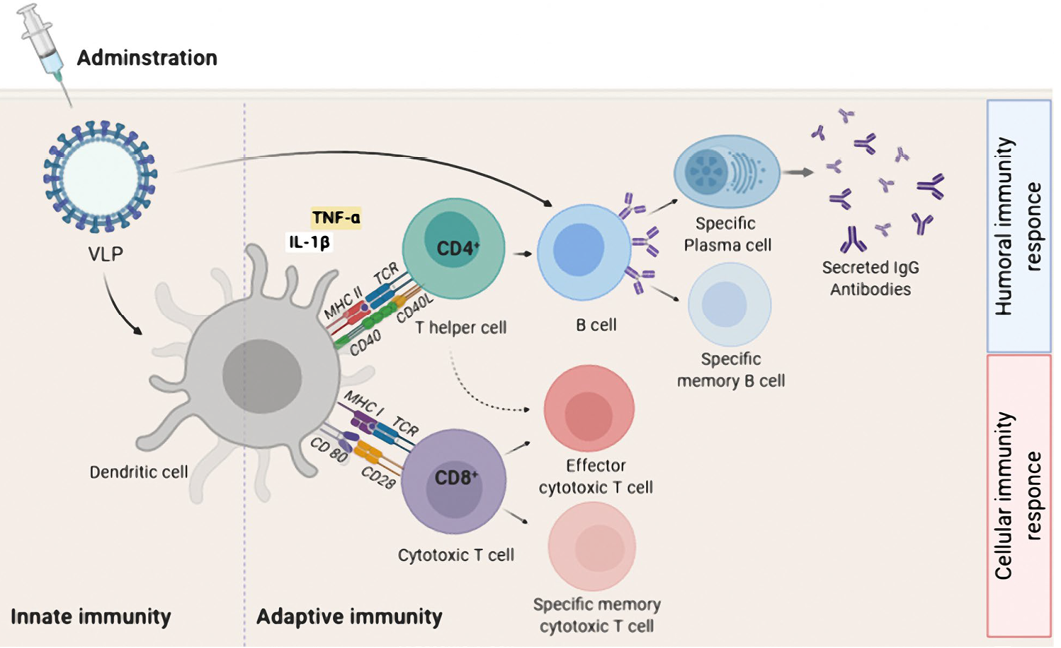
Adaptive immune activation induced by VLP-based vaccine. After administration, a VLP-based vaccine is taken up by APC such as dendritic cells. The phagocytosed VLP-based vaccine is processed and presented by both MHC-II and MHC-I for detection by CD4+ and CD8+T cells, respectively. For induction of humoral immune responses, B cells interact with CD4+ T helper cell (TH) to uptake VLP-based vaccine by B cell receptor. The interaction between CD4+ TH cells and B cells occurs for sufficient secretion of IgG antibodies by plasma cells as well as the generation of B memory cells. For induction of cellular immunity responses, immature CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) proliferate and differentiate into effector and specific memory CTL. Effector CD4+ TH cells, increase antigen presenting by APC by secreting cytokines, and also assist activated CTL.