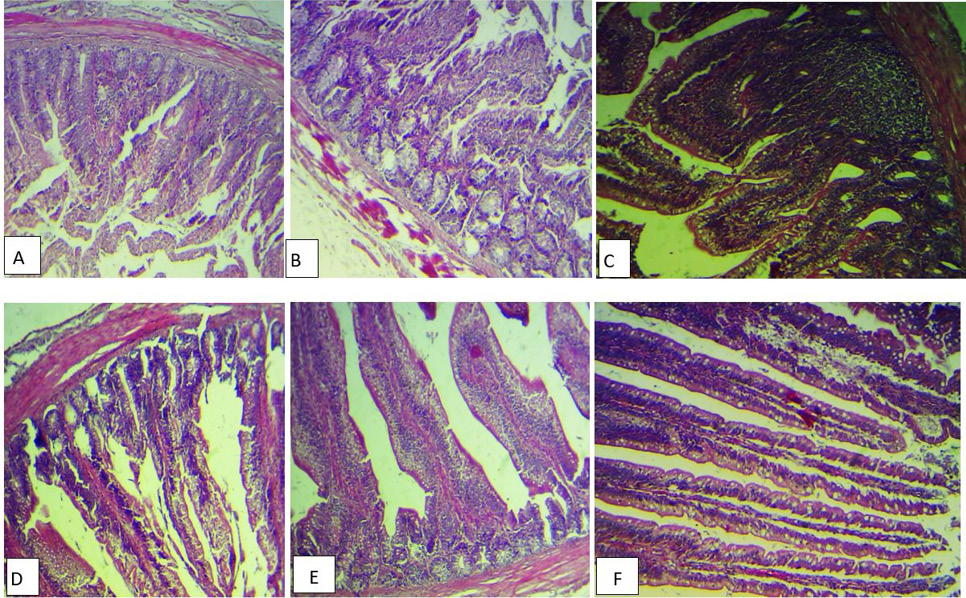
(A) Histopathological section of intestine broiler inoculated with E. coli alone showing congestion of the serosa blood vessels (), sloughing and fusion of intestinal villi (), with inflammatory cells infiltration (H&E stains ,40x). B, Histopathological section of intestine for E. coli group showing atrophy of intestinal villi (), necrosis in some glands (), with intermascularis edema (H&E stains, 40x). C, Histopathological section of intestine inoculated with E. coli and treated with berberine group showing hyperplasia of the intestinal associated lymphoid tissues with increase in goblet cells number (H&E stains, 40x). D, Histopathological section of intestine for E. coli treated with berberine group showing normal intestinal villi with increase in the numbers of the goblet cells (H&E stains, 40x). E, Histopathological section of intestine for E. coli treated with enerofloxacin group showing necrosis of the intestinal villi with inflammatory cells infiltration (H&E stains, 40x). F, Histopathological section of intestine for E. coli treated with berberine and enerofloxacin showing normal intestinal villi with increase in the numbers of the goblet cells (H&E stains, 40x).