Gene Cloning and Characterization of Pcal_0222, α-Amylase from Pyrobaculum calidifontis
Gene Cloning and Characterization of Pcal_0222, α-Amylase from Pyrobaculum calidifontis
Sadaf Ashraf1, Masood Ahmed Siddiqui1*, Kanwal Nisa1, Samar Ali1 and Naeem Rashid2
Multiple sequence alignment of P. calidifontis α-amylase with the sequences of other putative amylases from P. arsenaticum (NC_009376.1), P. oguniense (CP003316.1), P. islandicum (NC_008701.1), P. aerophilum (NC_003364.1) and with T. tenax (NC_016070.1). The identical residues are highlighted with soid black. Four highly conserved regions I, II, III and IV contain the amino acids DVVNH, GFRLDVAHG, EHVGN and FLENHDTD respectively have been shown with bold lines ( ̶̶ ̶ ). Asterisks (*) indicate the conserved residues of conserved regions among all α-amylases.
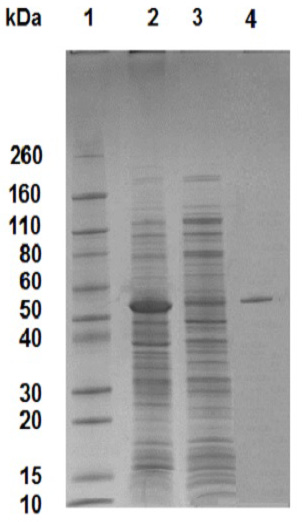
The 0.1% SDS-15% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) demonstrating the purified α-amylase. Lane 1, Novex™ Sharp Pre-stained Protein Standard; lane 2, cells carrying pET101-AMYL plasmid insoluble faction; lane 3, cells carrying pET101-AMYL plasmid soluble faction; lane 4, purified recombinant α-amylase.
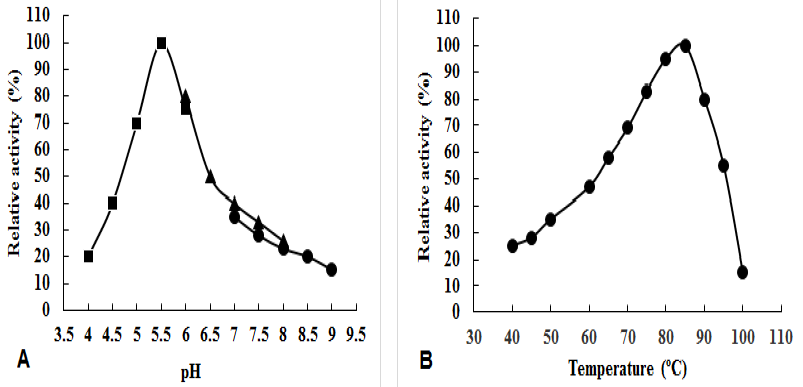
Enzymatic properties of α-amylase.
(A) Effect of pH on α-amylase activity using (■) 50 mM 50 mM Na-acetate buffer; (▲) 50 mM Phosphate buffer and (●) 50 mM Tris-HCl buffer. (B) Effect of temperature on α-amylase activity.