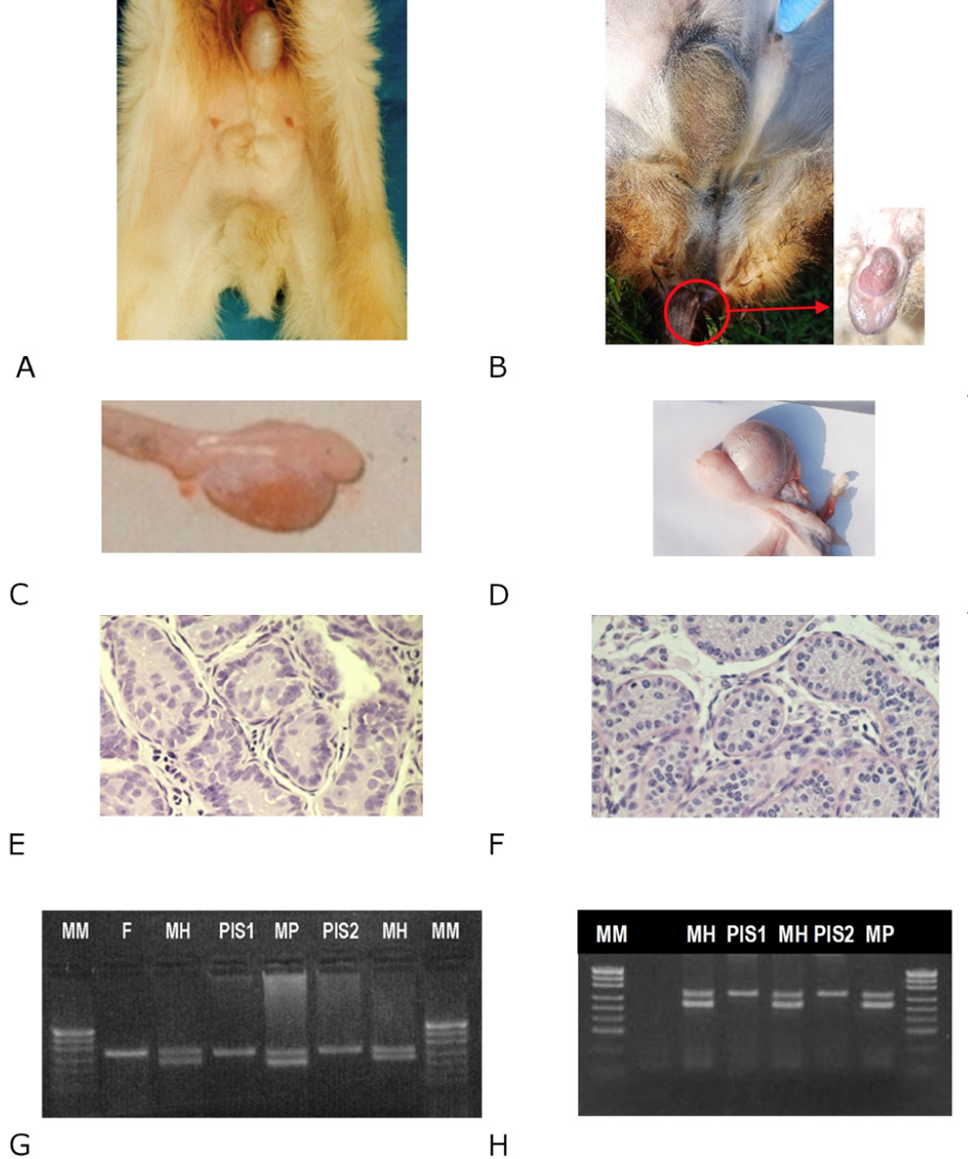
Phenotypic description of the PIS individuals (masculinization of external and internal genitalia, histological examination of the gonads) and a sex identification test (based on the AMGLX, AMGLY and SRY genes). A, Male-specific external genitalia; caudally displaced hypoplastic penis; absence of the urethral process; problems with urination. B, Male-specific external genitalia; one testis in the scrotum, the second one in the groin area; enlarged clitoris. C, Testes with epididymides. D, Testes with epididymides. E, In the testis of the animal, the seminiferous tubules lacked lumen and contained Sertoli cells and priomordial cells located on the basal lamina and occasionally in the center of the tubules. F, the seminiferous tubules lacked lumen and contained spermatogonia and Sertoli cells; the interstitial tissue with a small group of Leydig cells. G, AMGLX, AMGLY, MM, DNA ladder; F, female; MH, horned male; MP, polled male; PIS1 and PIS2, sex-reversed individuals; H – SRY, MM, DNA ladder; F, female; MH, horned male; MP, polled male; PIS1 and PIS2, sex-reversed individuals.