Antioxidant Activity and Determination of Total Polyphenol Levels in White Tea Leaves (Camellia sinensis L.)
Antioxidant Activity and Determination of Total Polyphenol Levels in White Tea Leaves (Camellia sinensis L.)
Fahrauk Faramayuda*, Soraya Riyanti and Sitty Mahanadhiandinie
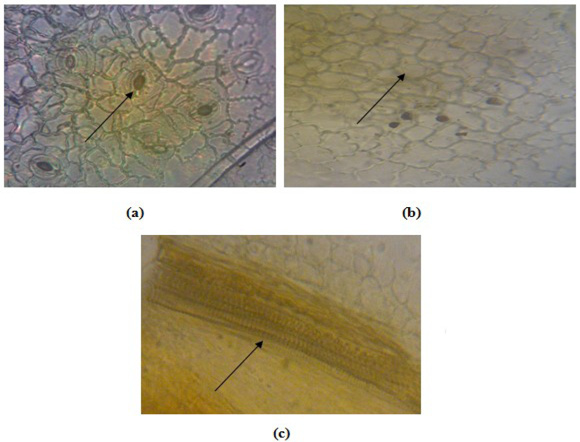
Microscopic examination of white tea leaves and white tea dry material 400x magnification. Stomata of anomocytic type, longitudinal leaf incision (a), polygonal epidermal tissue, longitudinal leaf incision (b), xylem carrier bundle with spiral thickening, dry material powder (c).
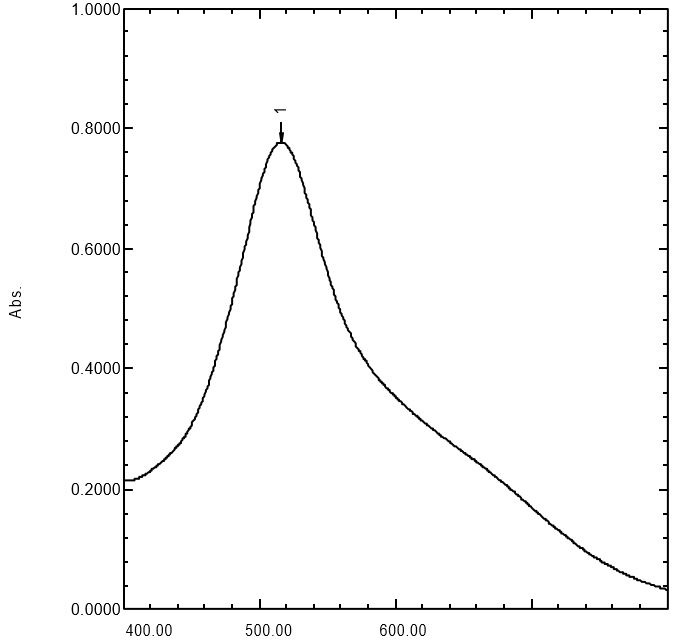
Absorption curve of DPPH solution. Reagent solution = DPPH solution 30 µg/mL in methanol at a wavelength (λ) max 515.50 nm with a maximum absorption of 0.778.
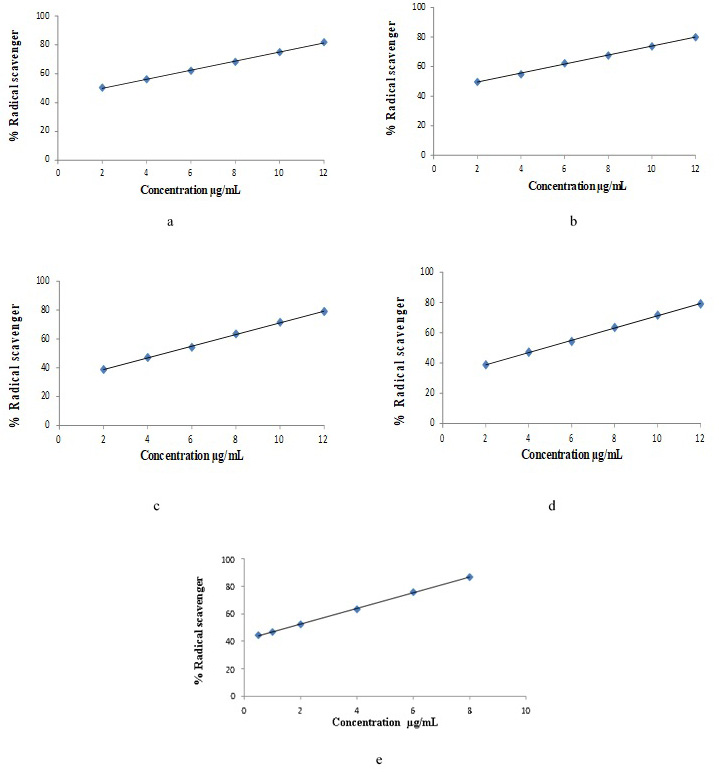
Linear regression curve of DPPH free radical scavenging percentage. quercetin (a), ethanol extract (b), water fraction (c), n-hexane fraction (d), ethyl acetate fraction (e).
