Alzheimer’s Disease: Pathogenesis, Hypothesis and Management
Alzheimer’s Disease: Pathogenesis, Hypothesis and Management
Rabia Anjum
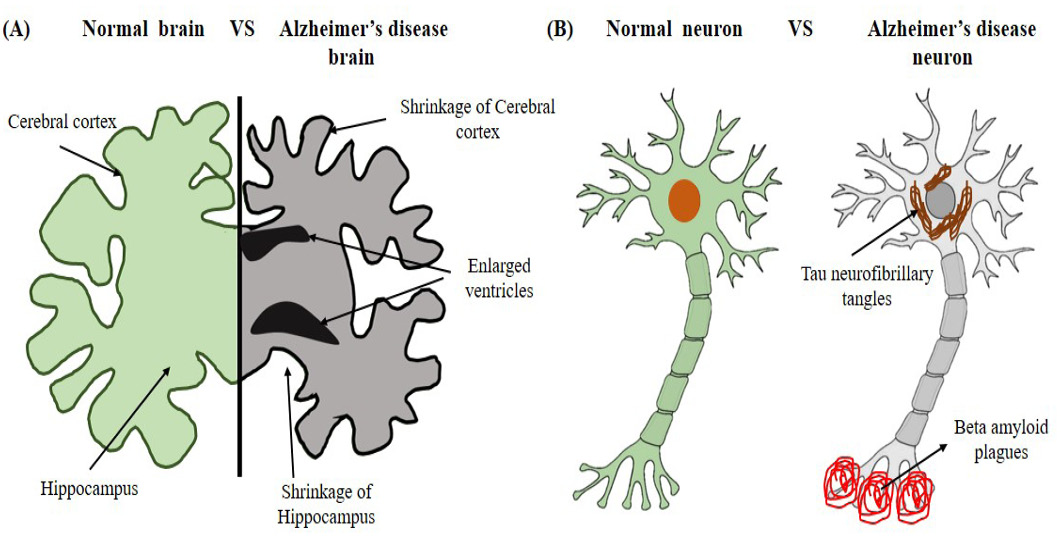
The physiological structure of brain and neuron of AD (A) shrinkage of cerebral cortex and hippocampus and enlarged ventricles in AD brain (B) Tau neurofibrillary tangles in cell body and beta amyloid plagues on the dendrites of AD neuron.
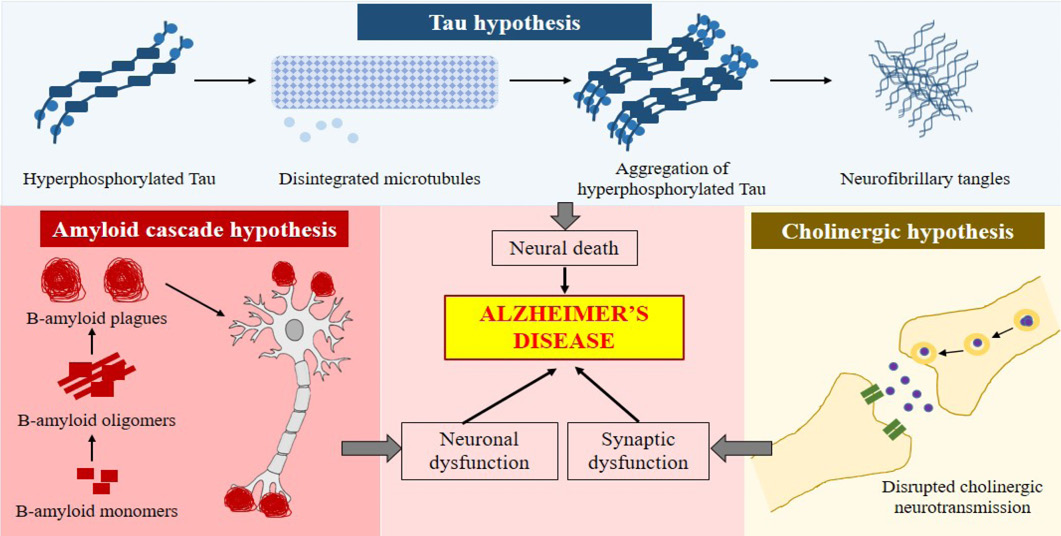
Schematic representation of different hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloid cascade hypothesis: β-amyloid monomers in the absence of proper signaling forms the β-amyloid plaques that cause neuronal dysfunction. Tau Hypothesis: Where increased production of hyperphosphorylated tau promote disintegration of microtubules and accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau fibrils causing neural death. Cholinergic hypothesis: Disrupted Acetylcholine effect the synaptic function.