Clinical Significance and Correlation of CXCL8 and its mRNA in the Children with Mycoplasmal Pneumonia
Clinical Significance and Correlation of CXCL8 and its mRNA in the Children with Mycoplasmal Pneumonia
Lin Sun1, Xiaofang Bu2, Jian Wang1*, Xiaorui Liu1 and Zhanyi Kong2
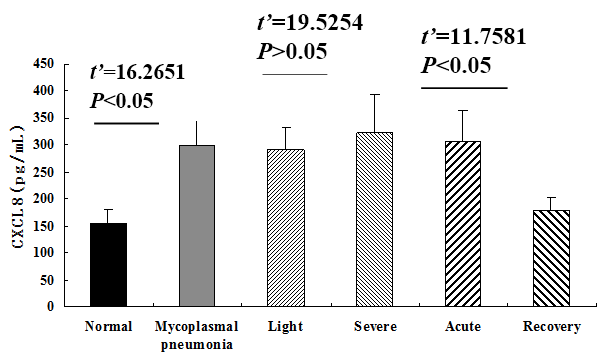
Levels of CXCL8 in serum of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. The high concentration of CXCL8 in peripheral blood was explored in the children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and was mostly occurred in the acute stage. There was no significant difference of the CXCL8 level in the patients between the light and severe.
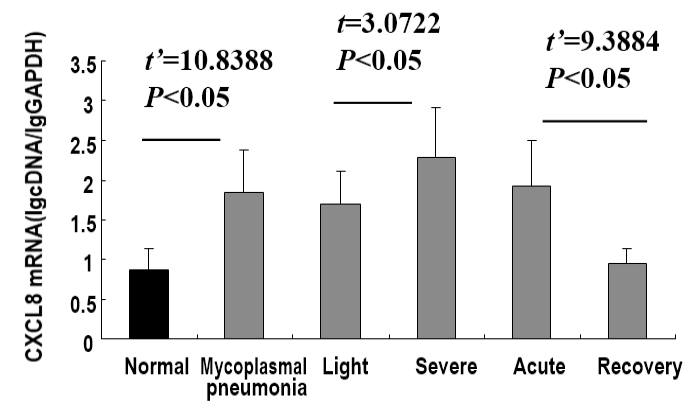
Levels of CXCL8 mRNA in PBMCs of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. The loads of CXCL8 mRNA in PBMCs were significantly increased in children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and were more common in acute stage and the severe cases.
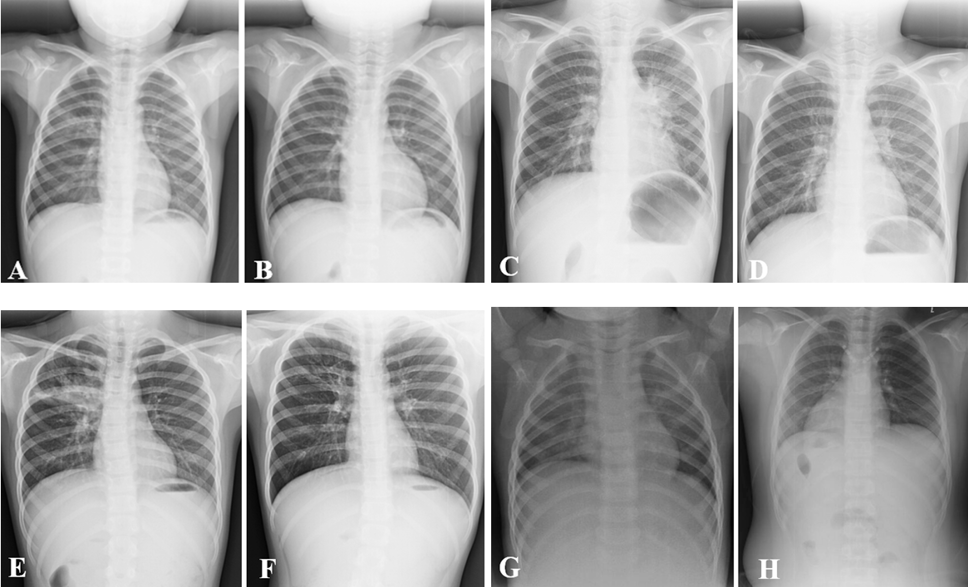
The Iconography features of Mycoplasma pneumoniae before and after treatment. A and B, Before and after the treatment of the patient (Light). C and D: Before and after the treatment of the patient (Severe). A, The obvious inflammatory infiltration accompanied with local patchy fuzzy shadow was found in the middle lobe of the right lung. B, The slight inflammation was residue after treatments. C, The patchy and fuzzy shadows could be seen in left hilar and left lower lung of the children with moderate mycoplasma pneumonia. D, Most fuzzy shadows in left hilar and left lower lung were markedly relieved. E, The interstitial inflammation was showed in double pulmonary and the clear atelectasis was also visual in the middle lobe of the right lung. F, Most of the interstitial inflammation was reduced, and the atelectasis in the middle lobe of the right lung was obviously disappeared. G and H were both as normal controls.