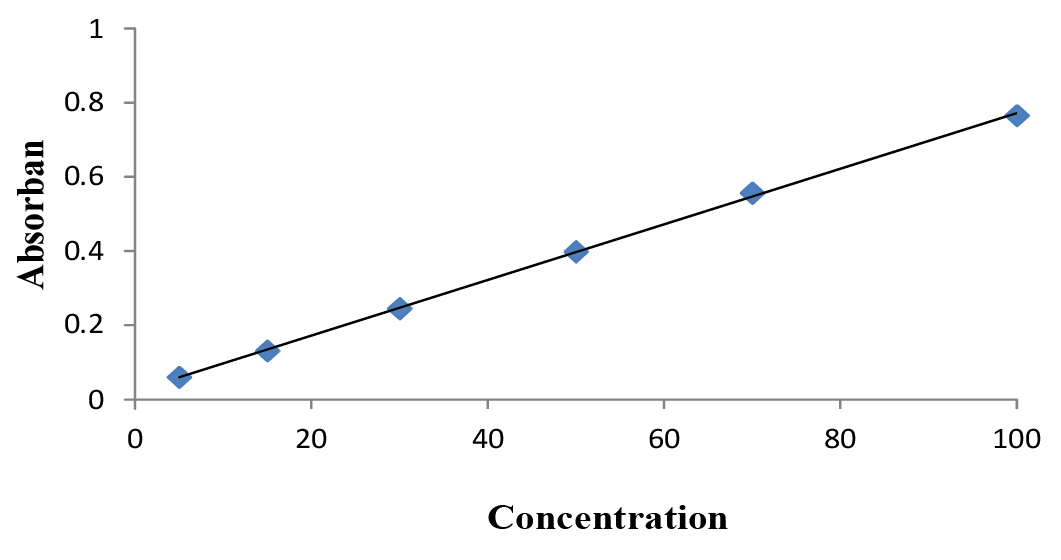
Tannic acid calibration curve at λ 779 nm.
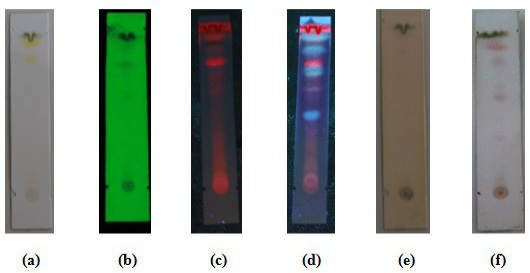
Thin layer chromatography of white tea leaf n-hexane fraction. Mobile phase: Chloroform: Methanol (9:1). visually observed (a); observed under 254 nm ultraviolet light, the presence of black spots with Rf 0.66, Rf 0.88 and Rf 0.93 (b); observed under 365 nm ultraviolet light, the presence of blue spots at Rf 0.66, Rf 0.77, Rf 0.88, and Rf 0.93 (c); sprayed with the sight of AlCL3 spots, the spots turned bright blue at Rf 0.44, Rf 0.67, Rf 0.77, Rf 0.88, and Rf 0.93 (d); used FeCl3 spot viewer, black spots appear with Rf 0.88 and 0.93 (e); given the appearance of vanillin sulfate spots, purple spots appeared at Rf 0.33, Rf 0.6, Rf 0.67, Rf 0.82 and Rf 0.88 (f).
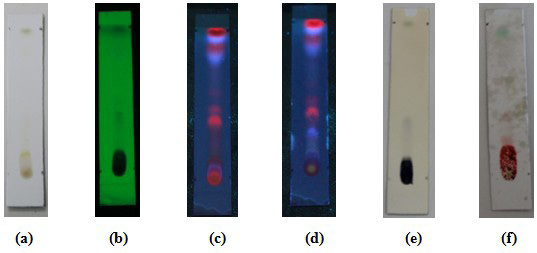
Thin layer chromatography of white tea leaf ethyl acetate fraction. Mobile phase: Toluene: Ethyl Acetate (5 : 5). Visuals (a); observed under 254 nm ultraviolet light, the presence of black spots with Rf 0.44 and Rf 0.51 (b); observed under 365 nm ultraviolet light, the presence of reddish orange spots at Rf 0.44, Rf 0.51, and the presence of blue spots at Rf 0.77 and 0.93 (c); sprayed with AlCL3 spot sight, the spots changed to a bright blue color at Rf 0.27, Rf 0.66, Rf 0.77, and Rf 0.93 (d); used FeCl3 spot viewer, blue-black spots appear with Rf 0.44 (e); Vanillin sulfate was used to show spots, light purple spots appeared at Rf 0.27, Rf 0.4, and blue spots appeared at Rf 0.93 (f).
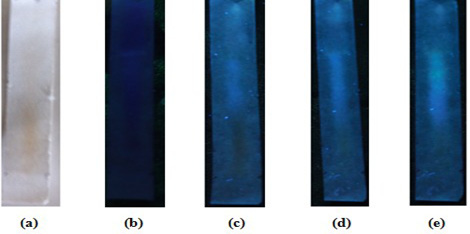
Paper chromatography of white tea leaf water fraction. Mobile phase: Butanol: Acetic Acid Water (4 : 1 : 5 ). Visual(a); observed under a 365 nm UV lamp (b); observed under 365 nm ultraviolet light, the presence of a tailed blue spot (c); sprayed with AlCL3 spot sight and observed under 365 nm ultraviolet light, a bright blue colored spot appears with tail (d); after being given ammonia vapor and observed under ultraviolet light at 365 nm, a yellowish green spot appeared at Rf 0.62 (e).
Macroscopic leaves and white tea dry material. White tea leaves (A), dry material white tea leaves (B).