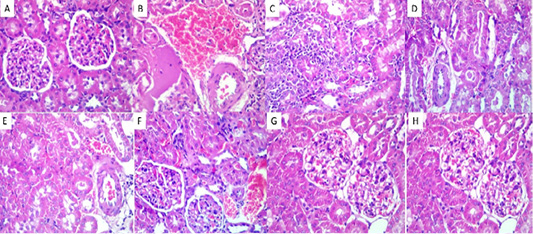
Histopathological results in the kidney. (A) The kidney of control rats showed a normal histological picture, H&E, X 40. (B) The kidney of diabetic rats showed notable vascular congestion with endothelial hypertrophy, interstitial edema, and tubular necrosis, H&E, X 40. (C) The kidney of 0.25 mg ZnO NPs-treated rats showed interstitial mononuclear cell infiltration, and vacuolation of the tubular epithelium with single-cell necrosis, H&E, X 40. (D) The kidney of 0.5 mg ZnO NPs-treated rats showed tubular attenuation, hyaline cast formation, congestion of the peritubular capillaries, regenerative tubular epithelium, and endothelial hypertrophy, H&E, X 40. (E) The kidney of 0.25 mg empagliflozin-treated rats showed cast formation, tubular attenuation, vascular congestion, endothelial hypertrophy, and the presence of few numbers of mononuclear cells in the interstitial tissue, H&E, X 40. (F) The kidney of 0.5 mg empagliflozin-treated rats showed vascular congestion, and endothelial hypertrophy, H&E, X 40. (G) The kidney of 0.25 mg ZnO NPs + 0.25 mg empagliflozin treated rats showed mild vascular congestion, and luminal debris, H&E, X 40. (H) The kidney of 0.5 mg ZnO NPs + 0.5 mg empagliflozin-treated rats showed an almost normal histological picture except for mild glomerular congestion, H&E, X 40.