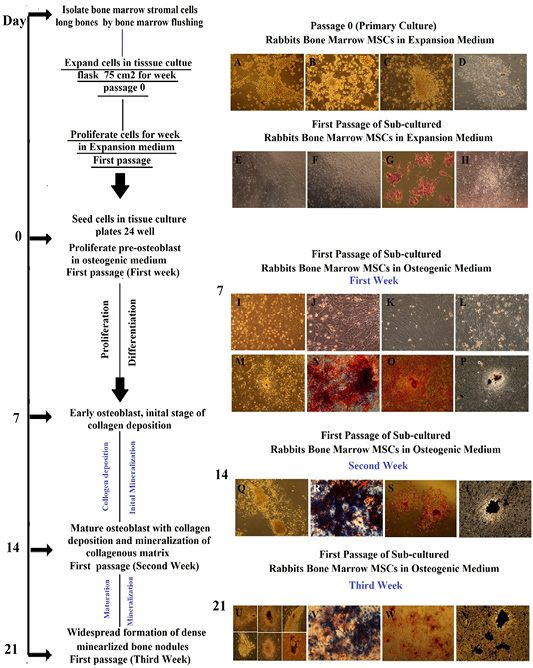
Morphology representation of cultured Rabbit BM-MSCs in expansion medium and their osteogenic differentiation potential with specific markers through first passage/ second and third week cultured in osteogenic medium; Morphology of cultured Rabbit BM-MSCs in expansion medium, passage 0 (primary cell culture). (A) at time 0, colonies of cells were seen by inverted phase contrast microscope in expansion medium, Cells were obtained by bone marrow flashing. (B) at day 2, elongated cells were appeared and selected by adherence to plastic, whereas floating cells are residual red blood cells and unattached mononuclear cells were maintained in expansion medium. (C) at day 3, following removal of non-adherent hematopoietic stem cell populations by changing medium for first time, adherent colonies. The number of colonies varied from 3-7 per flask. Central cells showed high nucleo cytoplamic ratio with little cytoplasm. (D) at day 7, fibroblastoid cell population proliferated and increased in density with time and nodular confluence (80-90%) was noticed. Confluence appeared as marked increase in fibroblastoid cell population in colonies (nodules). Morphology of sub-cultured Rabbit BM-MSCs in expansion medium, first passage. (E, F) thin and fiberoblast-like MSCs were seen and widespread in all culture plate after trypsinization. (G) By hematoxylin and eosin, the cells were polygonal with pink to light violet cytoplasm and blue nucleus. (H) Thin and fiberoblast-like MSCs were arranged and expanded in bundles and sheets at day 7 of first passage in expansion medium. Morphology of sub-cultured Rabbit BM-MSCs in osteogenic medium, first passage through first week of differentiation, alkaline phosphatase histochemical staining, Alizarin Red staining and von Kossa staining. (I-K) Rabbit BM-MSCs assumed a less elongated, polygonal, cubodial appearance with central rounded nuclei or multipolar after 48-72 h of subculture. (L-M) at day 7 showed coalescing cellular aggregates arranged in swirling sheets and bundles with interconnected multilayer foci showing central matrix-like substance like nodules. (N) Osteoblast expressing ALP enzyme were blue interspersed by negative red cells , Positivity of subculture for ALP staining was noticed as early as day 7 with percentage around 20%. (O) Orange red color was seen by positive cells in large amount and also, positive cells were interspersed with negative cells. (P) Black mineral deposits were seen in large amount and large size. Mineralized areas were interspersed by another un-calcified small cell colony. The characteristic halo, surrounding the bone nodule evidence of the enzymatic activity of the ALP, Inverted Phase Contrast Microscope Digital Camera Olympus, Magnification 10x, Morphology of sub-cultured Rabbit BM-MSCs in osteogenic medium, first passage through second week of differentiation, alkaline phosphatase histochemical staining, Alizarin Red staining and von Kossa staining. (Q) The number of nodules increased dramatically in size and becoming multilayered with deposition of collagen and mineralization of collagenous matrix(R) ALP staining was noticed with percentage around 60-80% at day14. (S)The mineralized nodules were labeled as red spots with alizarin stain and increased in size dependant on time and number of cells. (T) Mineral deposits were stained black with von kossa stain. Morphology of sub-cultured Rabbit BM-MSCs in osteogenic medium, first passage through thrid week of differentiation, alkaline phosphatase histochemical staining, Alizarin Red staining and von Kossa staining. (U) The number of nodules increased dramatically in size with widespread formation of dense mineralized bone structure. (V) Decline in staining intensity for ALP was noticed with percentage around 60% at day 21. (W) The mineralized nodules were labeled as red spots and increased in number and staining intensity in a time dependent manner covering more than 80 % of culture plate. (X) Mineral deposits were stained black with von kossa stain and almost of black mineral deposits areas were mostly located in the central confluent multilayered clusters of cells.