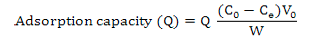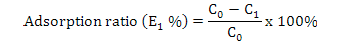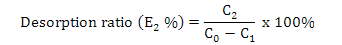Extraction, Purification and Anti-Hyperlipidemic Activities of Total Flavonoids from Corn Silk
Extraction, Purification and Anti-Hyperlipidemic Activities of Total Flavonoids from Corn Silk
Jiandong Wu, Miao Ye and Zaigui Wang*
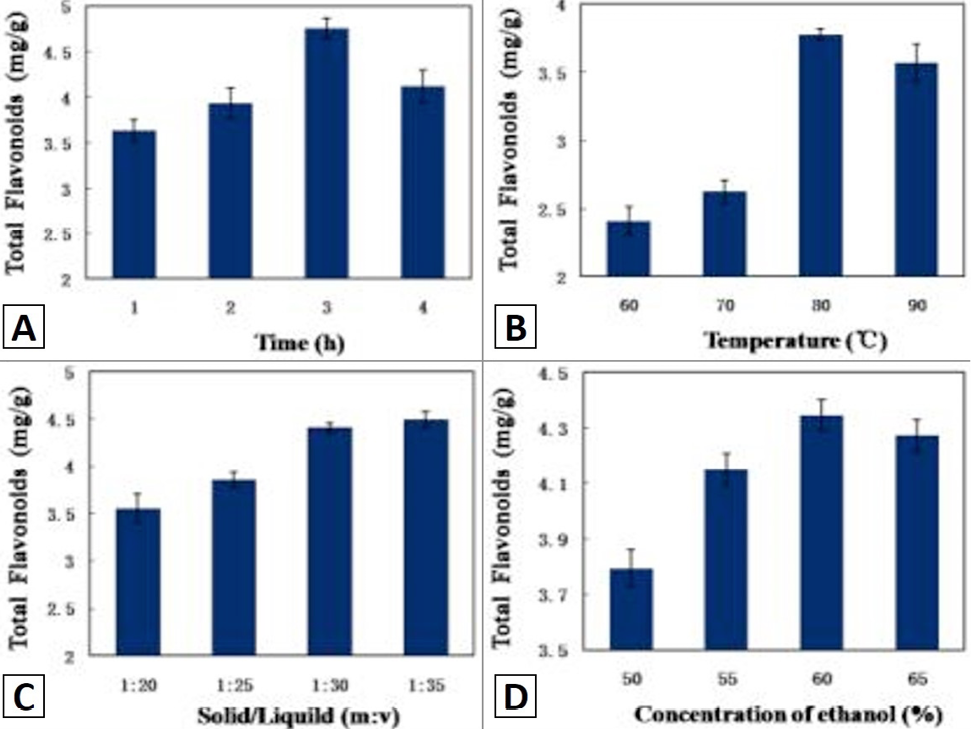
Yield of total flavonoids from corn silk (mg/g) by extraction: A, for different durations with the material ratio (the weight of corn silk to the volume of 60% ethanol: g/mL) of 1:30 at 80°C; B, at different temperature with the material of 1:30 for 3 h; C, with different material ratio at 80°C for 3 h; D, for different ethanol concentration with material ratio of 1:30 for 3 h at 80°C. Experiments were repeated at least three times with similar results.
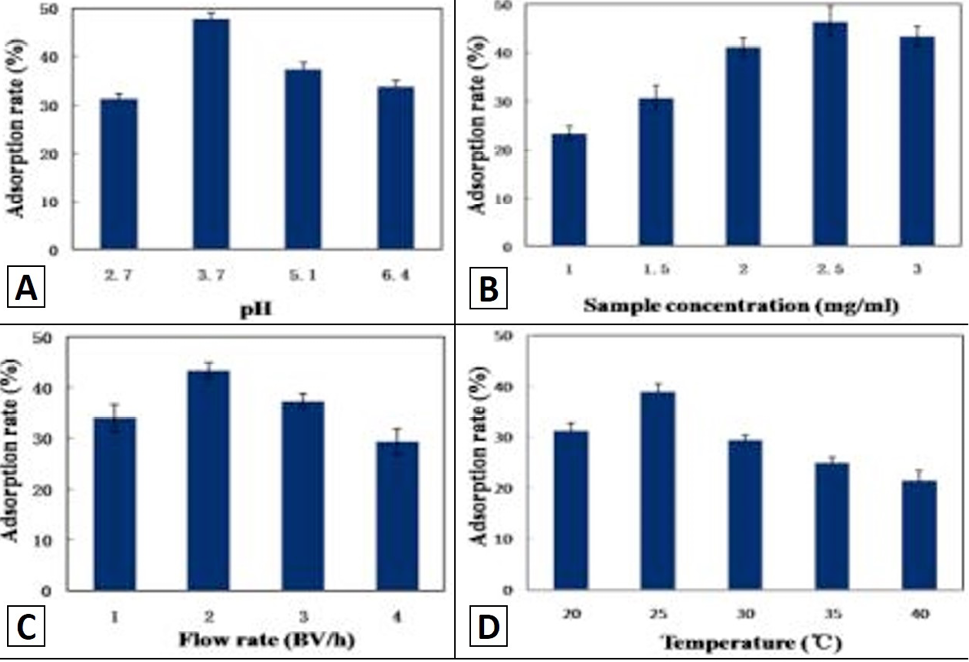
The adsorption rate of macroporous resin AB-8 by purification: A, with different pH value of sample; B, at different sample concentration (mg/mL); C, for different flow rate (BV/h); D, at different temperature (°C). Experiments were repeated at least three times with similar results.
