Foliar Calcium Application Ameliorates Salinity-Induced Changes of Tomato Crop Grown in Saline Conditions
Foliar Calcium Application Ameliorates Salinity-Induced Changes of Tomato Crop Grown in Saline Conditions
Abdur Rab1*, Muhammad Sajid1, Naveed Ahmad1, Khalid Nawab2, Syed Ghias Ali3
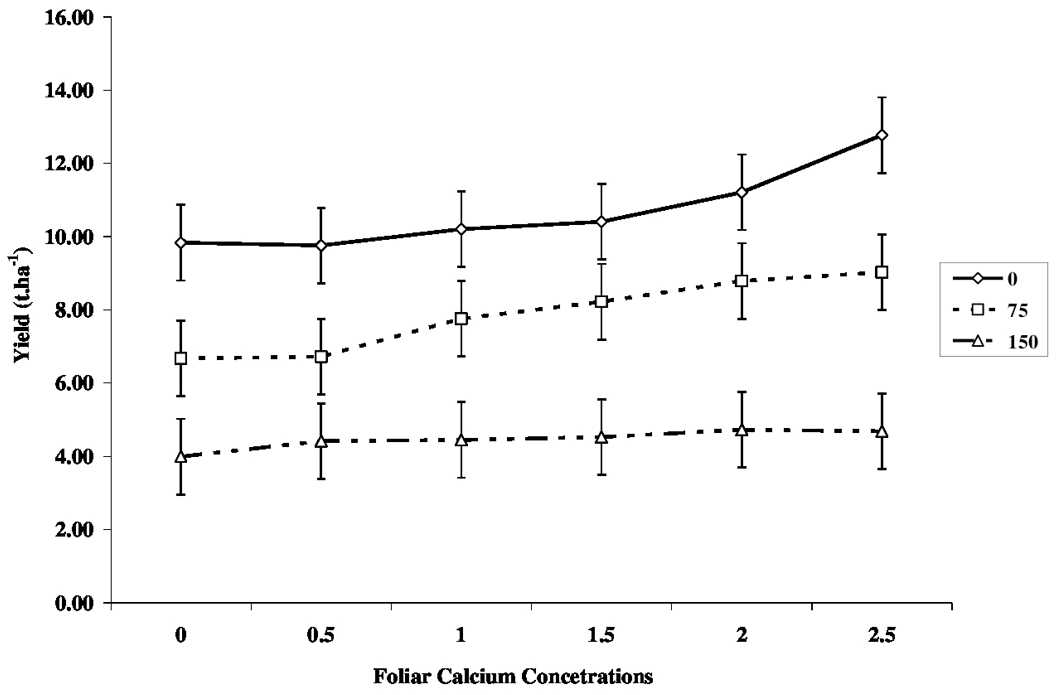
The influence of salinity levels and calcium concentration applied as a foliar spray on the yield of tomato crop.
The vertical error bars represent LSD at p ≤ 0.05
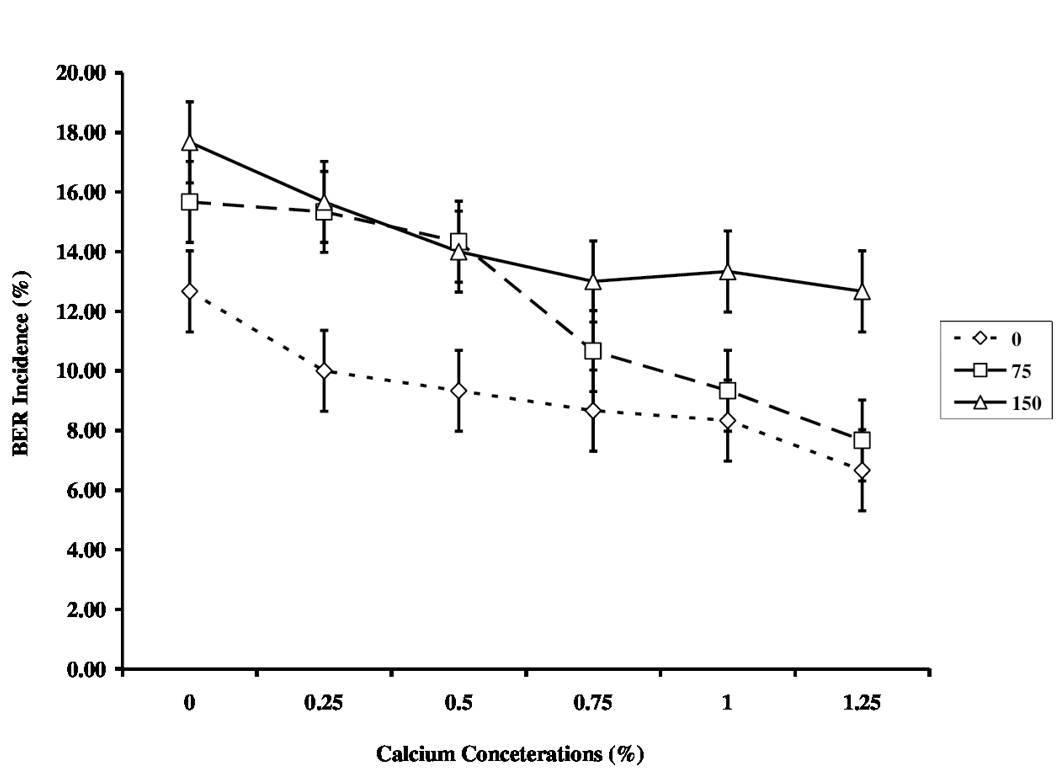
The Blossom End Root (BER) incidence in relation to salinity levels and calcium concentration applied as a foliar spray.
The vertical error bars represent LSD at p ≤ 0.05