Drying of Onion Paste to Develop Powders by Foam-Mat Drying Process using Egg Albumin as Foaming Agent
Drying of Onion Paste to Develop Powders by Foam-Mat Drying Process using Egg Albumin as Foaming Agent
M. Javed Iqbal1, Rizwan Shukat1, Muhammad Farooq2*, Iftikhar Ahmed Solangi2, Naila Ilyas3, Rahman Ullah4, A. Shakoor5, Muhammad Bakhtiar6 and Faraz Ahmed7
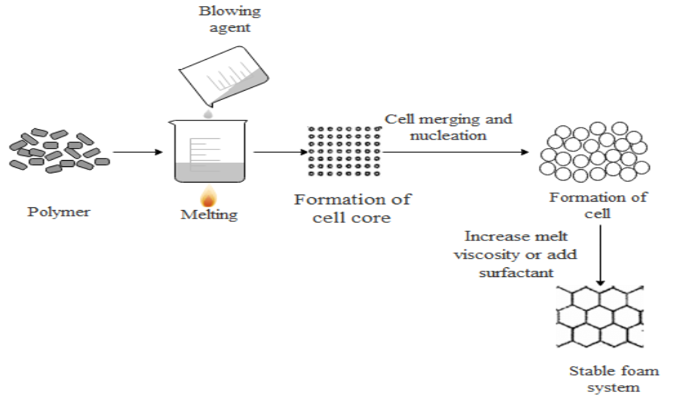
Schematic diagram of the foaming process system
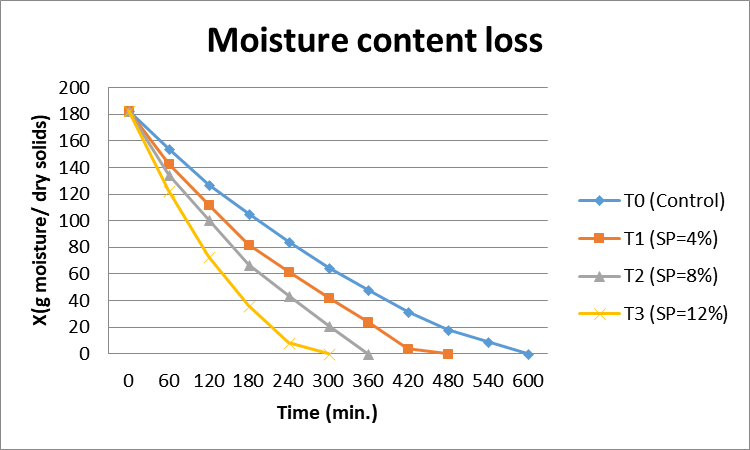
Effect of soy protein concentration level on moisture during foam mat drying of onion paste at 65°C.
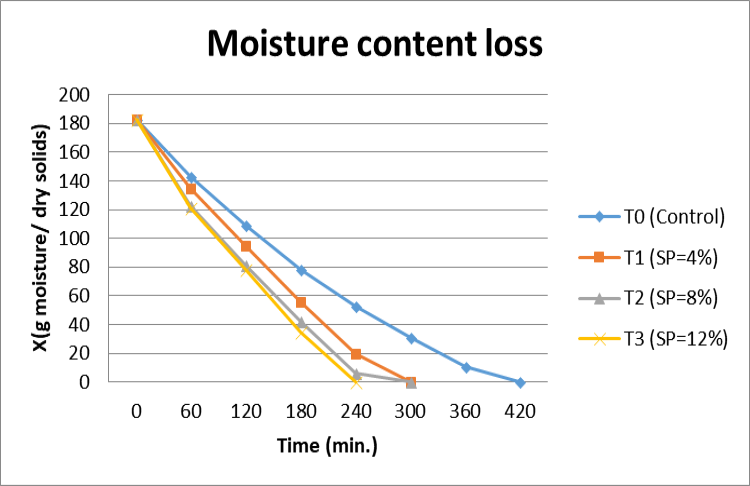
Effect of soy protein concentration level on moisture during foam mat drying of onion paste at 75°C.