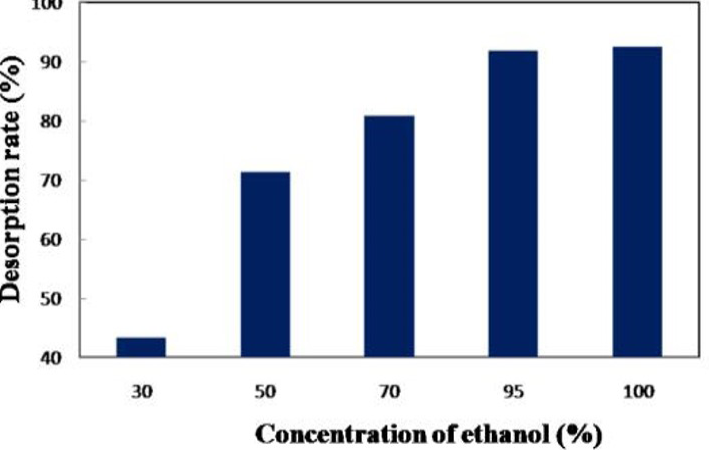
Effect of different ethanol-water solutions on the desorption ratio of total flavonoids on AB-8 resin.
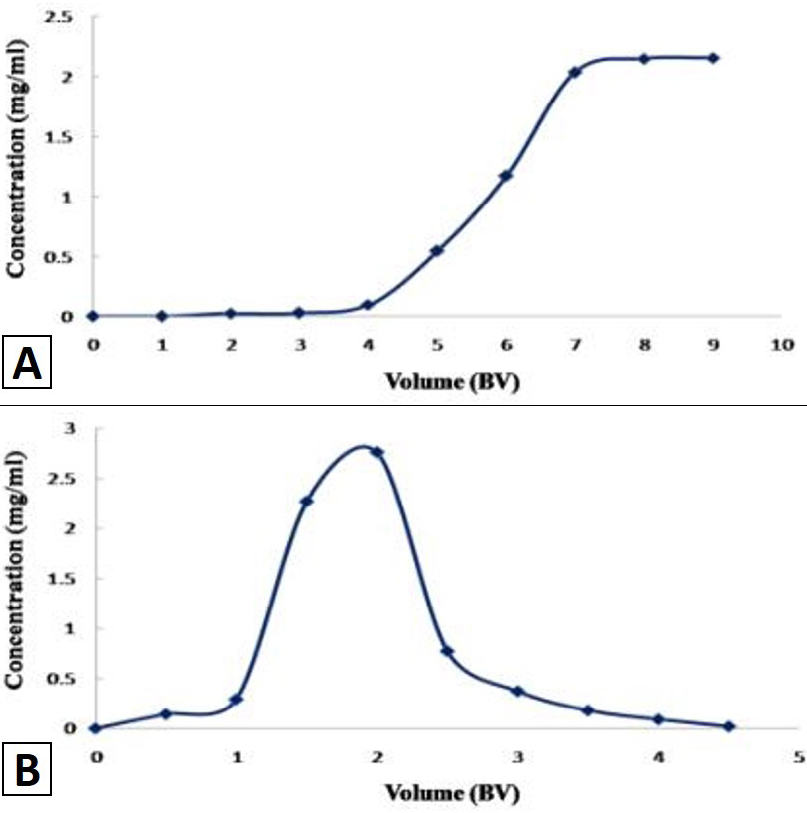
Dynamic breakthrough (A) and dynamic adsorption (B) curves of total flavonoids on column packed with AB-8 rein. Experimental condition: temperature, 25°C; flow rate, 2 BV/h; concentration of total flavonoids, 2.5 mg/mL.
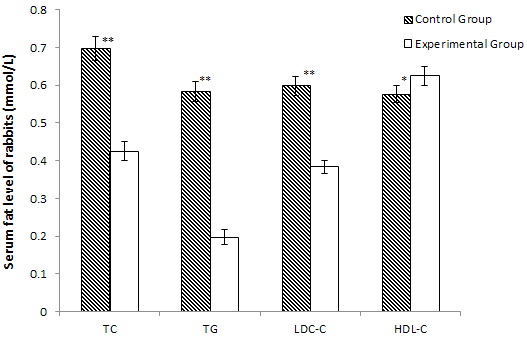
Effects of total flavonoids on the serum flat level in rabbits. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, each group contains ten mice (n=10), *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01. TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglycerides; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol.