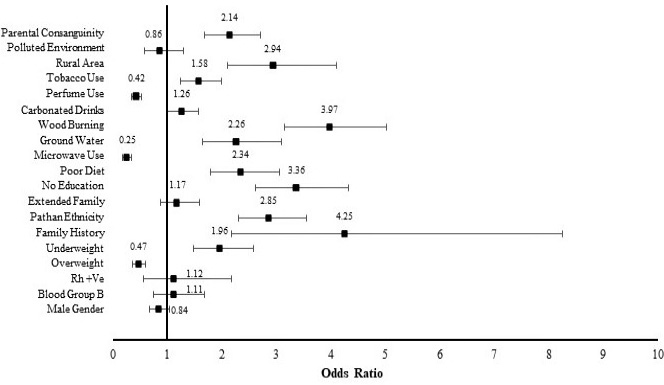
Odds ratios were calculated comparing the exposure of risk factor to patients and controls (CI 95%, p*= 0.05). It is indicated that lower BMI (ref. normal and higher BMI), poor diet (ref. standard BMI), all forms of tobacco use (ref. no use), consanguineous parental union (non-consanguineous parental union), family history of leukemia and solid cancers (ref. no family history), lack of basic education (ref. educated) and hailing to Pathan ethnicity (ref. other ethnicities additively) were high risks variables significantly associated to leukemia. In lifestyle related factors, wood burning, consumption of unprocessed ground water for drinking purposes, living in a residential rural set up were found to increase leukemia risk significantly and use of carbonated drinks was only observed to cause a slight but significant risk for leukemia; However, wearing perfume and microwave use has been observed to have protective effect for leukemia risk. The reference used for above factors were gas burning, water from all other sources, urban residential set up, no consumption of carbonated drinks, no use of perfume and no use of microwave, respectively. No significant risk-based association was noticed for extended family type, blood group B, Rh +ve, and gender in the studied population for leukemia patients in comparison to controls, taking nuclear family, all other blood groups than B, Rh -ve and female gender as reference.