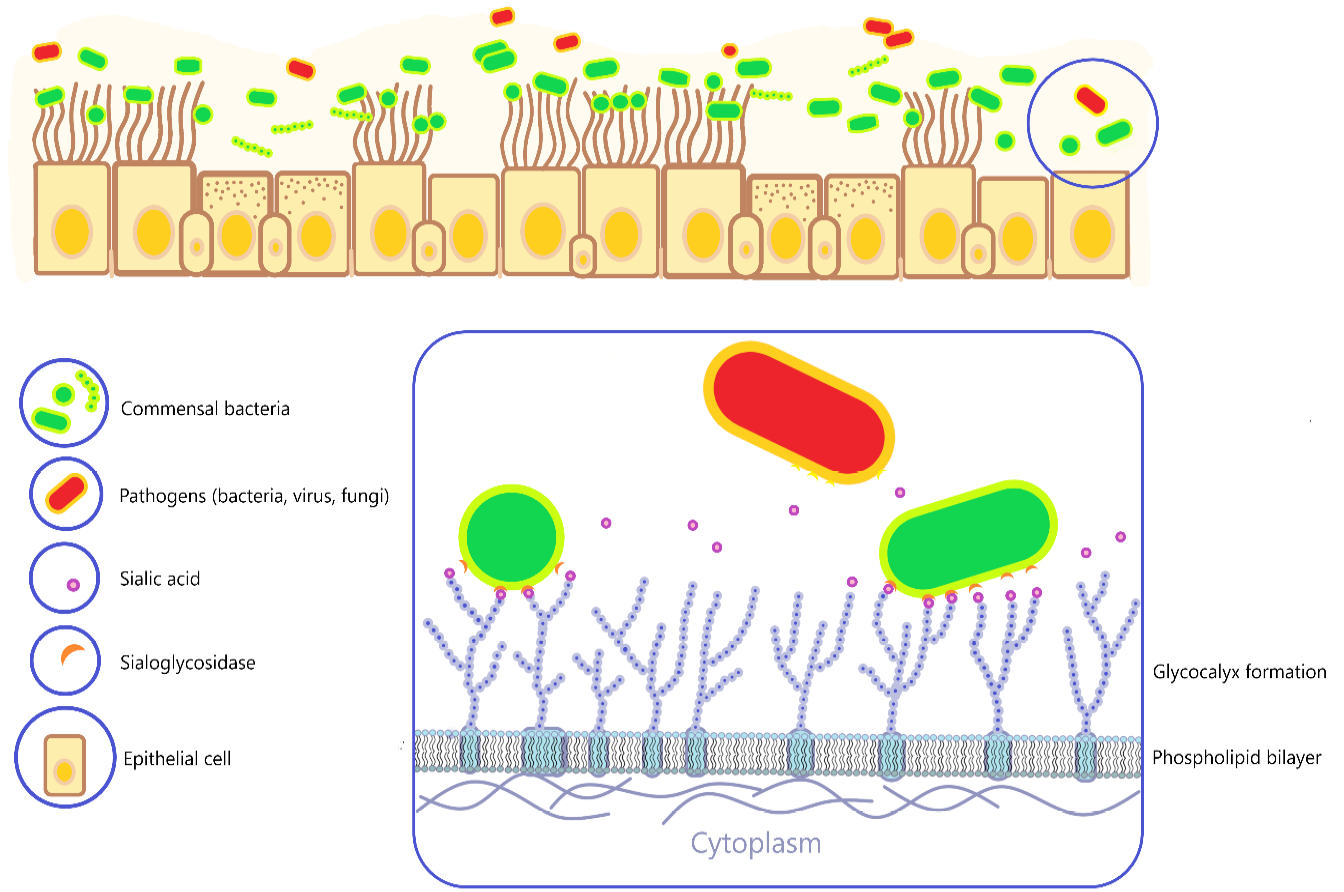
Figure 1:
Physiological condition of respiratory tract microbiome illustration. Diverse commensal bacteria in the respiratory tract live with a balanced composition without pathological conditions. Various pathogens (bacteria, viral and fungal) with relatively limited numbers are less likely to infect the host if there is no drastic changes in conditions. Glycocalyx is glycoprotein and glycolipid that cover the surface of the host epithelial cell membrane. Sialic acid which is in the structure has a place to attach to several normal microorganisms and pathogens which are assisted by sialoglycosidase.