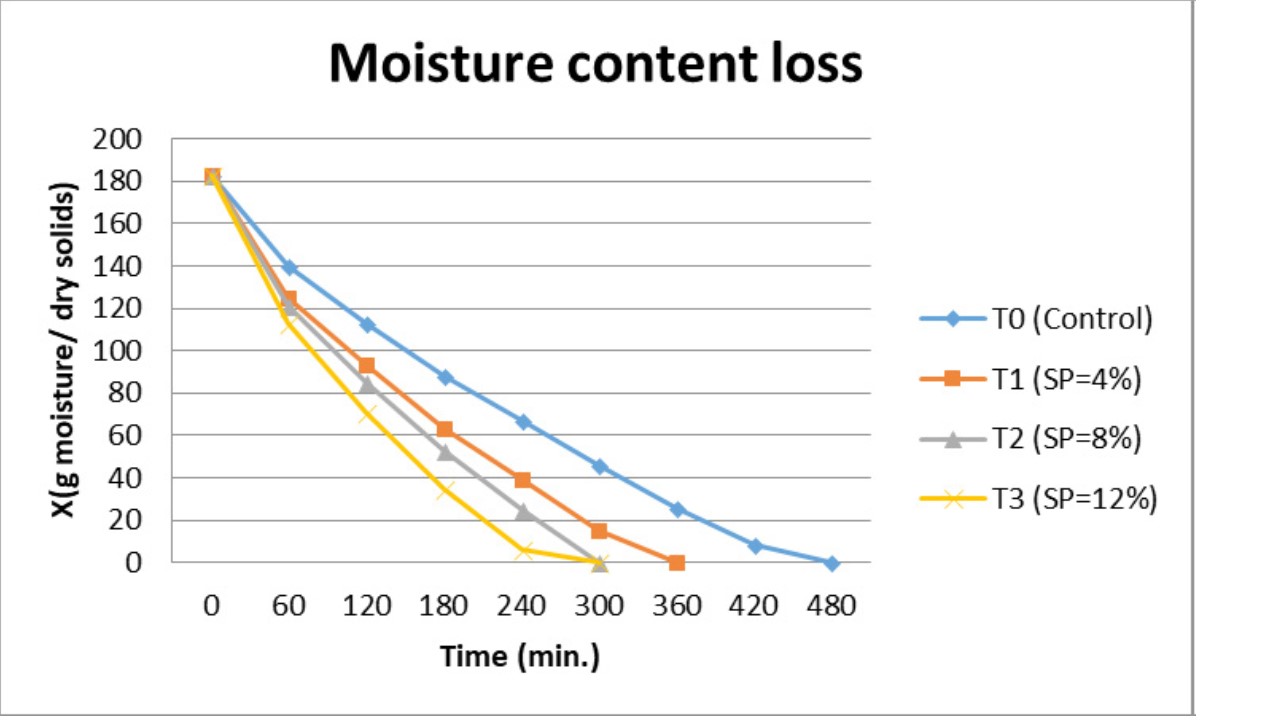
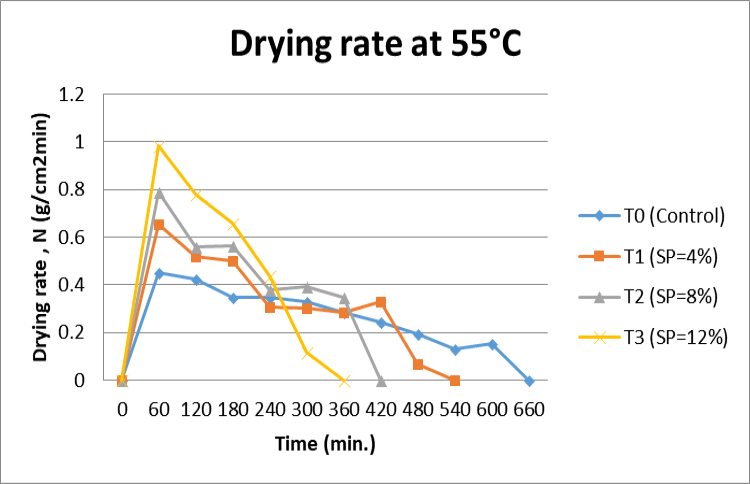
Effect of soy protein concentration level on drying rate of foam mat dried onion paste at 55°C.
