Ecological Effect Evaluation of Artificial Reefs Based on Spatial Heterogeneity of Demersal Nekton Community in Beibu Gulf
Ecological Effect Evaluation of Artificial Reefs Based on Spatial Heterogeneity of Demersal Nekton Community in Beibu Gulf
Lei Zeng1,2,3,4, Pimao Chen1,2,3,4, Zhenzhao Tang1,3,4, Jie Yu1,2,3,4 and Guobao Chen1,2,3,4*
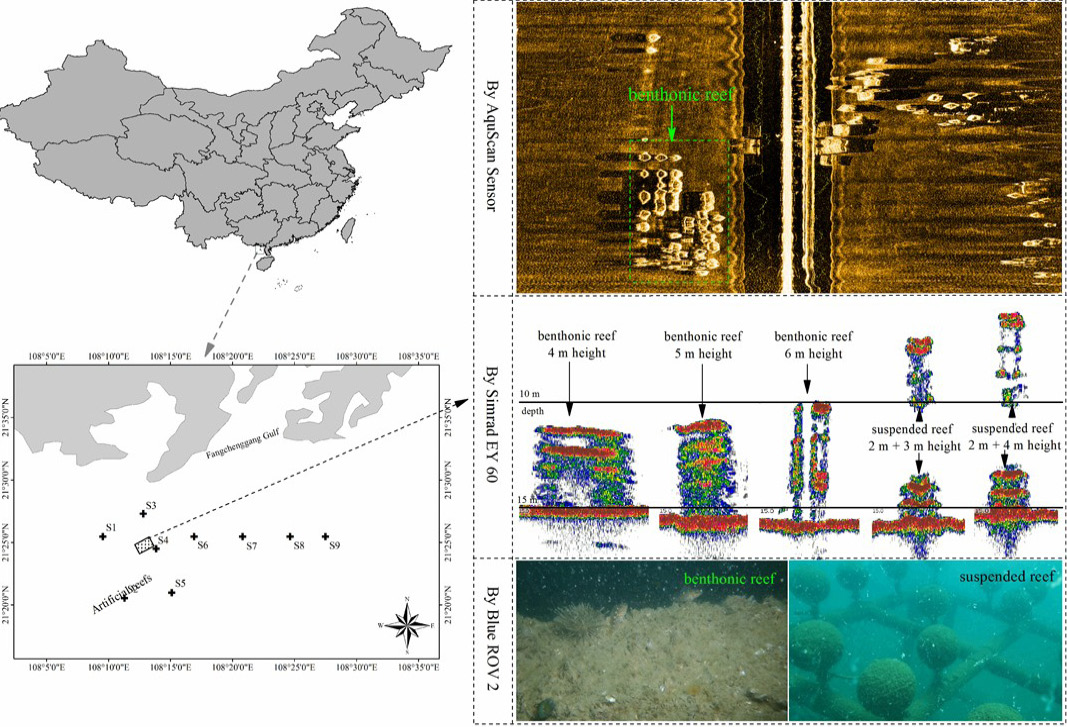
The distribution of sample sites (S1~S9, left side) and artificial reefs (ARs) detected by different ways (right side).
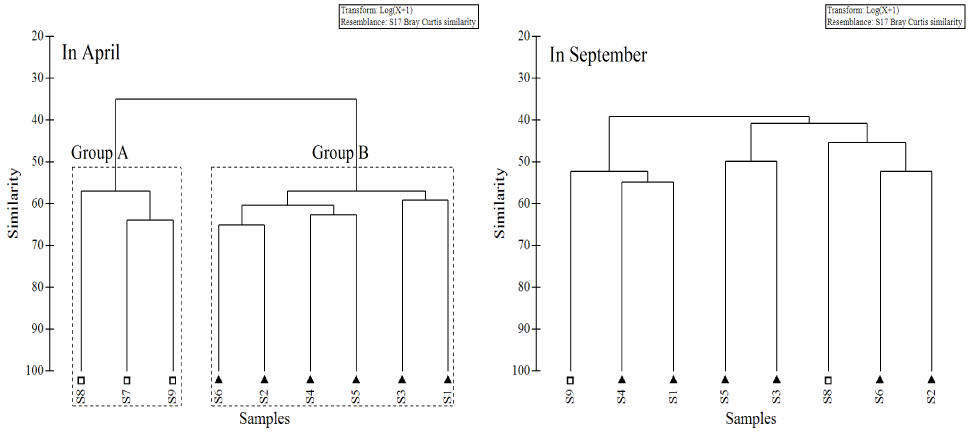
Spatial pattern of nekton community in the study area based on CLUSTER analysis (Group A: artificial reefs ecological effect region; Group B: control region).
