Improve the Soil Properties under Two Different Methods (i.e., Tillage Practices and Organic Manuring) of the Wheat Crop
Improve the Soil Properties under Two Different Methods (i.e., Tillage Practices and Organic Manuring) of the Wheat Crop
Manzoor Ali Magsi1*, Naimatullah Laghari1, Ahmed Ali Tagar1, and Habibullah Magsi2
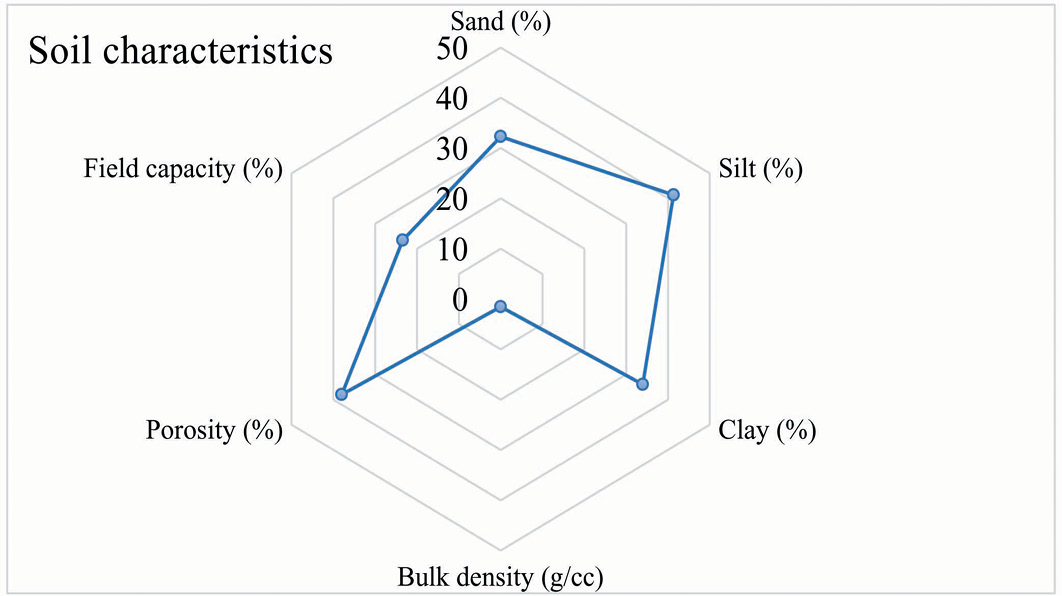
Soil characteristics of experimental site area.
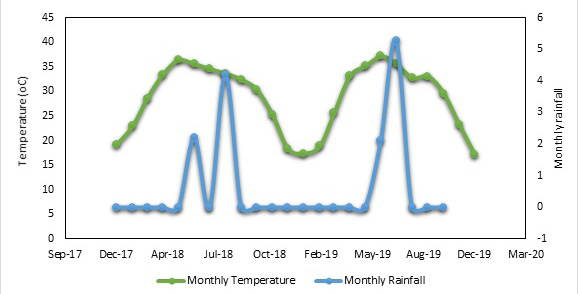
Monthly metrological data of the experimental site.
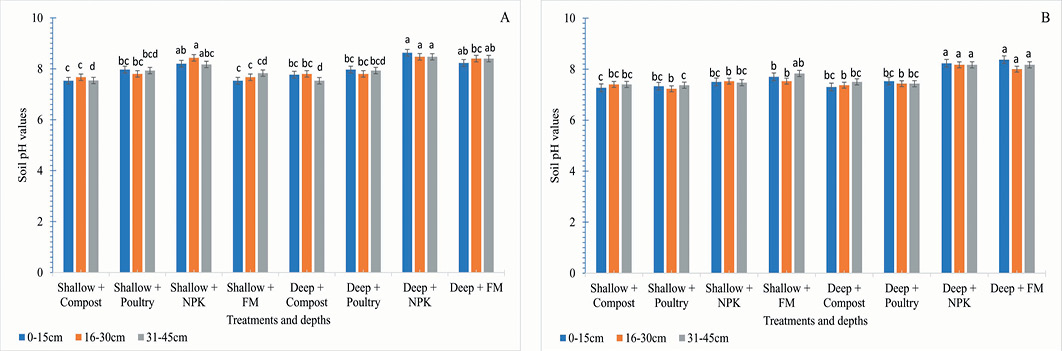
Effect of tillage intensity, fertilizer and manuring on pH values were determined (A) 2019-20 and (B) 2020-21.
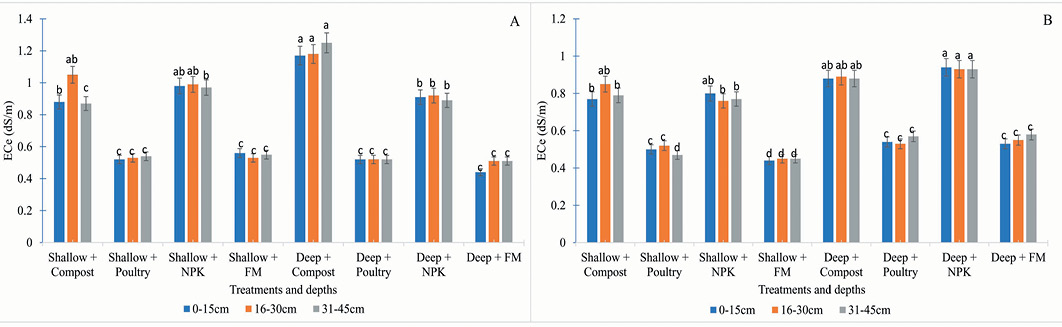
Effect of tillage intensity, fertilizer and manuring on ECe (dS/m) were determined (A) 2019-20 and (B) 2020-21.
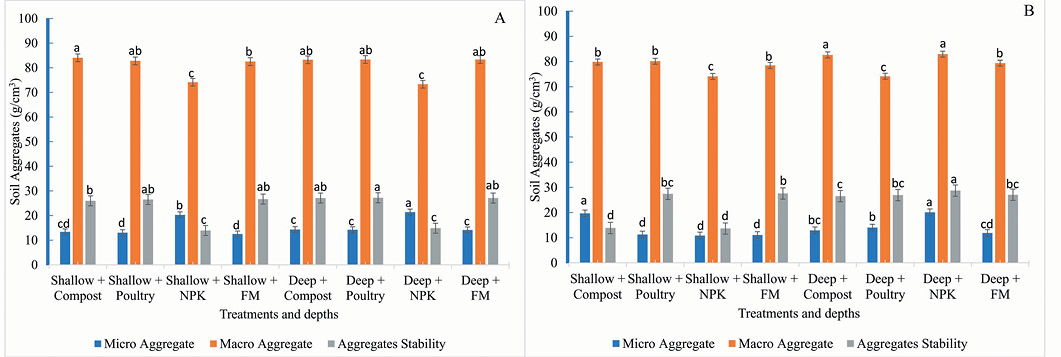
Effect of tillage intensity, fertilizer and manuring on soil aggregates with wheat crop during 2019-20 (A) and 2020-21 (B).
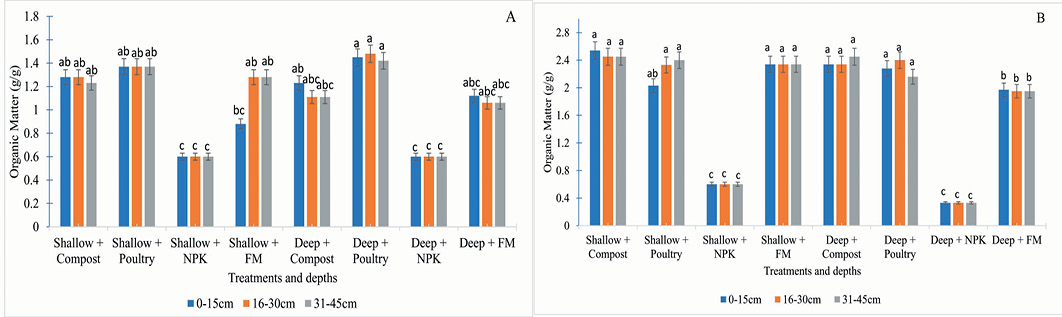
Effect of tillage intensity, fertilizer and manuring on organic matter during the year 2019-20 (A) and 2020-21 (B).
