Isolation and Characterization of Medicinally Important Marine Penicillium Isolates
Isolation and Characterization of Medicinally Important Marine Penicillium Isolates
Ibrar Khan1,2,3,*, Sadia Qayyum2, Shehzad Ahmed2, Kashif Syed Haleem2, Mujaddad-ur-Rehman1, Guang-Lei Liu3 and Zhen-Ming Chi3
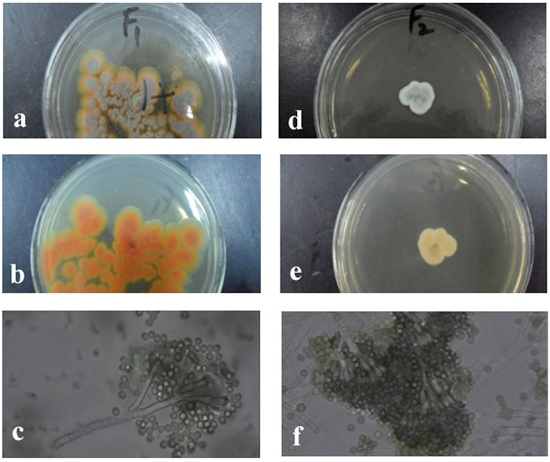
The colony morphology of the strain F1 (Penicillium viticola) F2 (Penicillium restrictum) (a, front; b, back; c, mycelium and the chains of its conidia).
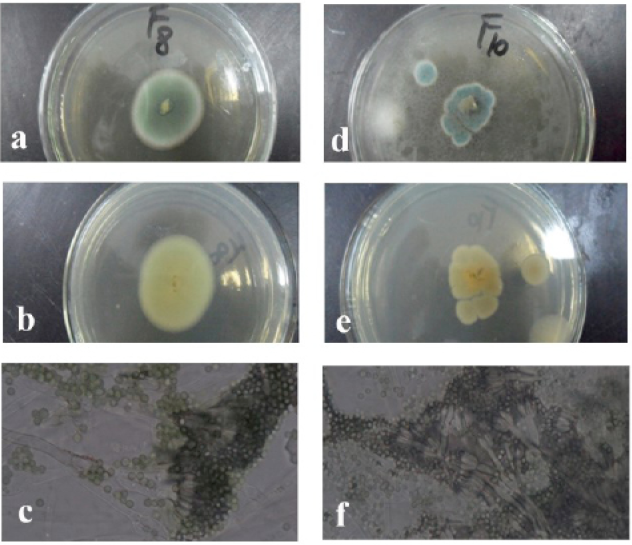
The morphologies of the colony of the strain F8 (Penicillium ruben) (a, front; b, back; c, mycelium and the chains of its conidia and the strain) F10 (Penicillium implicatum) (d, front; e, back; f, mycelium and the chains of its conidia).
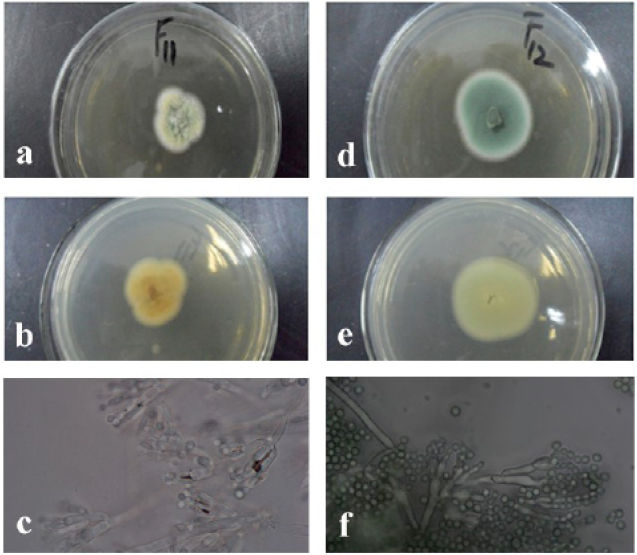
The morphologies of the colony of the strain F11 (Penicillium piceum) (a, front b, back and c, mycelium and the chains of its conidia; the strain F12 (Penicillium oxalicum) (d, front; e, back; f, mycelium and the chains of its conidia).
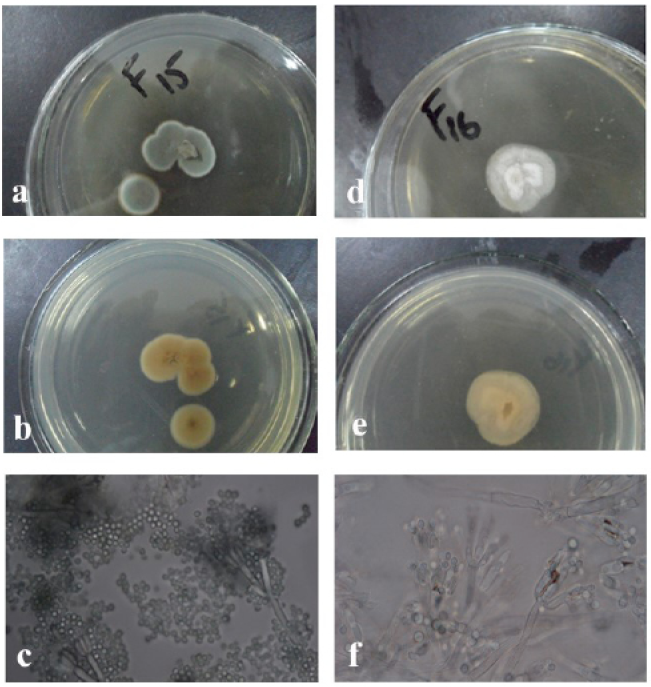
The morphologies of the colony of the strain F15 (Penicillium sumatrense) (a, front; b, back; c, mycelium and the chains of its conidia; the srain F16 (Penicillium vinaceum) (d, front; e, back; f, mycelium and the chains of its conidia).
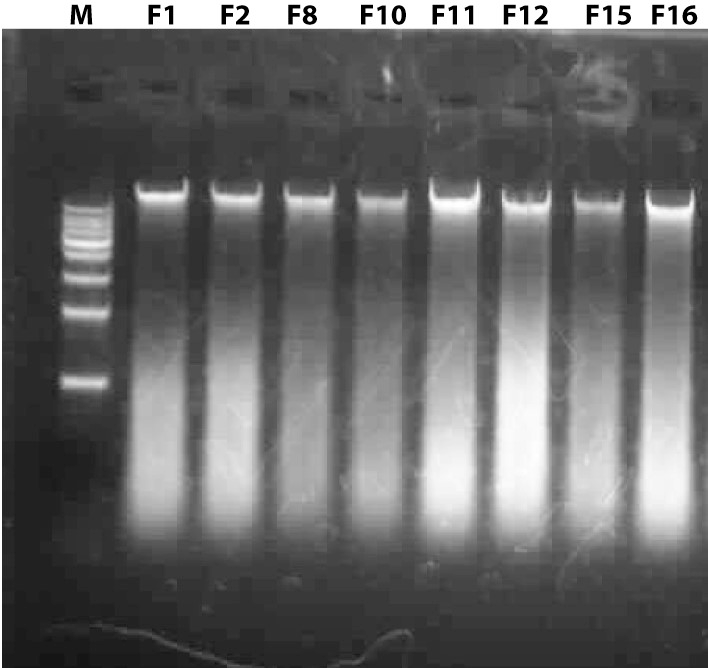
Genomic DNAs of the fungal isolates; lane M: 1 kb DNA ladder, Lane F1, F2 F8, F10, F11, F12, F15, and F16 are the genomic DNAs of them.
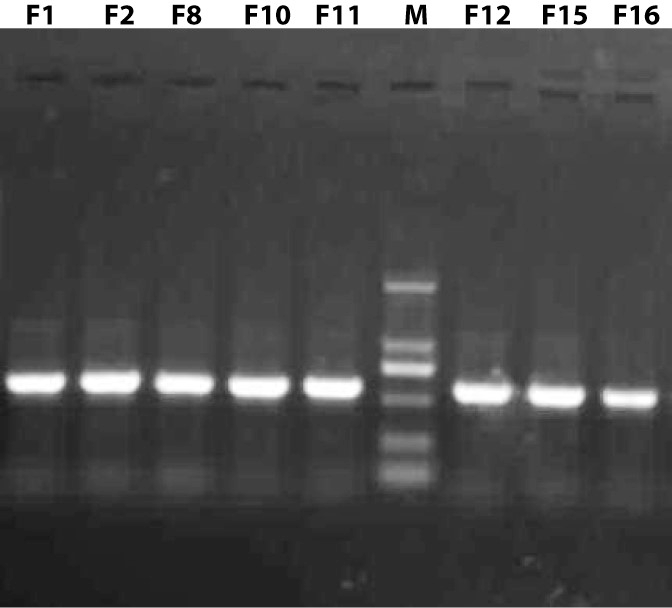
Resolving pattern of PCR amplified ITS sequences on 1% Agarose gel; Lanes F1, F2, F8, F10, F11, F12, F15, and F16 showed PCR products of the fungal isolates and Line M: DNA ladder, fragment size from top to bottom is 2000bp, 1000bp, 750bp, 500bp, 250bp and100bp.
The phylogenetic tree of the all fungal isolates and other Penicillium species relatives based on a neighbor-joining analysis of ITS sequences. Aspergillus flavus CBS 260.73 was used as out group.