Immune-Related Gene Expression in Response to Different Strains of Egyptian Low Pathogenic H9N2 Infection in Chicken Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
Immune-Related Gene Expression in Response to Different Strains of Egyptian Low Pathogenic H9N2 Infection in Chicken Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
Ahmed Samy, Wesam Mady, Naglaa M. Haggag, Samah H. Mohamed, Ebtissam N. AlShamy, M.K. Hassan
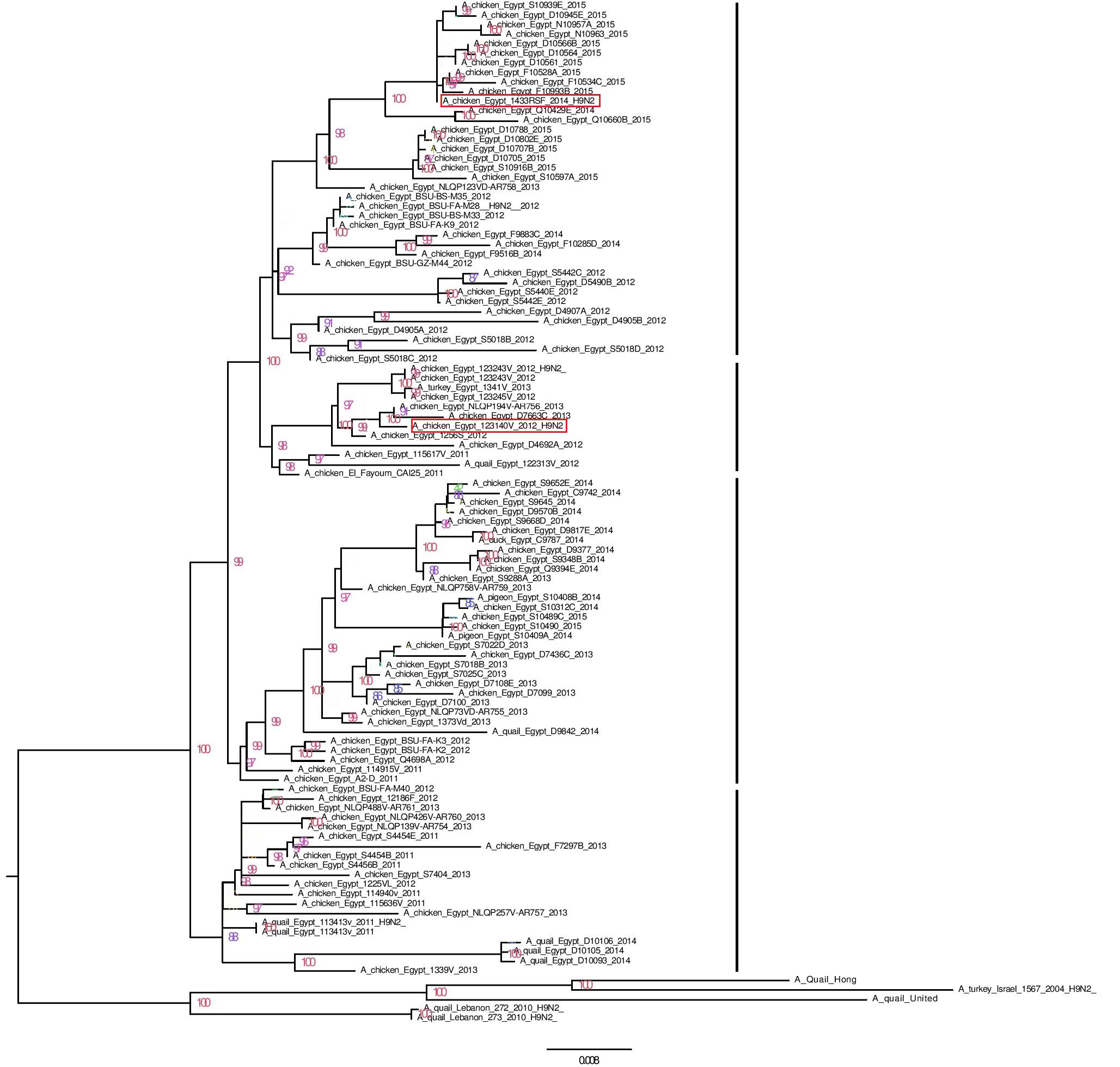
phylogenetic relationship of the HA nucleotide sequences of V3 and RSF/1 to Egyptian H9N2 strains and G1-like ancestor strains (based on the full HA nucleotide sequences)
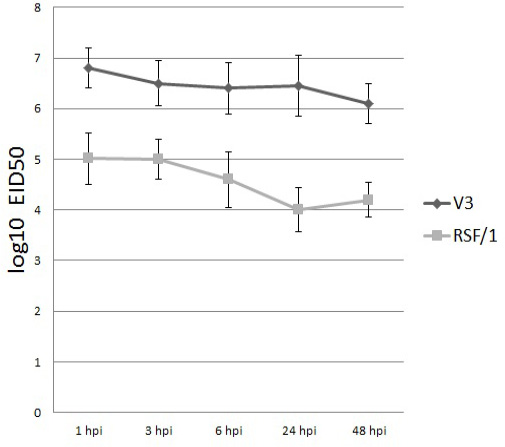
Viral titer of V3 (black column) and RSF/1 (gray column) in PBMCs culture supernatant at different time points. Viral titer measured by quantitative RT-real time PCR and expressed by log10 EID50. Data showed are the mean with error bar calculated from three replicates at each time point
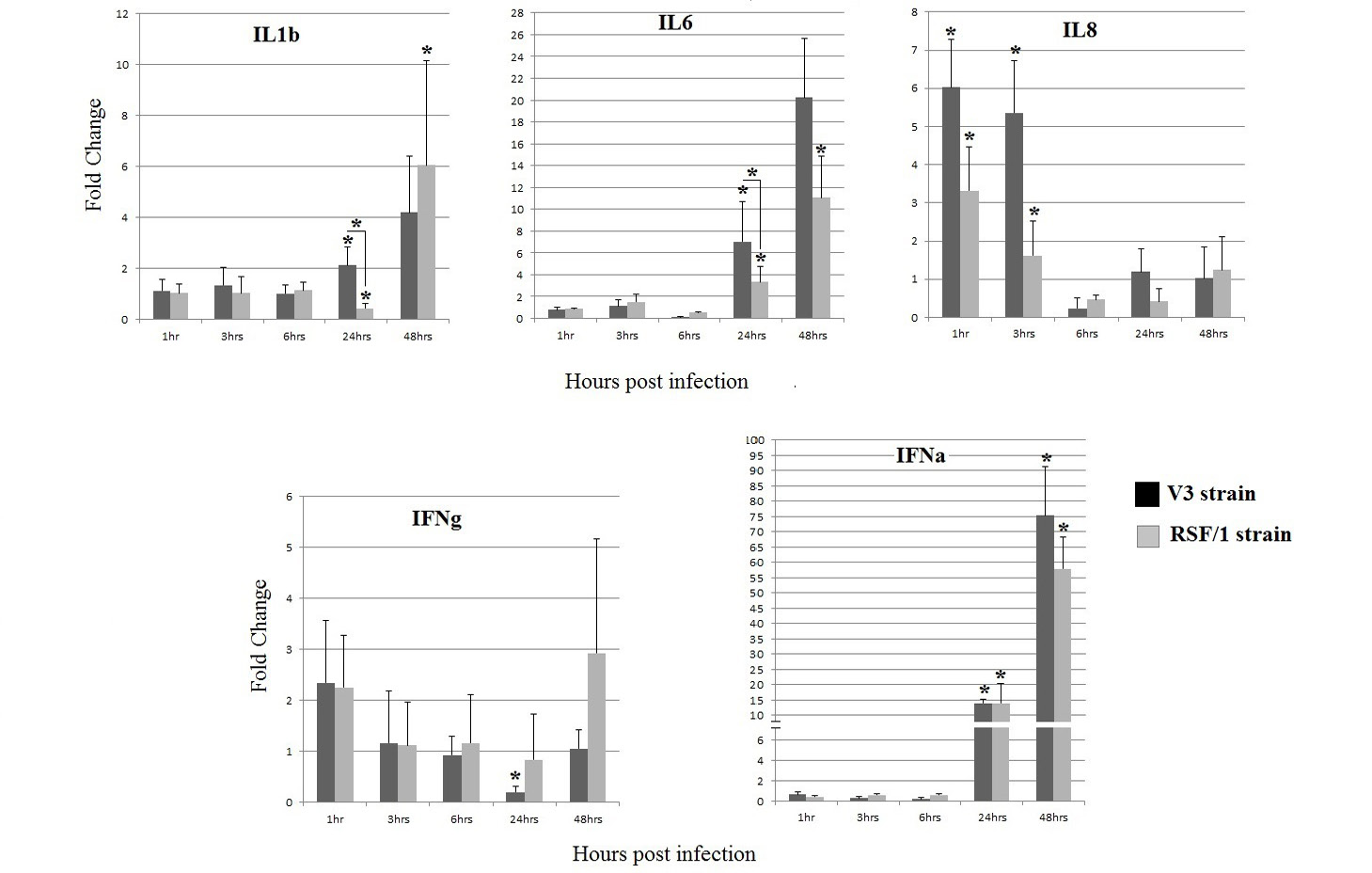
Cytokines gene relative expression in PBMCs cell culture infected with V3 strain (black column) and RSF/1 strain (gray column): *P < 0.05, asterisk over error bar represent significant difference between infected and non-infected cells. While asterisk over horizontal line represent significant difference between both strains. Data showed are the mean with error bar calculated from three replicates at each time point
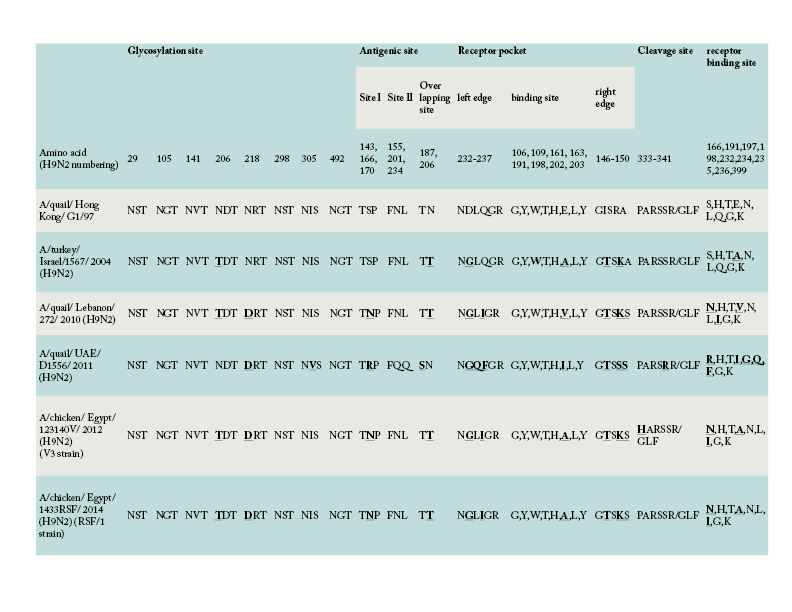
Amino acid comparison of the HA gene of V3 and RSF/1 strains used in the present study with the ancestor G1-like strain and other regional strains