Evaluation of Codon Optimized DNA Vaccine Against Avian Influenza A Viruses using Local Egyptian Strain of H9N2
Evaluation of Codon Optimized DNA Vaccine Against Avian Influenza A Viruses using Local Egyptian Strain of H9N2
Wesam Hasan Mohamed Mady 1*, Bing Liu2, Dong Huang2, A. Arafa1, M.K. Hassan1, M.M. Aly1, Pucheng Chen2, Yongping Jiang2* and Hualan Chen2
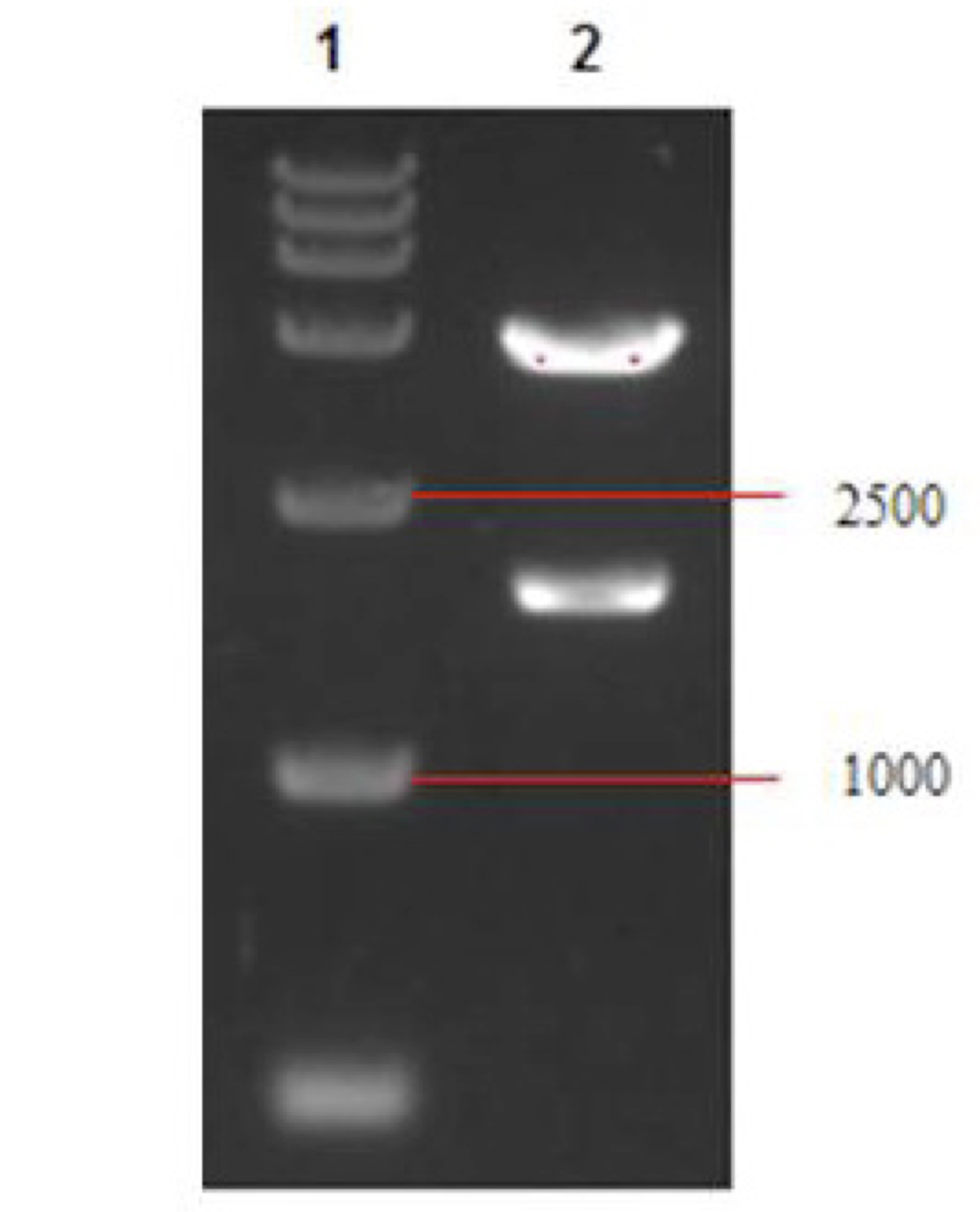
The restriction enzyme digestion analysis. Lane (1) is the molecular weight marker, and lane (2) is the digested opti-H9 gene with EcoR1 and XhoI restriction enzymes and showing the bands of expected sizes (1.7 Kb for HA and 4.7 Kb for pCAGGS plasmid vector).