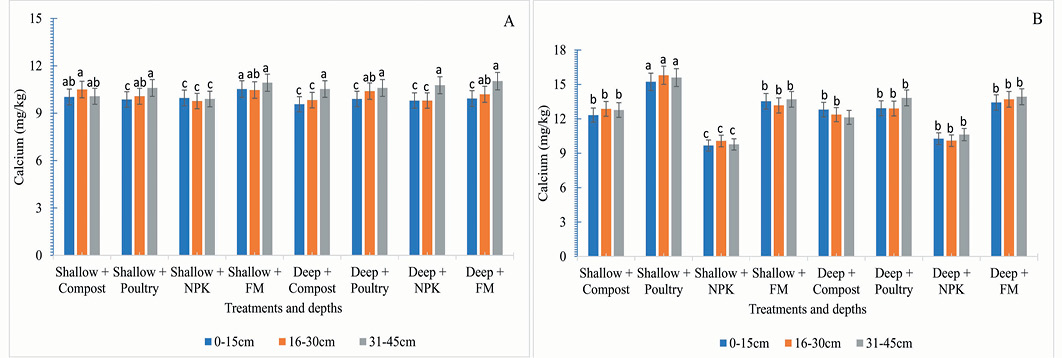
Effect of tillage intensity, fertilizer and manuring on calcium (mg/kg) were found in 2019-20 (A) and 2020-21 (B).
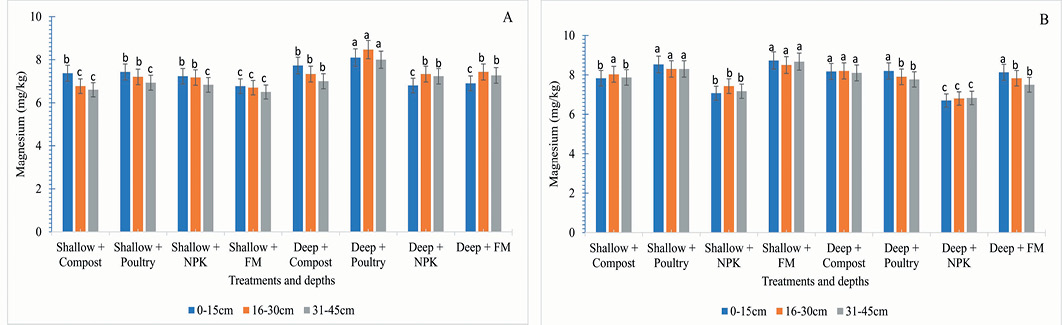
Effect of tillage intensity, fertilizer and manuring on magnesium (mg/kg) were determined cropping year 2019-20 (A) and 2020-21 (B).
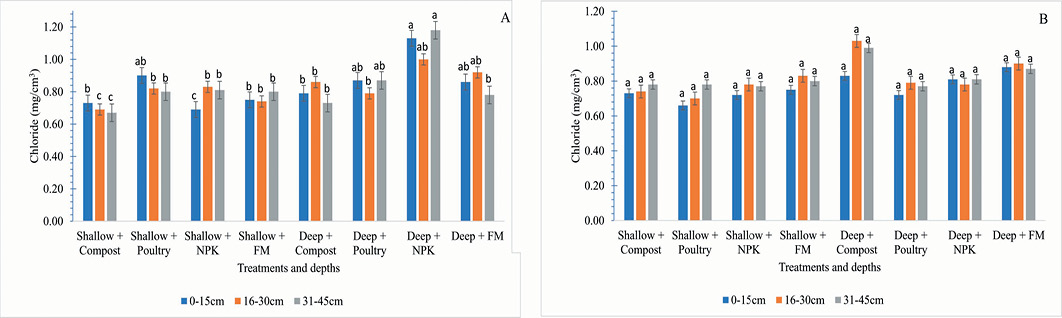
Effect of tillage intensity, fertilizer and manuring on chloride (mg/cm3) were determined cropping year 2019-20 (A) and 2020-21 (B).
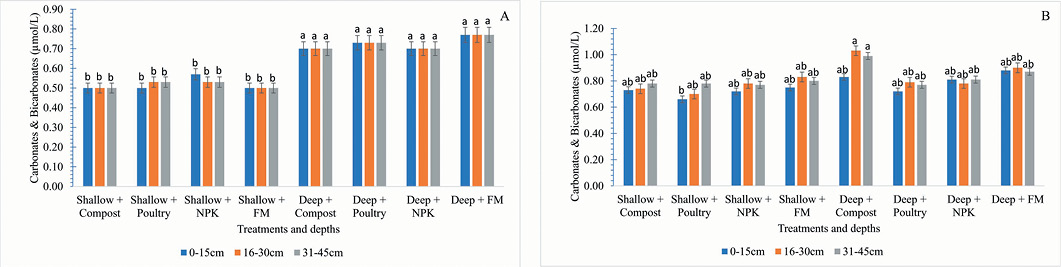
Effect of tillage intensity, fertilizer and manuring on carbonate and bicarbonate (µmol/L) were determined cropping year 2019-20 (A) and 2020-21 (B).