Ionic Composition of Wheat in Response to Silicon Application under Saline Growth Environment
Ionic Composition of Wheat in Response to Silicon Application under Saline Growth Environment
Mukkram Ali Tahir1, Noor-us-Sabah1*, Ghulam Sarwar1, Muhammad Aftab2, Abdul Moeez1, Muhammad Zeeshan Manzoor1 and Aneela Riaz3
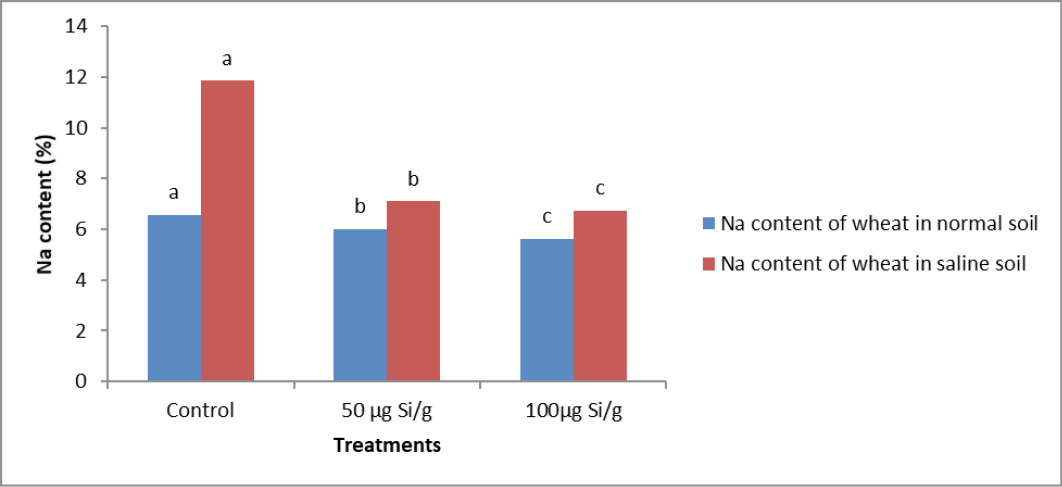
Impact of various silicon concentrations on Na content of wheat shoot (%) under normal and salt affected soils.
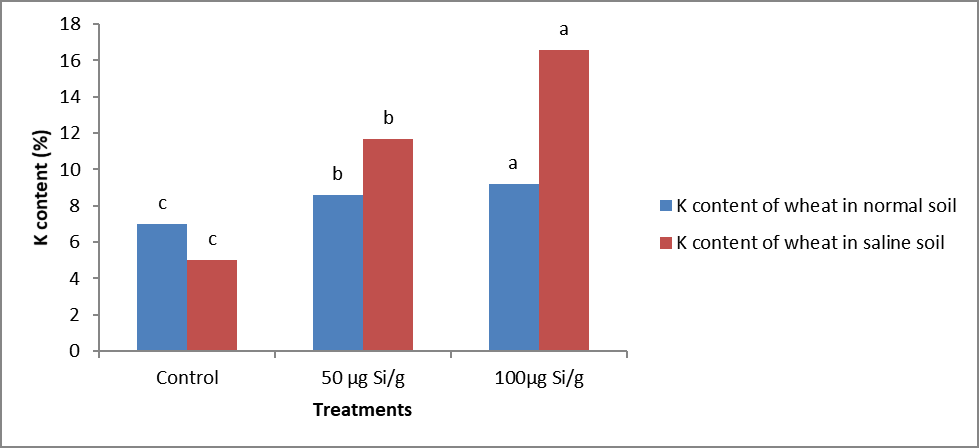
Impact of various silicon concentrations on K content of wheat shoot (%) under normal and salt affected soils.
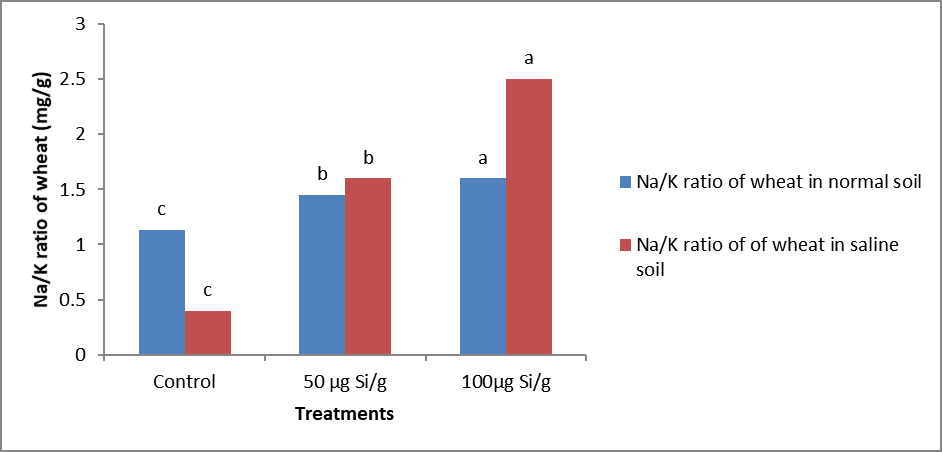
Impact of various silicon concentrations on Na/K ratio of wheat (mg/g) under normal and salt affected soils.
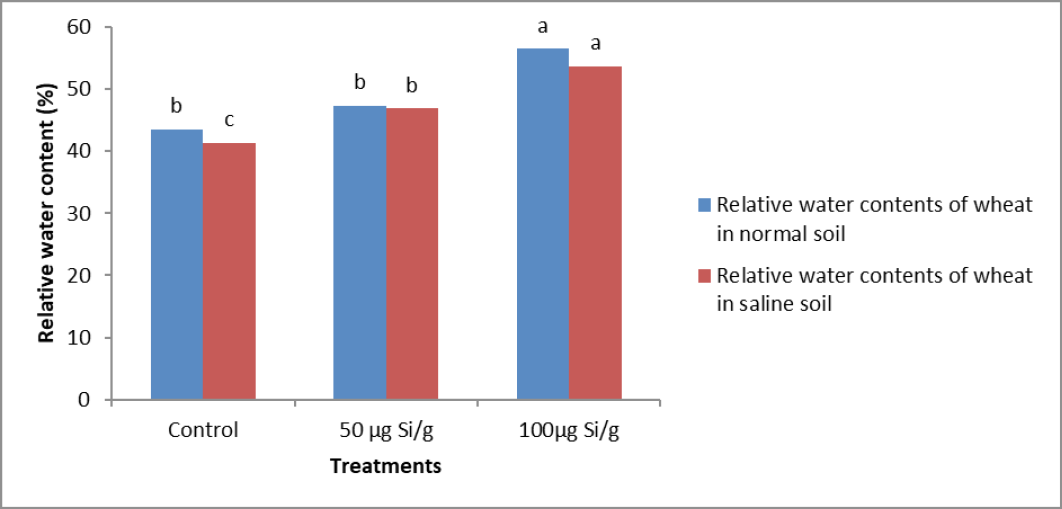
Impact of various silicon concentrations on relative water content of wheat (%) under normal and salt affected soils.
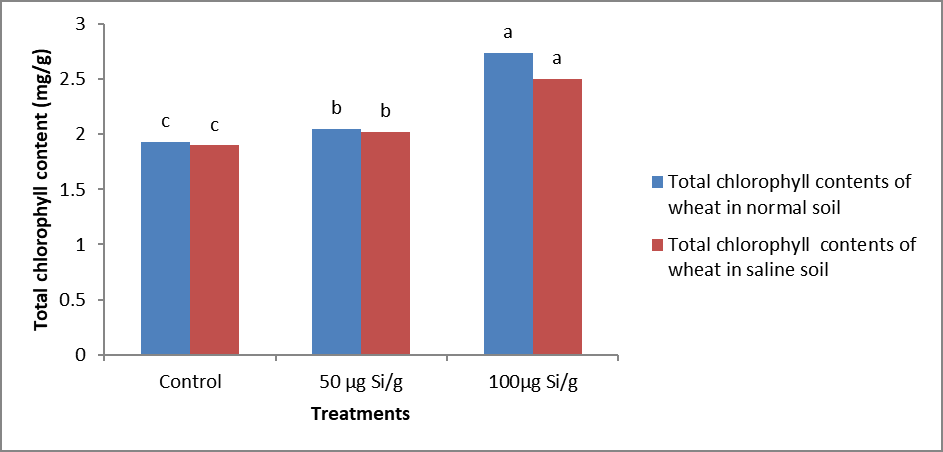
Impact of various silicon concentrations on total chlorophyll content of wheat (%) under normal and salt affected soils.