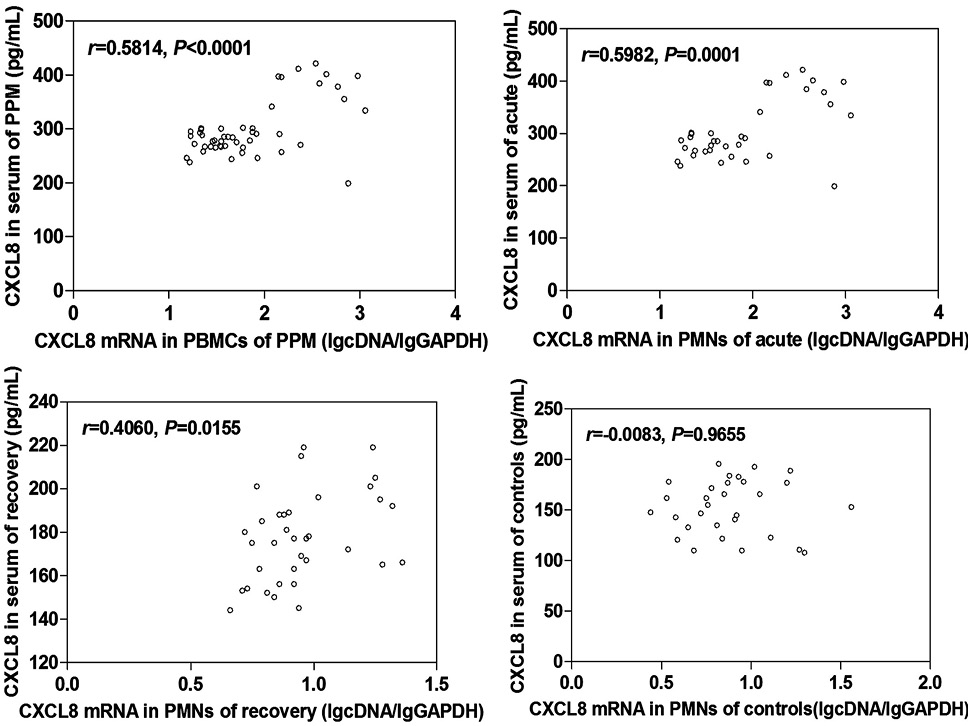
The correlation between CXCL8 content and its mRNA expression in different course of mycoplasma pneumonia in children. The level of CXCL8 was positively correlated with the expression of its mRNA in the children. With the sequential treatment of erythromycin and azithromycin, the correlation between them decreased significantly.
