Diversity and Epidemiological Study of Hard Ticks Infesting Goats and Sheep of Hazara Division, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan
Diversity and Epidemiological Study of Hard Ticks Infesting Goats and Sheep of Hazara Division, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan
Hidayat Ullah1, Sadia Tabassum1, Sultan Ayaz2, Shumaila Noreen1, Atta Ur Rehman1, Naveed Akhtar3, Muhsin Ali3, Zaib Ullah3* and Sajid Mahmood1,4
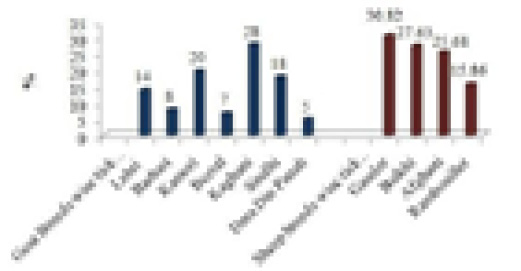
Goats and sheep breeds wise ticks infestation.
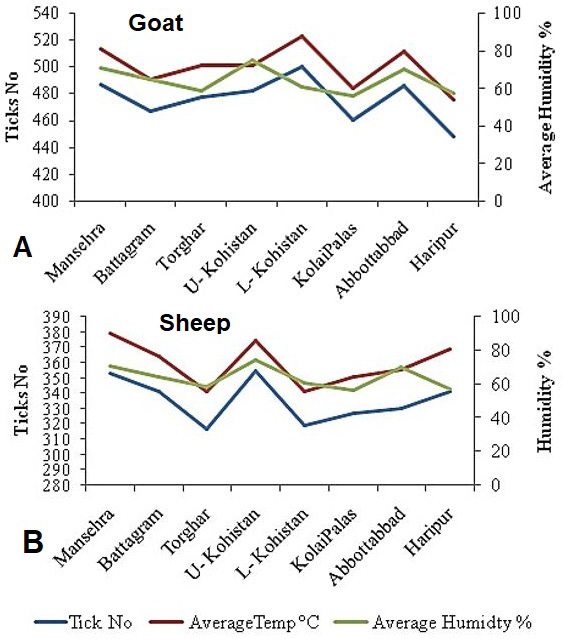
Ticks number on goats (A) and sheep (B) in correlation with temperature and humidity.
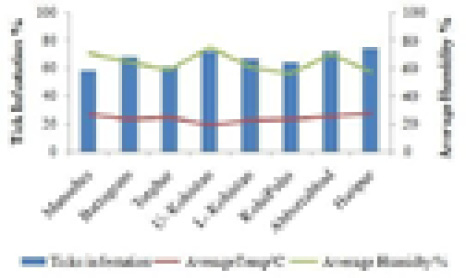
Infestation of ticks on goats and sheep in correlation with temperature and humidity.
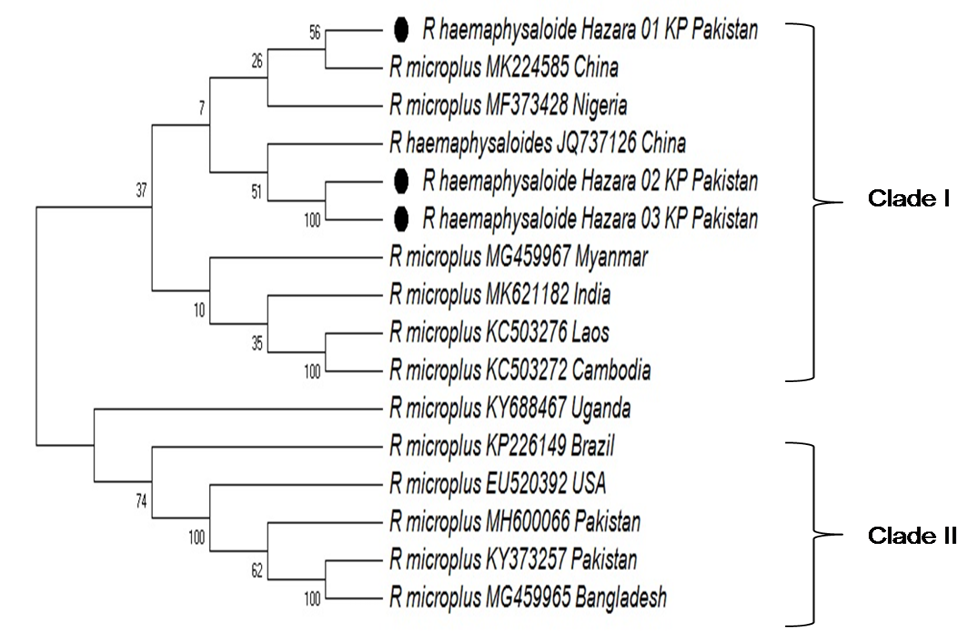
Phylogenetic relationship of R. haemaphysaloides of Hazara division KP, Pakistan with other ticks sequence based on ITS2 sequences. Phylogenetic tree was constructed by using the Neighbor-Joining method with bootstrap consensus 1000 replicates the evolutionary distance were computed using the Maximum composite likelihood method. Bootstrap consensus values are shown below the branches. The tree was generated by using MEGA X software.