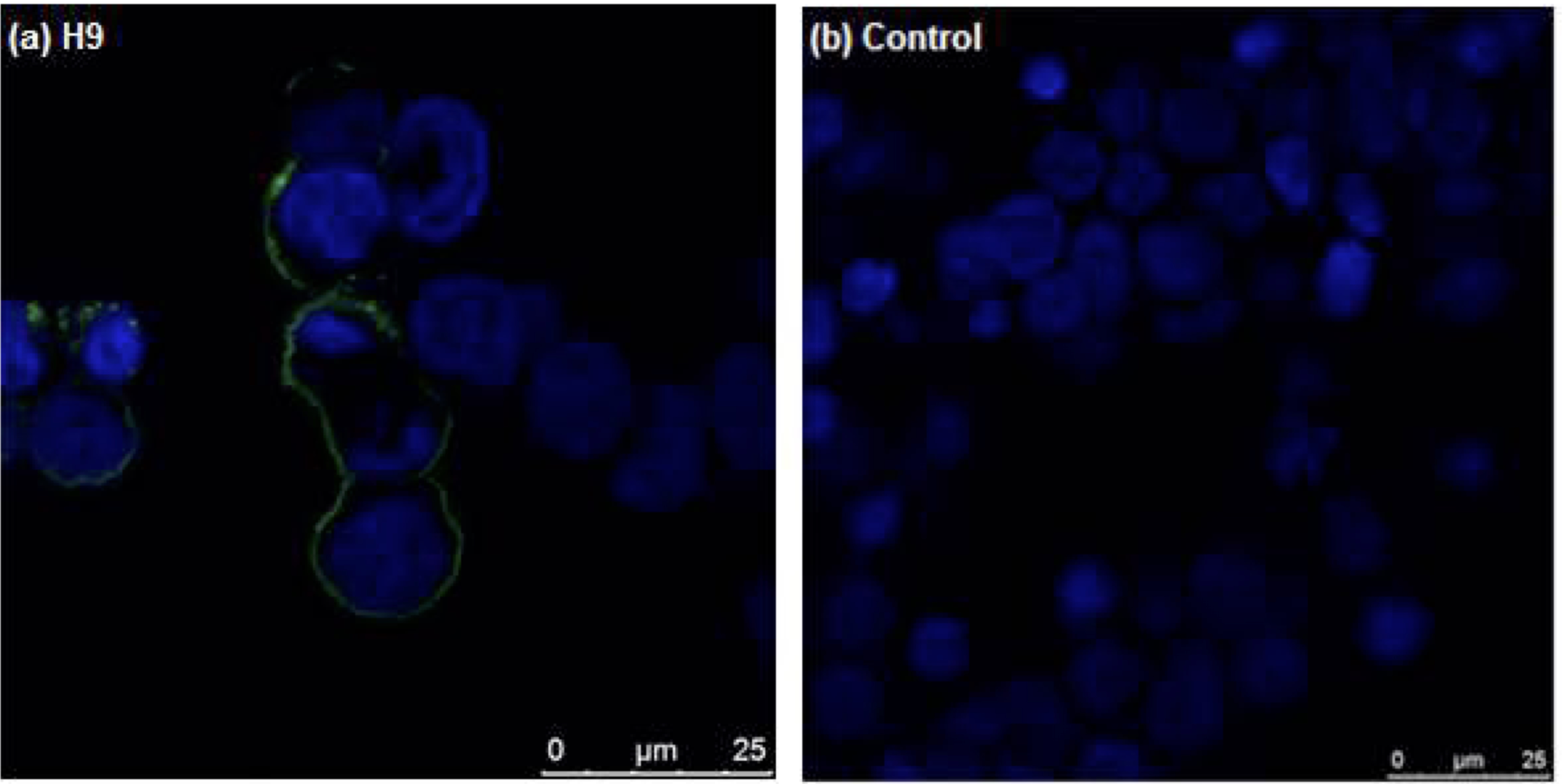
(a) Immunofluorescence staining of 293T-HEK cells transfected with pCAGG-optiH9 showing the specific fluorescence. (b) Negative control 293T-HEK cells showing no fluorescence.
