Effect of Anthropogenic Disturbance Intensity on the Vigilance Mode of Wintering Hooded Crane (Grus monacha)
Effect of Anthropogenic Disturbance Intensity on the Vigilance Mode of Wintering Hooded Crane (Grus monacha)
Xinran Wang1,2 and Lizhi Zhou1,2*
The study sites including the mudflats, grasslands and paddy fields in Shengjin Lake National Nature Reserve (NNR), China.
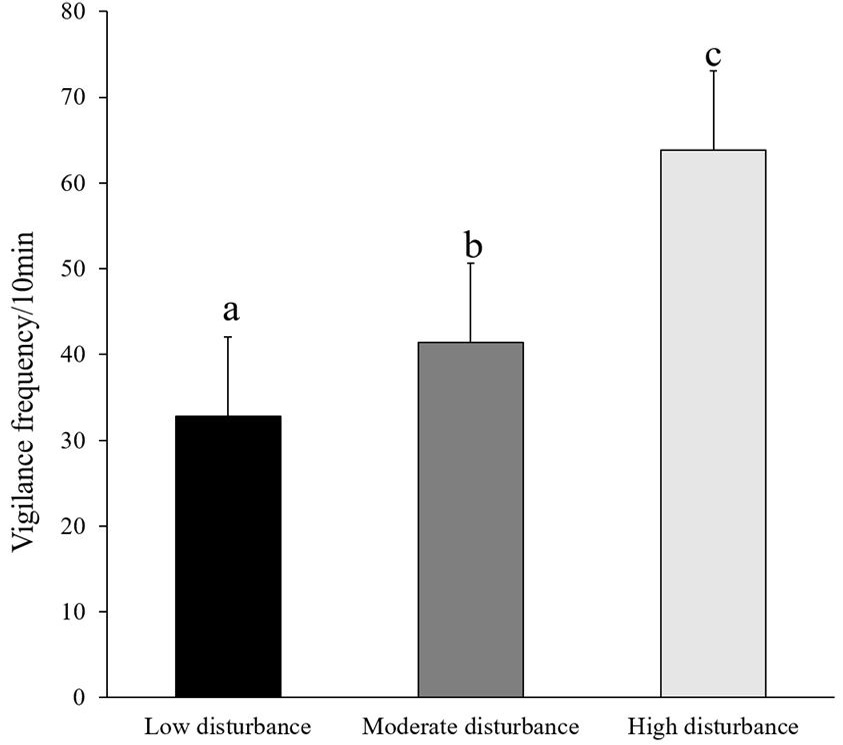
Vigilance frequency under different disturbances. The letter a, b and c indicate that there are significant differences in vigilance frequency at three interference intensities.
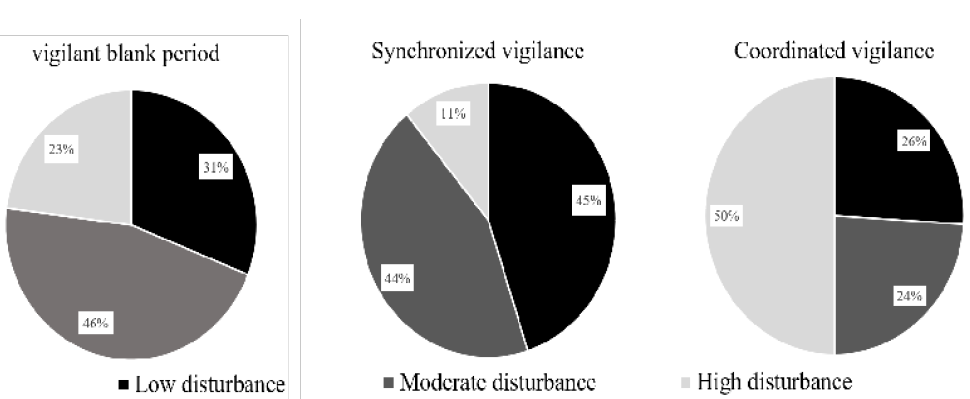
Time ratios of synchronized vigilance time, coordinated vigilance time, and vigilance blank period under three disturbance intensity. Black represents low disturbance, dark gray represents moderate disturbance, and light gray represents high disturbance.
Synchronous vigilance waves in three disturbance intensities. Different letters represent difference in the frequency and duration of the synchronization vigilance waves under different disturbance intensities. a, b and c represent differences.