Bovine Tuberculosis (bTB): Detection of Mycobacterium bovis Infection with Specie-specific Primers in Sputum Samples in Pakistan
Bovine Tuberculosis (bTB): Detection of Mycobacterium bovis Infection with Specie-specific Primers in Sputum Samples in Pakistan
Asad Ullah1*, Umar Sadique2, Ibadullah Jan2, Imad Khan1, Raheela Taj3, Mumtaz Ali Khan4, Salah-ud-din4, Naimat Ullah Khan1
Sample collection site, district Peshawar Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP) province. Pakistan.
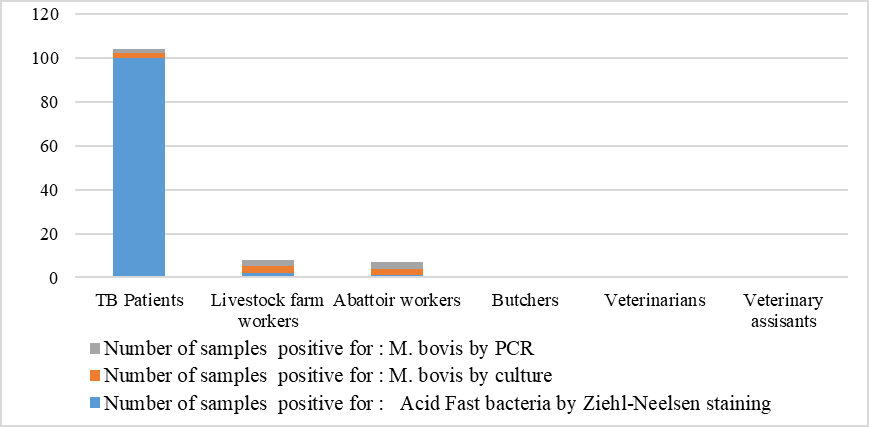
Graph showing the overall results of Ziehl-Neelsen staining, Culture and PCR of the occupational groups in the study area.
PCR amplicon showing specie-specific 500bp DNA of Mycobacterium bovis (S5, 7-12 and S14). S1-4, 6 & 13 are negative samples.
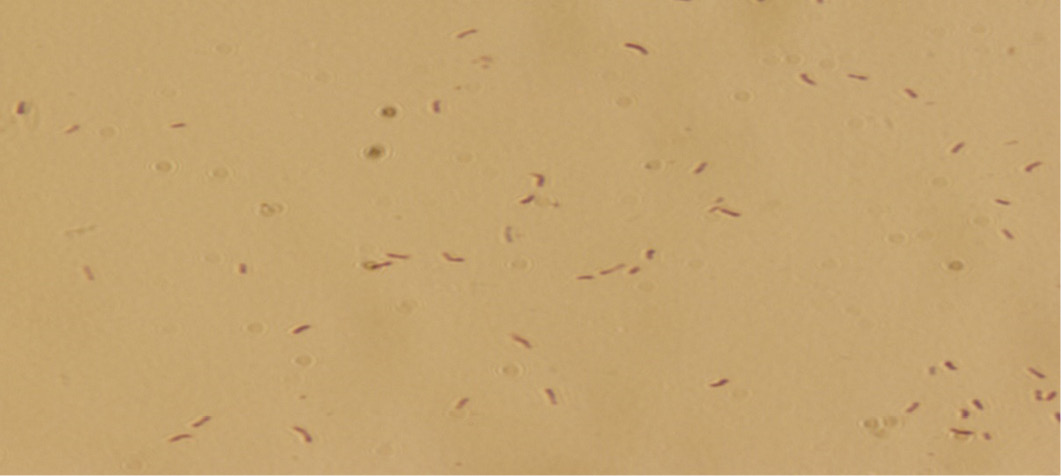
Ziehl-Neelsen staining of sputum samples of TB patients showing acid-fast bacilli.
Ziehl-Neelsen staining of sputum samples of livestock farm workers showing acid-fast bacilli.
Ziehl-Neelsen staining of sputum samples of abattoir workers showing acid-fast bacilli.