Spatial variation of nekton densities (mean±SD, ind/km2) between group A and B.
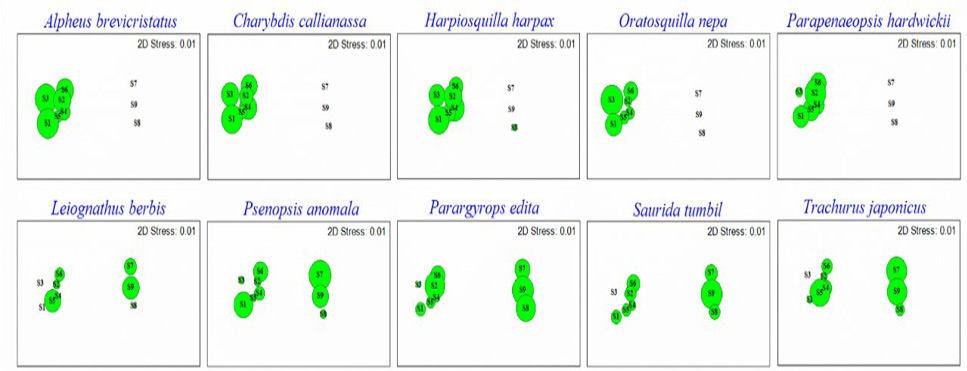
Distribution pattern of the dominants contributing to spatial heterogeneity of nekton community based on NMDS analysis (the size of the bubbles showing the abundance of the dominants species).
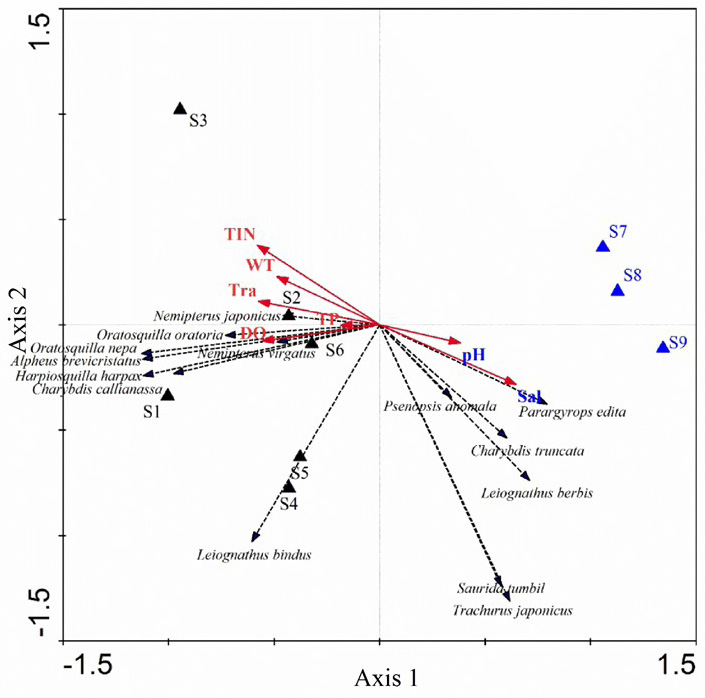
RDA ordination of nekton community composition and the relationship with physicochemical environmental parameters in different sample sites (S1~S9).