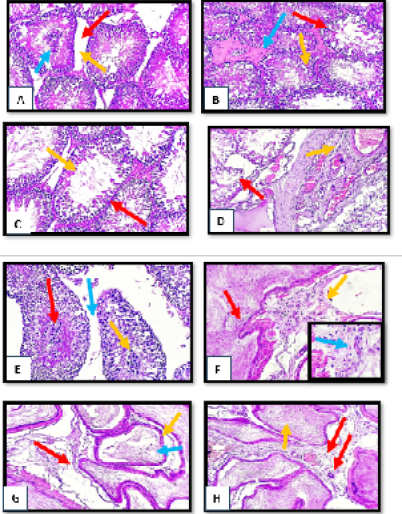
Figure 2:
Histopathological section of testes and epididymis tissue from tetrodotoxin treated group (1µg/kg.bw) of male albino rats (A) disruption of seminiferous tubules (red arrow) with absence of leydig cells (yellow arrow) with central clamping of necrotic spermatogonia (blue arrow).(B) sever degenerative changes of spermatogonia cells (red arrow) with irregular appearance of spermatid (yellow arrow) with presence of edematous substance between degenerated seminiferous tubules (blue arrow).(C) marked reduction of spermatogonia cells lining (red arrow) with sperm irregularity (yellow arrow).(D) disorganized irregular seminiferous tubules (red arrow) with subcapsular dilation and congestion (yellow arrow).(E) clumping of degenerated spermatocyte (red arrow) with necrotic sperms (yellow arrow) with obvious widening of interlobular septa (blue arrow).(F) focal hyperplasia of epididymal lining (red arrow) with blood vessels congestion (yellow arrow) with sever mononuclear cells infiltration in the vascular connective tissue (blue arrow) (H&E stain, X10, inset X40).(G) moderate widening of some epididymal tubules (red arrow) with giant tubules appearance (yellow arrow) with slight degeneration of mature sperms (blue arrow) (H&E stain, X10, inset X40).(I) fibrovascular tissue with newly form capillaries between epididymal tubules (red arrow) with sperms stasis (yellow arrow). (H&E stain, X10).