Insight into the Mechanism of Doxorubicin-induced Nephrotoxicity through Gene Expression Analysis of Oxidative Stress, Kidney Injury and Inflammation Markers
Insight into the Mechanism of Doxorubicin-induced Nephrotoxicity through Gene Expression Analysis of Oxidative Stress, Kidney Injury and Inflammation Markers
Uzma Jabeen1, Asmat Salim2*, Irfan Khan2, Nadia Naeem3 and Rubina Mushtaq4
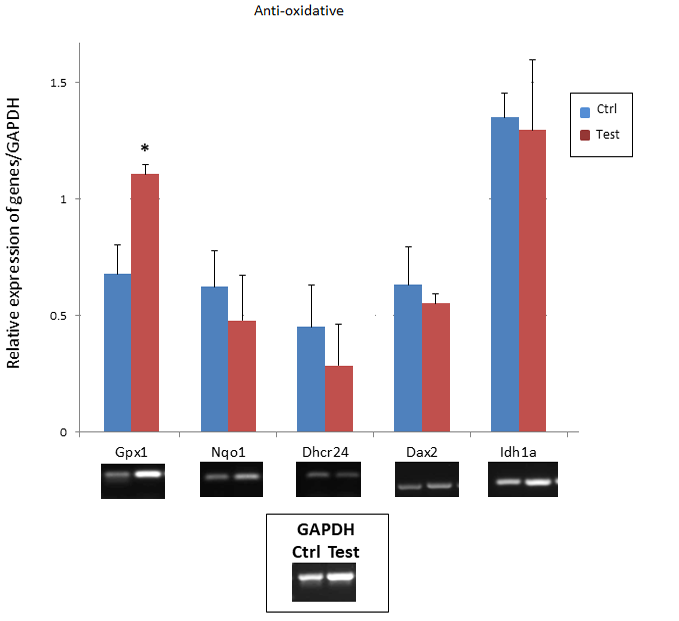
Agrose gels showing RT-PCR expression analysis of the oxidative stress induced genes, glutathione peroxidase-1(Gpx1), NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 (Nqo1), 24-dehydrocholesterol reductase (Dhcr24), dual oxidase 2 (Duox2), and isocitrate dehydrogenase-1 (Idh1) in the kidney tissue following DOX injection (3 mg / kg; i.p.) in SD rats. All data are expressed as the means ± standard error of the mean. Data were subjected to Student’s t-test and values corresponding to P < 0.05 is considered statistically significant.
Agrose gels showing RT-PCR gene expression analysis of the anti-inflammatory cytokine, interleukin-10 (IL10) in the kidney tissue following DOX injection (3 mg / kg; i.p.) in SD rats. All data are expressed as the means ± standard error of the mean. Data were subjected to Student’s t-test and values corresponding to P < 0.05 is considered statistically significant.
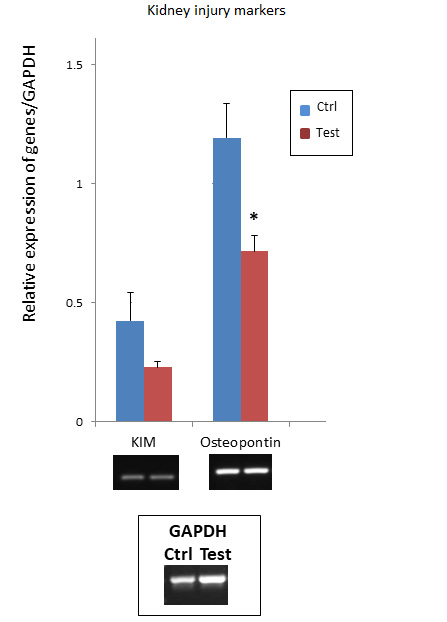
Agrose gels showing RT-PCR gene expression analysis of the kidney injury biomarkers, kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) and osteopontin (OPN) in the kidney tissue following DOX injection (3 mg / kg; i.p.) in SD rats. All data are expressed as the means ± standard error of the mean. Data were subjected to Student’s t-test and values corresponding to P < 0.05 is considered statistically significant.