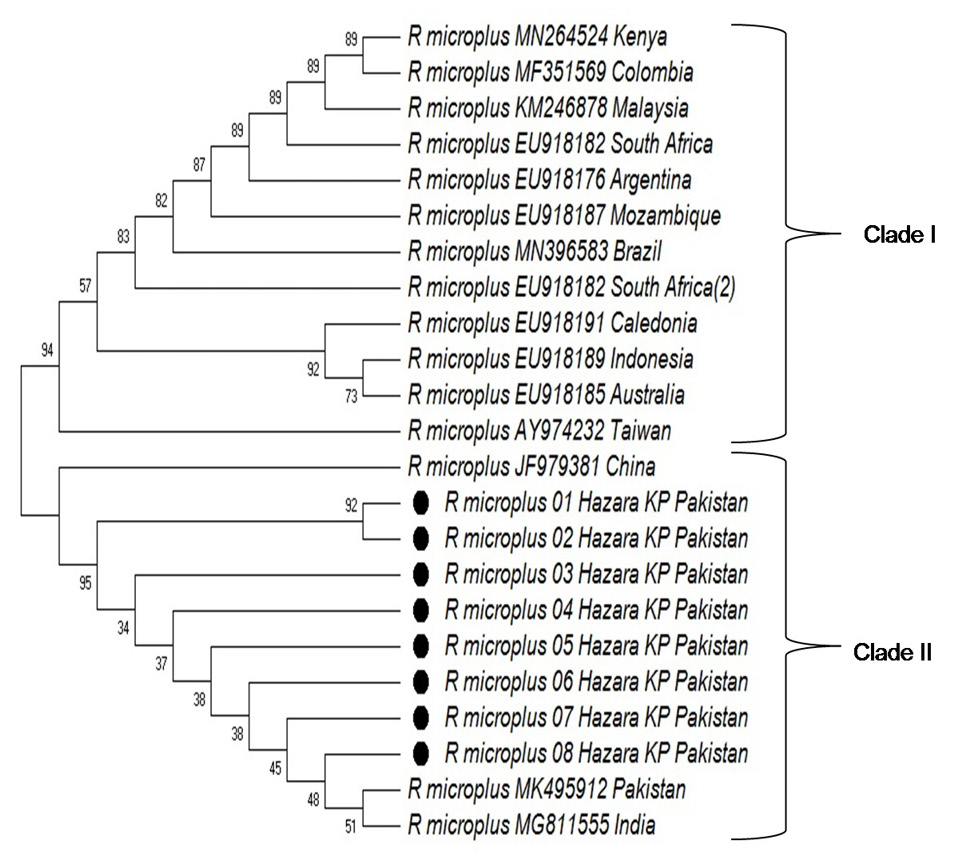
Phylogenetic relationship of R. microplus of Hazara division KP, Pakistan with other ticks sequence based on 16SrRNA sequences. Phylogenetic tree was constructed by using the Neighbor-Joining method with bootstrap consensus 1000 replicates the evolutionary distance were computed using the Maximum composite likelihood method. Bootstrap consensus values are shown below the branches. The tree was generated by using MEGA X software.
Phylogenetic relationship of R. haemaphysaloides of Hazara division KP, Pakistan with other ticks sequence based on 16SrRNA sequences. Phylogenetic tree was constructed by using the Neighbor-Joining method with bootstrap consensus 1000 replicates the evolutionary distance were computed using the Maximum composite likelihood method. Bootstrap consensus values are shown below the branches. The tree was generated by using MEGA X software.