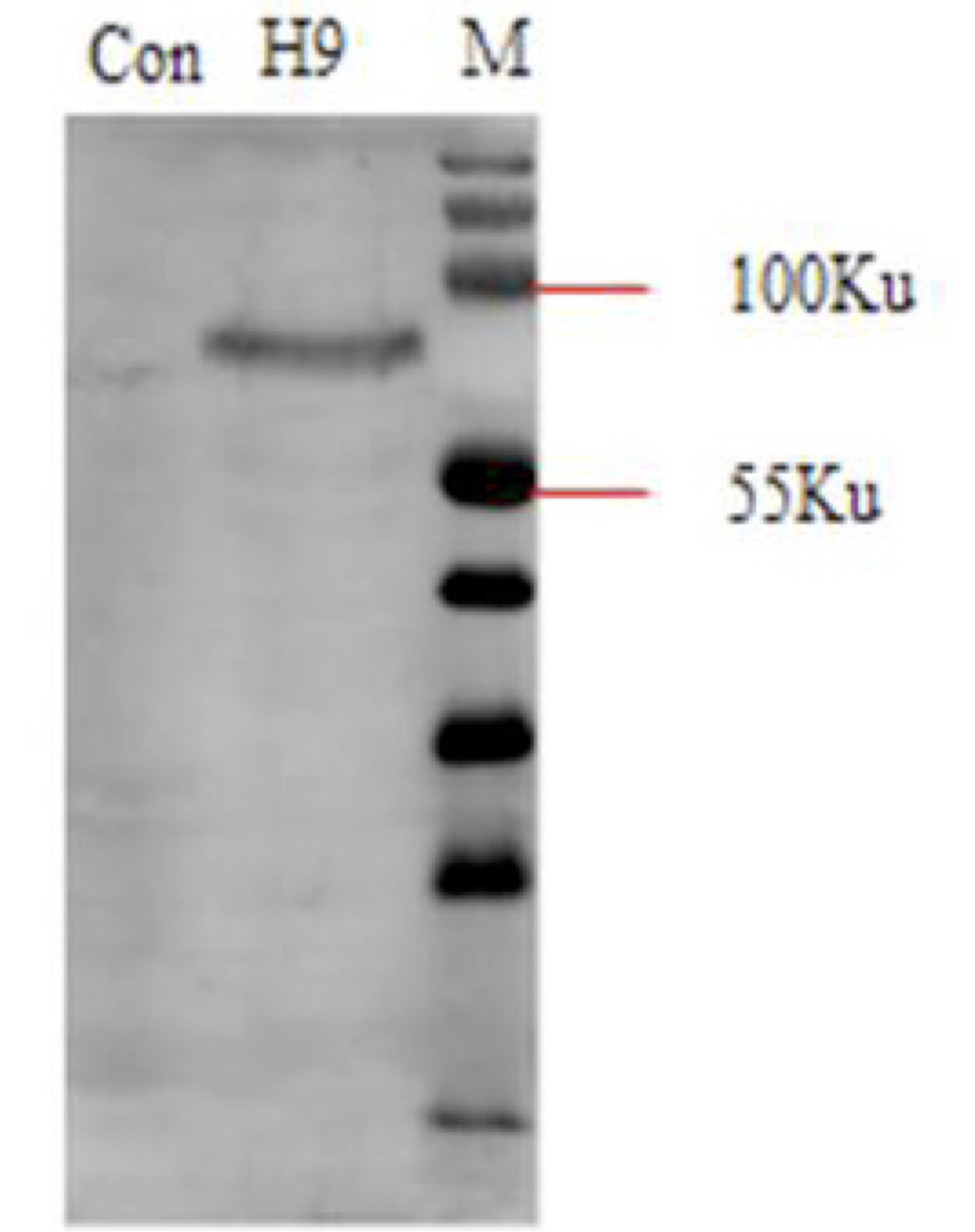
Western blot analysis of pCAGGS plasmid expressing opti-H9 HA, M is the molecular weight marker, H9 is the expressed HA protein of pCA-Egy-H9 showing the specific band of approximately 70 KDa, and con is the negative control.
