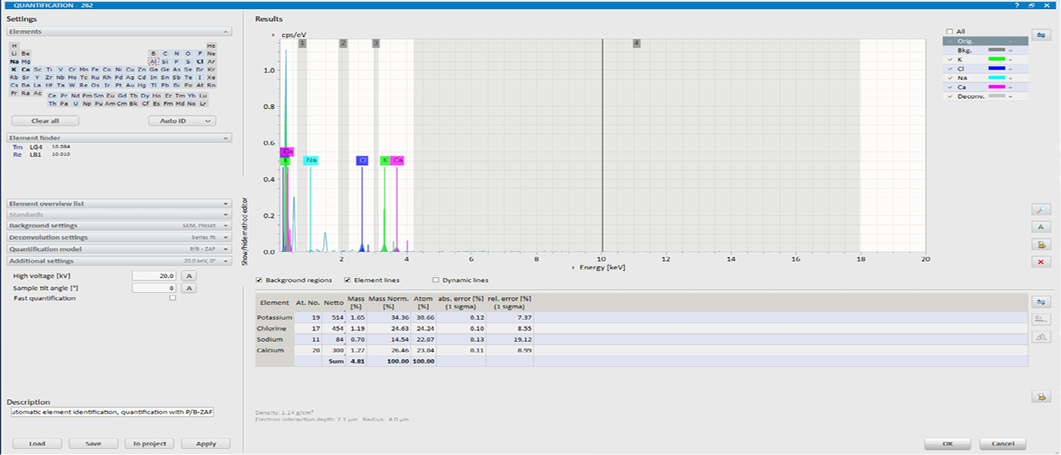
EDX image of LMDS without arsenic.
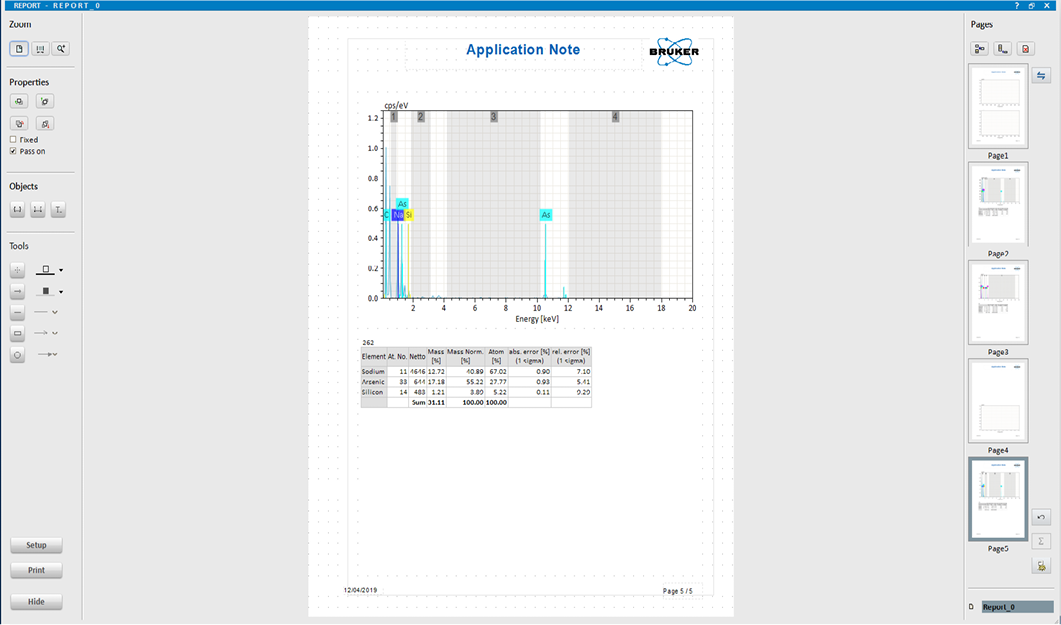
EDX image of LMDS with arsenic.
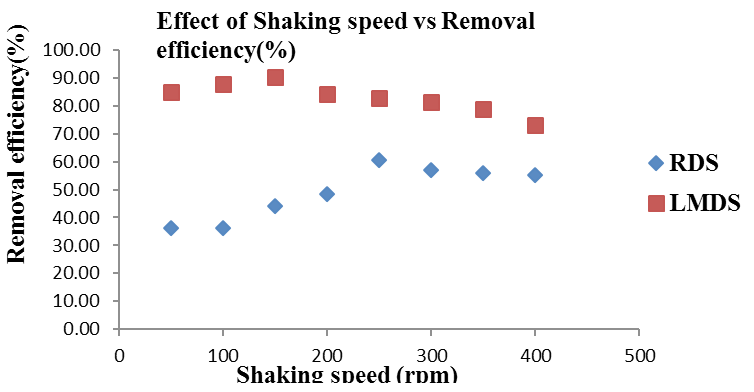
Effect of shaking speed for Arsenic removal onto RDS and LMDS. Adsorbent dose= 0.3 g, Solution concentration (25 ppm / 50 mL), Contact time= 30 minutes.
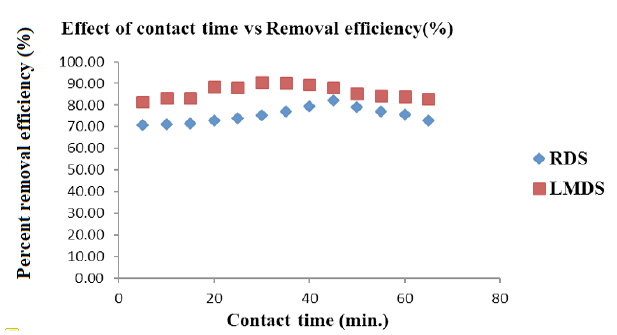
Effect of contact time for Arsenic removal onto RDS and LMDS. Adsorbent dose= 0.3 g, Shaking speed (RDS, LMDS= 250 rpm, 150 rpm), Solution concentration (25 ppm / 50 mL).
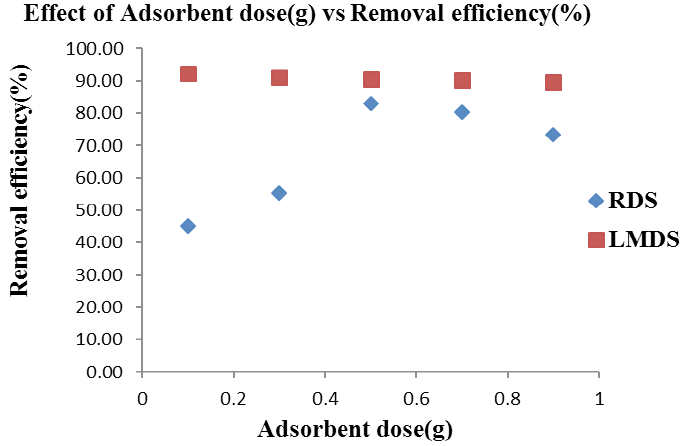
Effect of adsorbent dose (g) on Arsenic removal onto RDS and LMDS. Shaking speed (RDS, LMDS= 250rpm, 150 rpm), Solution concentration (25 ppm / 50 mL), Time= 30 minutes.
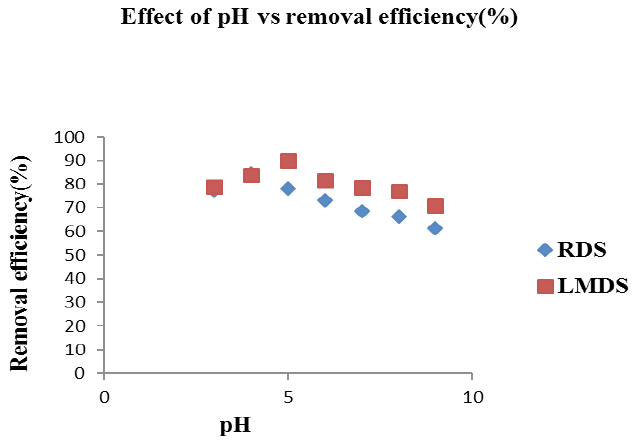
Effect of pH on lead removal onto RDS and LMDS. Adsorbent dose (RDS, LMDS= 0.3g), Shaking speed (RDS, LMDS= 250 rpm, 150 rpm), Solution concentration (25 ppm / 50m L), Time=30 minutes.
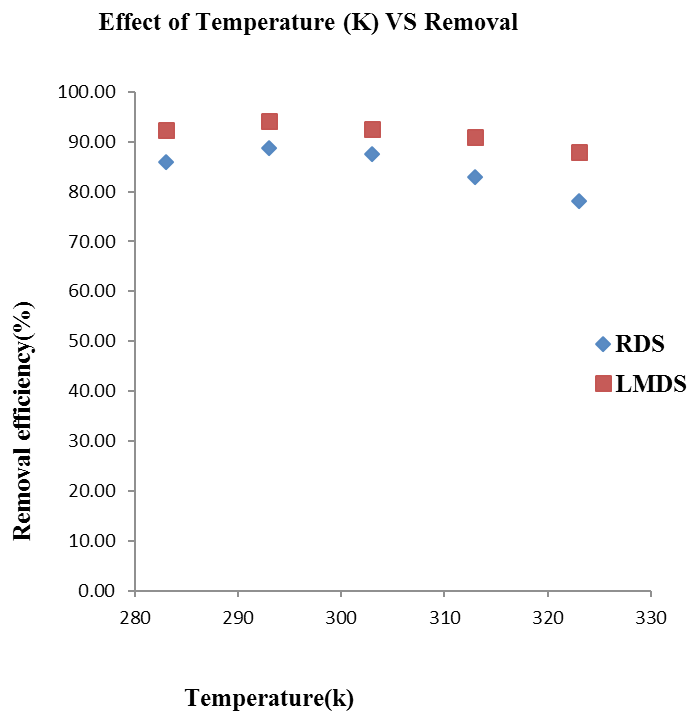
Effect of temperature (K) on Arsenic removal onto RDS LMDS. Adsorbent dose = 0.3g, Shaking speed (RDS, LMDS = 250 rpm, 150 rpm), Solution concentration (25 ppm / 50m L), Time=30 minutes.
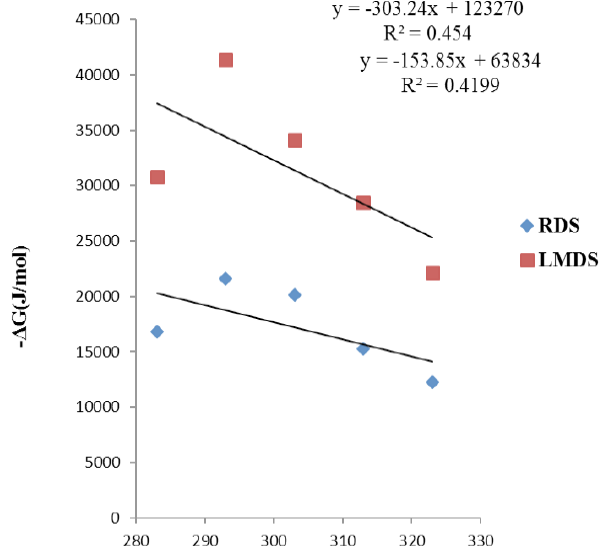
Thermodynamic study of RDS , LMDS.
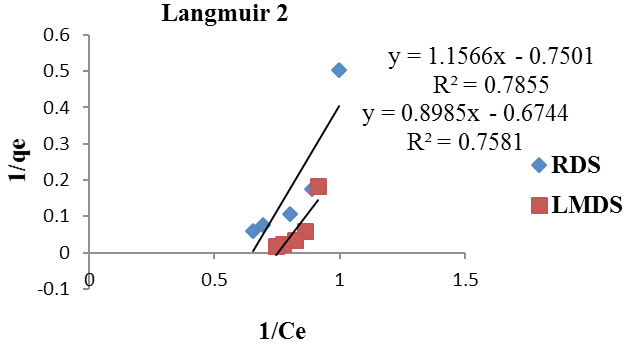
Langmuir 2 Isotherm for RDS, LMDS.
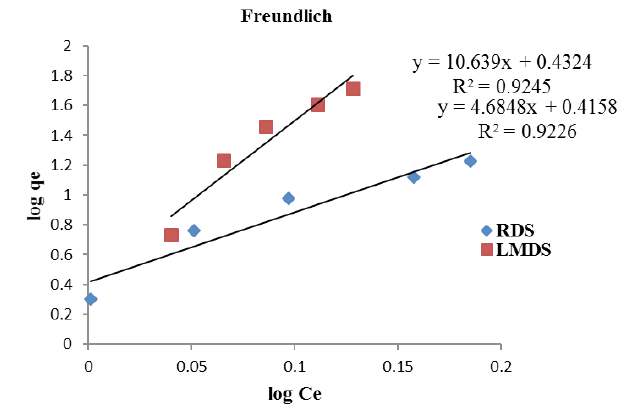
Freundlich Isotherm for RDS, LMDS.
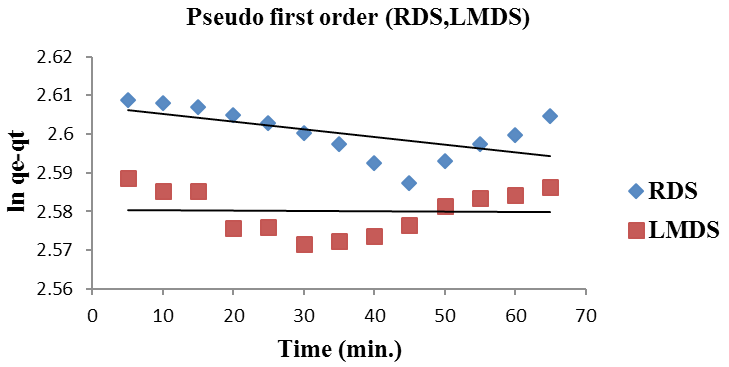
Pseudo first order kinetics for (RDS, LMDS).
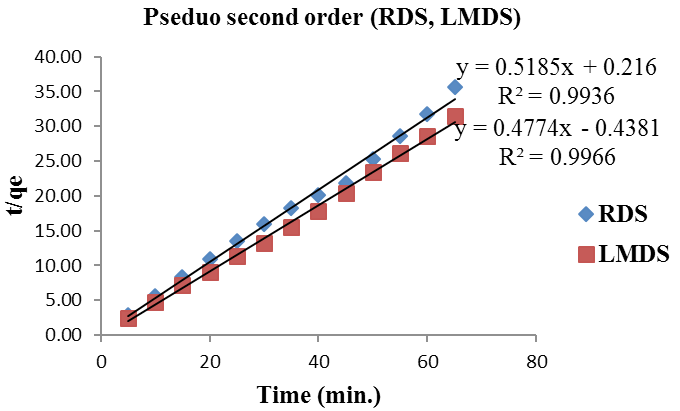
Pseudo second-order kinetics for (RDS, LMDS).