In Silico Analysis of Genome Wide Non-Synonymous Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Indigenous Cattle Breeds of Pakistan
In Silico Analysis of Genome Wide Non-Synonymous Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Indigenous Cattle Breeds of Pakistan
Umer Farooq1,2, Nimra Murtaza2, Abubakar Siddique1, Bilal Saleem1, Obaid Ur Rehman1, Nageen Zahra1, Muhammad Uzair1, Muhammad Naeem Riaz1,3* and Muhammad Ramzan Khan1*
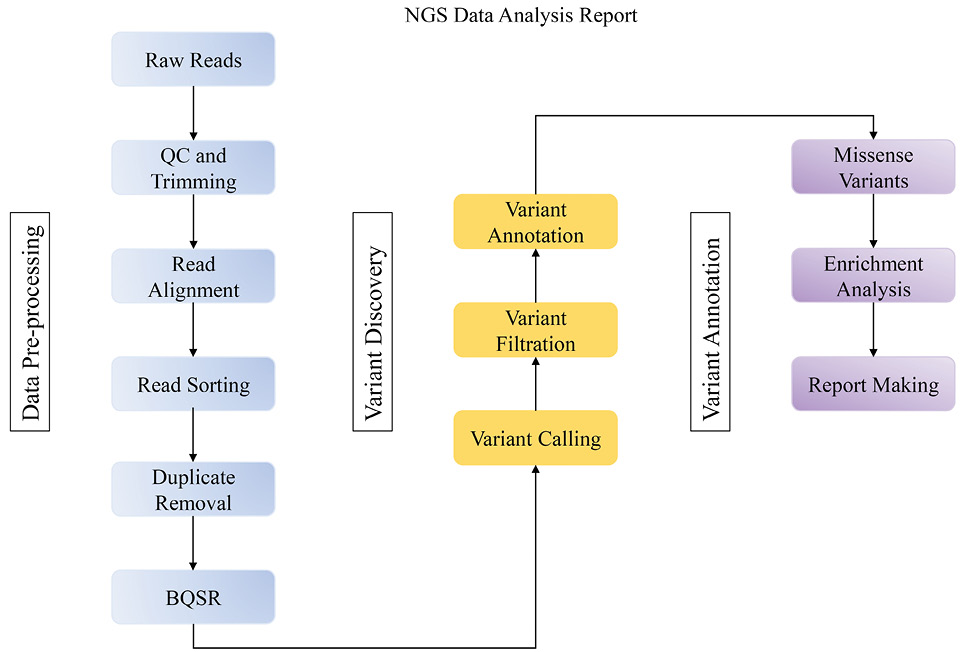
Bioinformatics workflow for analyzing whole genome sequencing data.
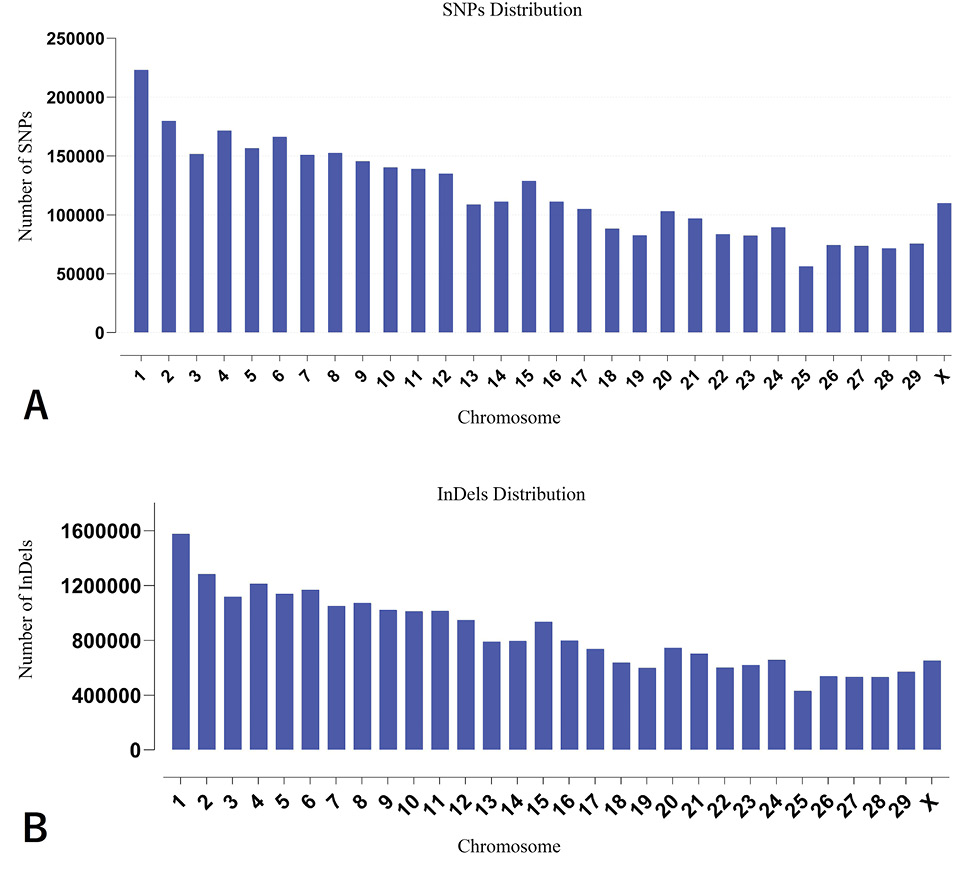
Number of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) distribution by chromosome (A) and number of insertion/deletions (InDels) distribution by chromosome (B).
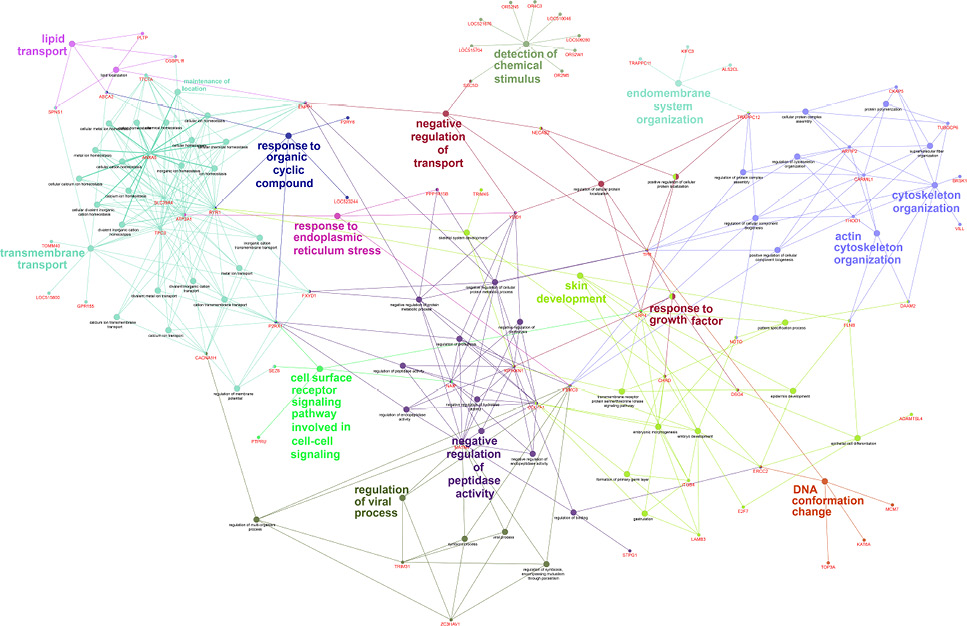
ClueGO gene ontology analysis of 134 genes with deleterious nsSNP identified in all samples. ClueGO identifies the enriched go terms and visualizes them in grouped annotation network. This network shows the relationship between the terms based on the similarity of their associated genes. Each node represents a gene ontology term and the associated genes.