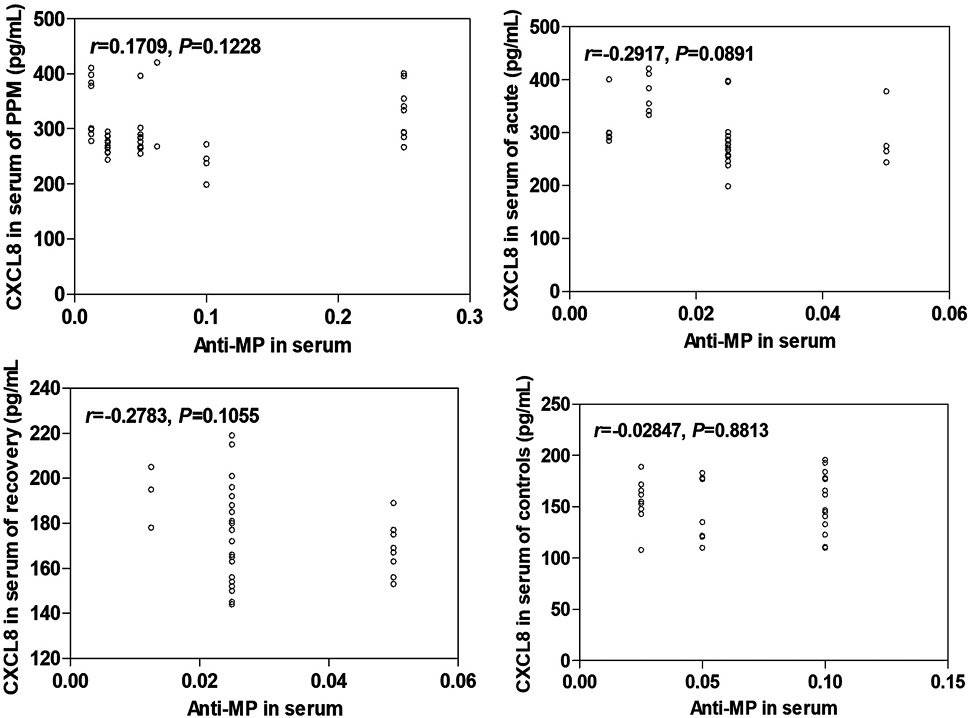
The correlation between serum CXCL8 level and serum Anti-MP level in children with mycoplasma pneumonia in different course of disease. The weak correlations between the levels of CXCL8 and Anti-MP all had been explored in the acute and convalescent stages.
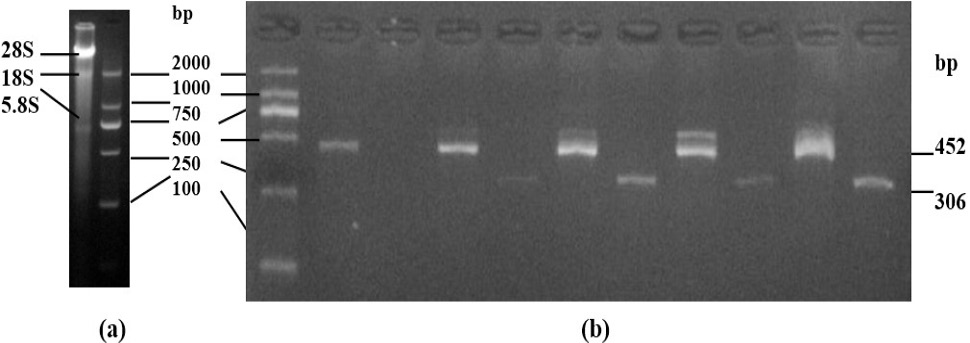
(a). The electrophorogram of total RNA from PBMCs. (b). Expression of CXCL8 mRNA in the PBMCs of mycoplasmal pneumonia. Note: M: DL2000; 1, 2 for GAPDHC and CXCL8 of normal control; 3, 4, 5, 6 for GAPDH and CXCL8 of mycoplasmal pneumonia (light 1 and light 2); 7, 8, 9, 10 for GAPDH and CXCL8 of mycoplasmal pneumonia (severe 1 and severe 2).
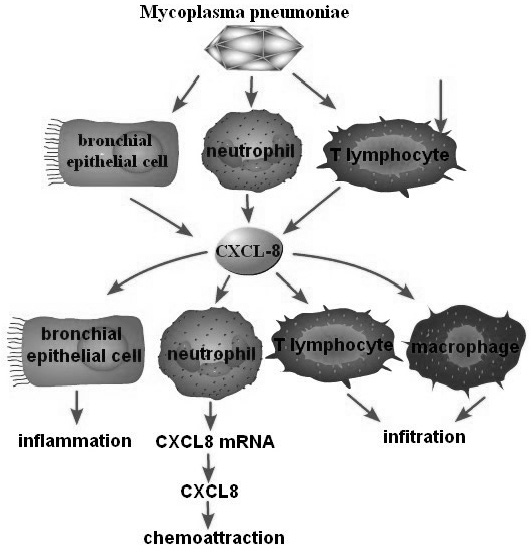
CXCL8 expression induced by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. CXCL8 can be induced by Mycoplasma pneumoniae via the pathway of signal transduction in bronchial epithelial cells and neutrophils.