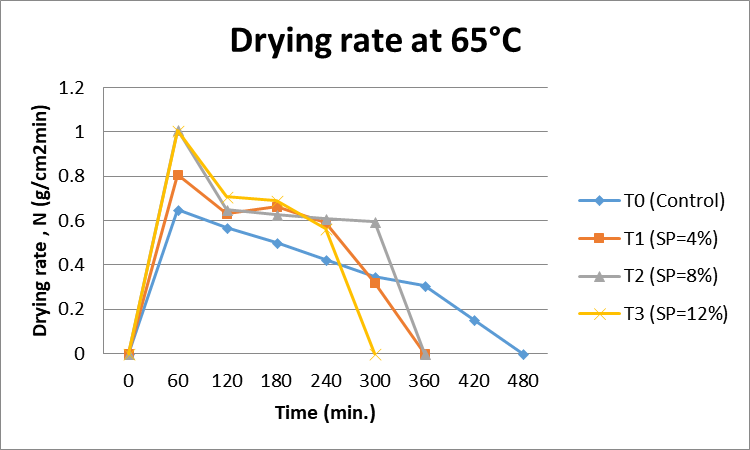
Effect of soy protein concentration level on drying rate of foam mat dried onion paste at 65°C.
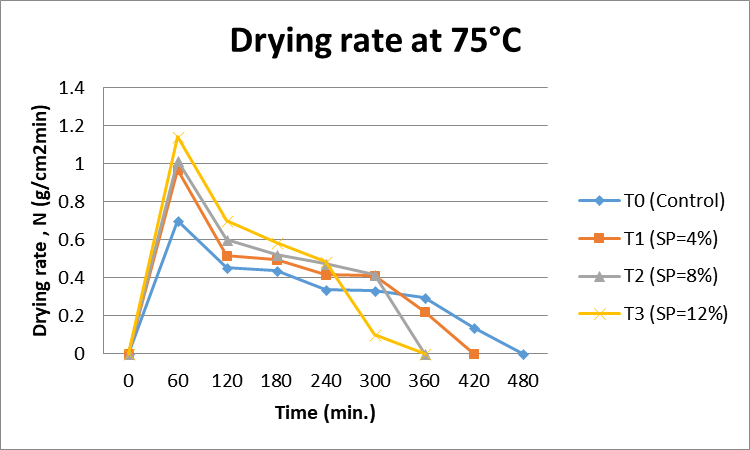
Effect of soy protein concentration level on drying rate of foam mat dried onion paste at 75°C.
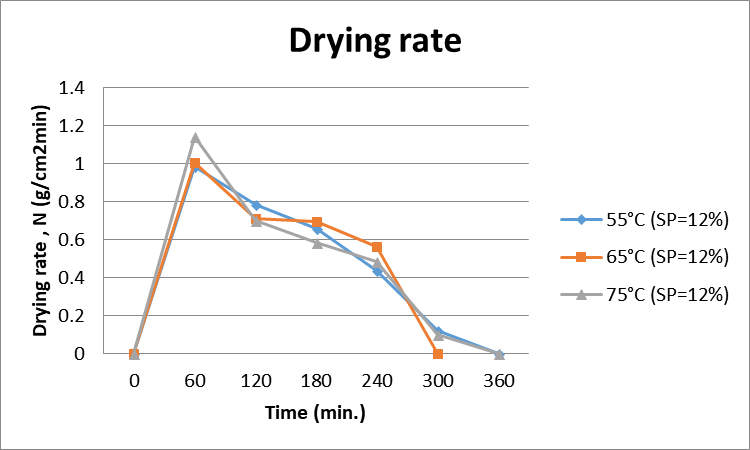
Effect of different temperatures (55°C, 65°C and 75°C) on drying rate of onion powders developed by 12% soy protein as foaming agent.