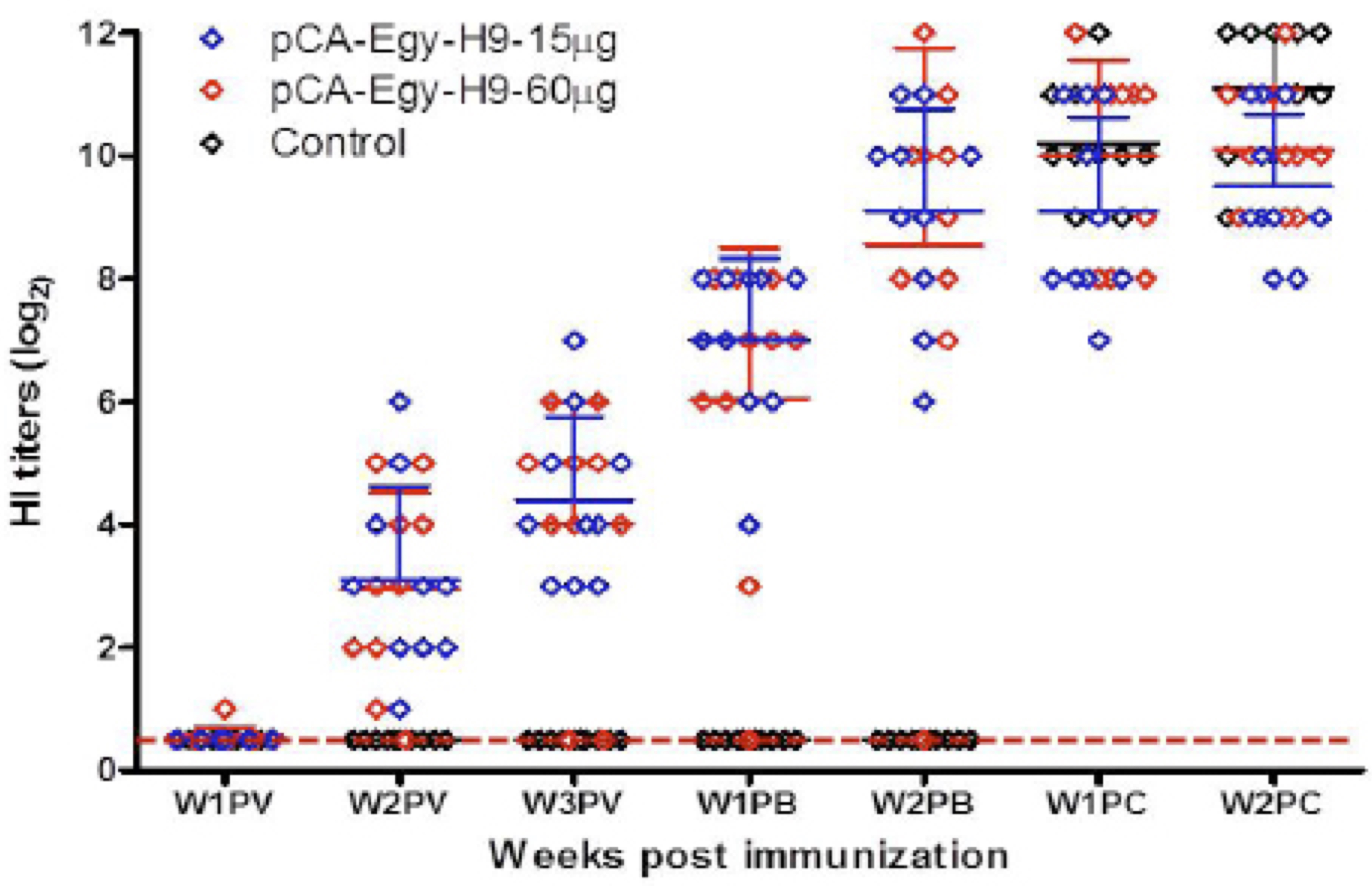
HI antibody titer (Log2) in the chickens immunized with the pCA-Egy-H9 plasmid DNA vaccine.
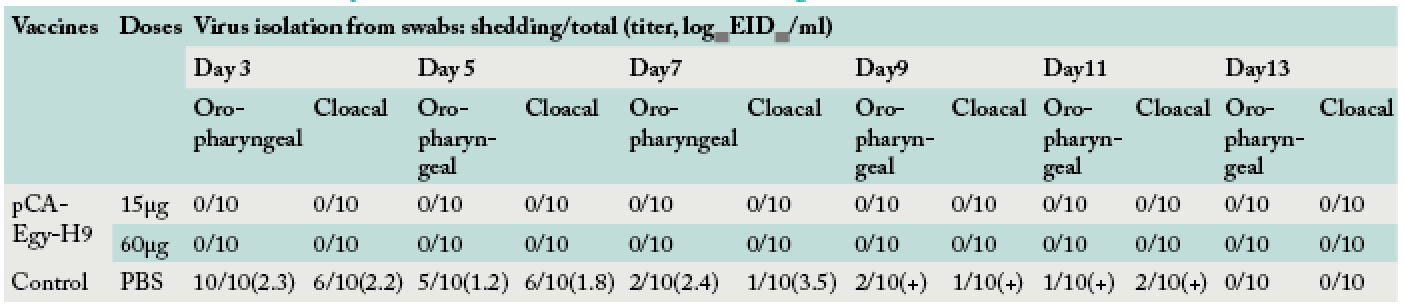
The virus titrations from swabs post H9N2 virus challengeA