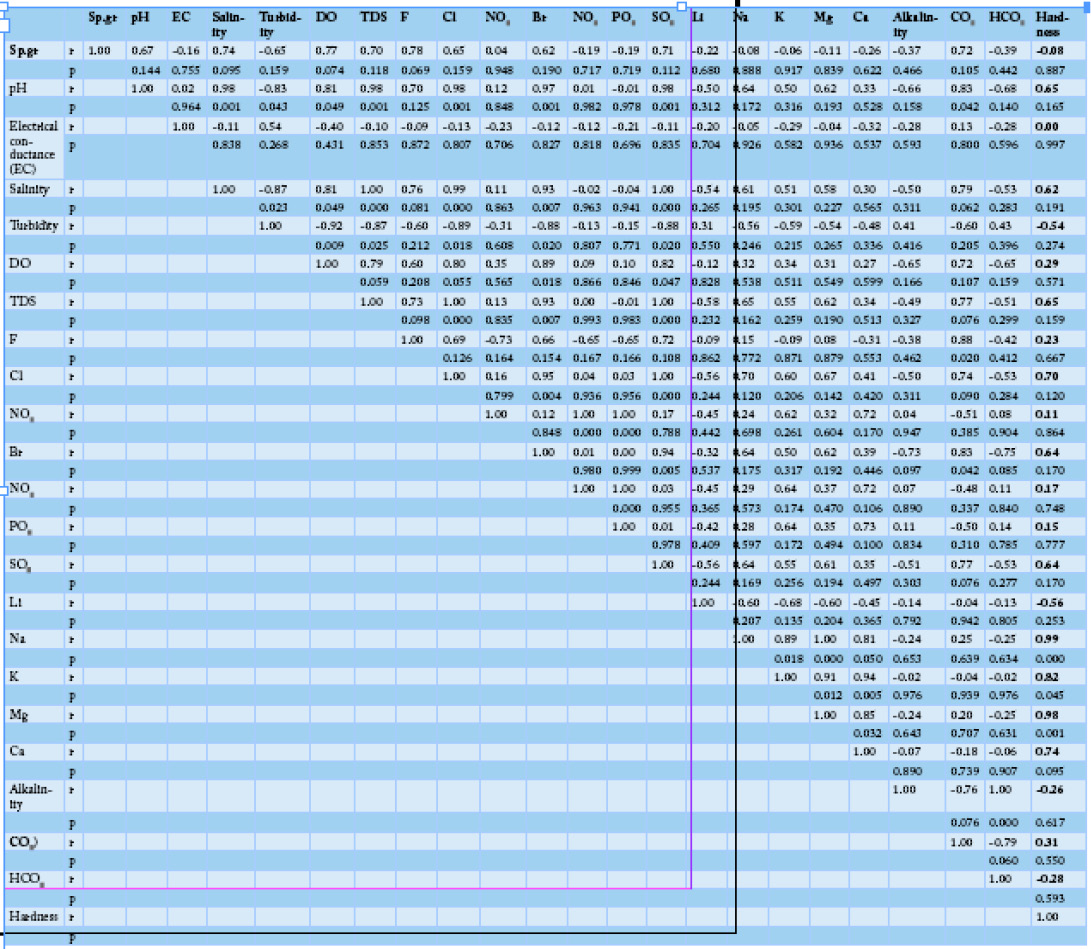
Influence of Parasite Infestation and Water Quality Deterioration During Mass Fish Mortality Event in Manzala Lake and its Corresponding Fish Farms
Influence of Parasite Infestation and Water Quality Deterioration During Mass Fish Mortality Event in Manzala Lake and its Corresponding Fish Farms
Magdy M. Fahmy1, Nisreen E. Mahmoud 1*, Mohamed R. Mousa2, Manal M. Zaki3, Elshaimaa Ismael3, Mai Abuowarda1
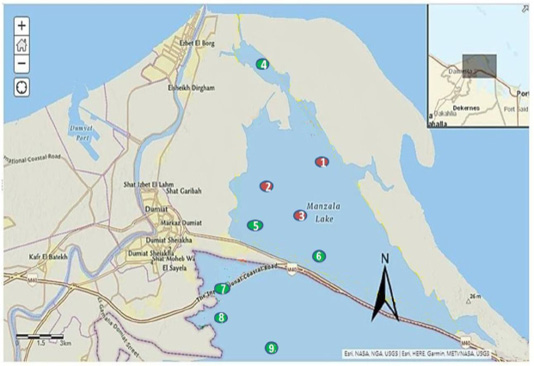
Manzala Lake Map showed the sites of sampling: (1-3) Marine fish farms in the northern area in Manzala Lake, (4-9) Free fishing areas of Manzala Lake, (5) Berket Shata, (6) El-Saiala, (7) El-Zarka, (8) Al-Homra. (9) El-Hosayneya. Map was carried out using ArcGIS (ArcMap) version 10.1 Software.
Field visits findings: (a) Greenish to brownish putrified algae copvering large areas of water surface under which small dead fishes were detected, (b) Large quantities of moldy waste products were picked up on both sides of the lake, (c) Dreger and suction machines worked in the lake during the mass mortality, (d) Variations of the lake water color in different locations. (e) Mass mortality of different species of fish scattered in farm ponds and along their bridges as well as in Manzala water; f: A. regius, g: D. labtax., h: Sparus aurata.
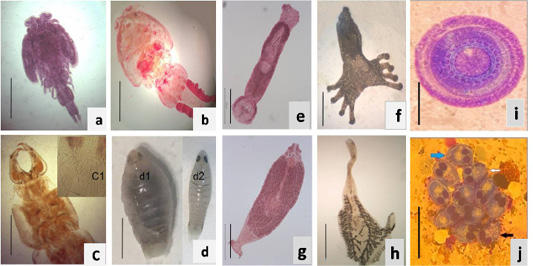
The isolated ectoparasite species: Crustacean species; (a) Caligus elongatus male, (b) Caligus species female (c) Learnanthropus kroyeri anterior end, (c1) Learnanthropus kroyeri posterior end, scale bar=0.4mm.(d) Livoneca redmani.(d1)Adult female. (d2) Juvenile stage, scale bar=0.7mm. Monogenean species; (e) Furnistinia echeneis. (f) Diclidophora merlangi, (g) Diplectanum aequanus, (h) Loxuroides spp. Scale bar=0.2 mm in a &c. Scale bar=0.5mm in b &d. Protozoan species : (Giemsa stain); (i) Trichodina truttae, scale bar=40 μm (b) Myxobolus tilapae stained spore, scale bar=20 μm. in a and b.
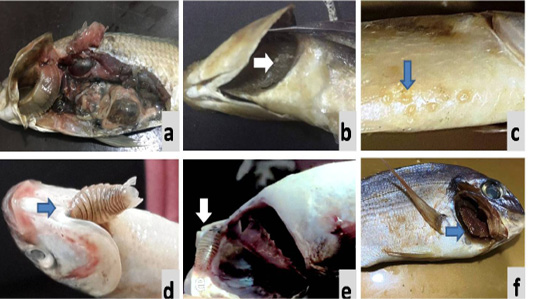
Macroscopic and Postmortem lesions: (a) affected Tilaplia species showed paleness of gills and internal organs, (b) Gills of Mugil spp. infested with Caligus species, (c) Skin of Mugil spp. infested with Caligus elongatus, (d) Mugil specie showed adult isopod Livoneca redmaniiin branchial cavity, (e) D. labrax showed isopods attached to the operculum, (f) S. aurata showed congestion of gills.
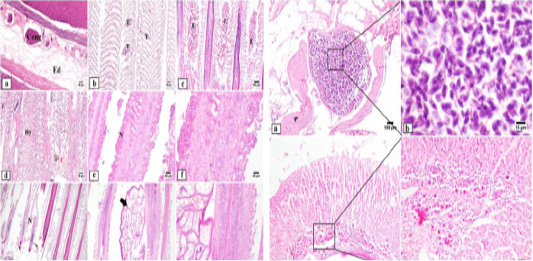
Photomicrograph of gills: Marked diffuse edema and severely congested blood vessels are seen in gill arch (a). Multifocal lamellar telangiectasia is noticed in affected gills (b). Heavy eosinophilic granular cells infiltration with variable number of inflammatory cells (c). Hyperplasia of the secondary gill lamellae admixed with necrosis of adjacent gill elements (d). Sever destruction and necrosis in the secondary gill lamellae with inflammatory cells infiltration (e-g). Attached isopod spp. (arrow) to the surface of gills with intense inflammatory reaction (h-i). Edema (Ed), congestion (Cong), telangiectasia (T), necrosis (N), hyperplasia (Hy), eosinophilic granular cells (E). Photomicrograph of subcutaneous and intestine of fish: Subcutaneous tissue showing Myxosporidian cysts with higher magnification showing numerous myxobolus spores (j-k). Intestine of fish showing edema of mucosa associated with intense inflammatory cells infiltration in the sub epithelial layer (l). Intestine of fish showing higher power of inflammatory cells infiltration with numerous numbers of eosinophilic granular cells (m).