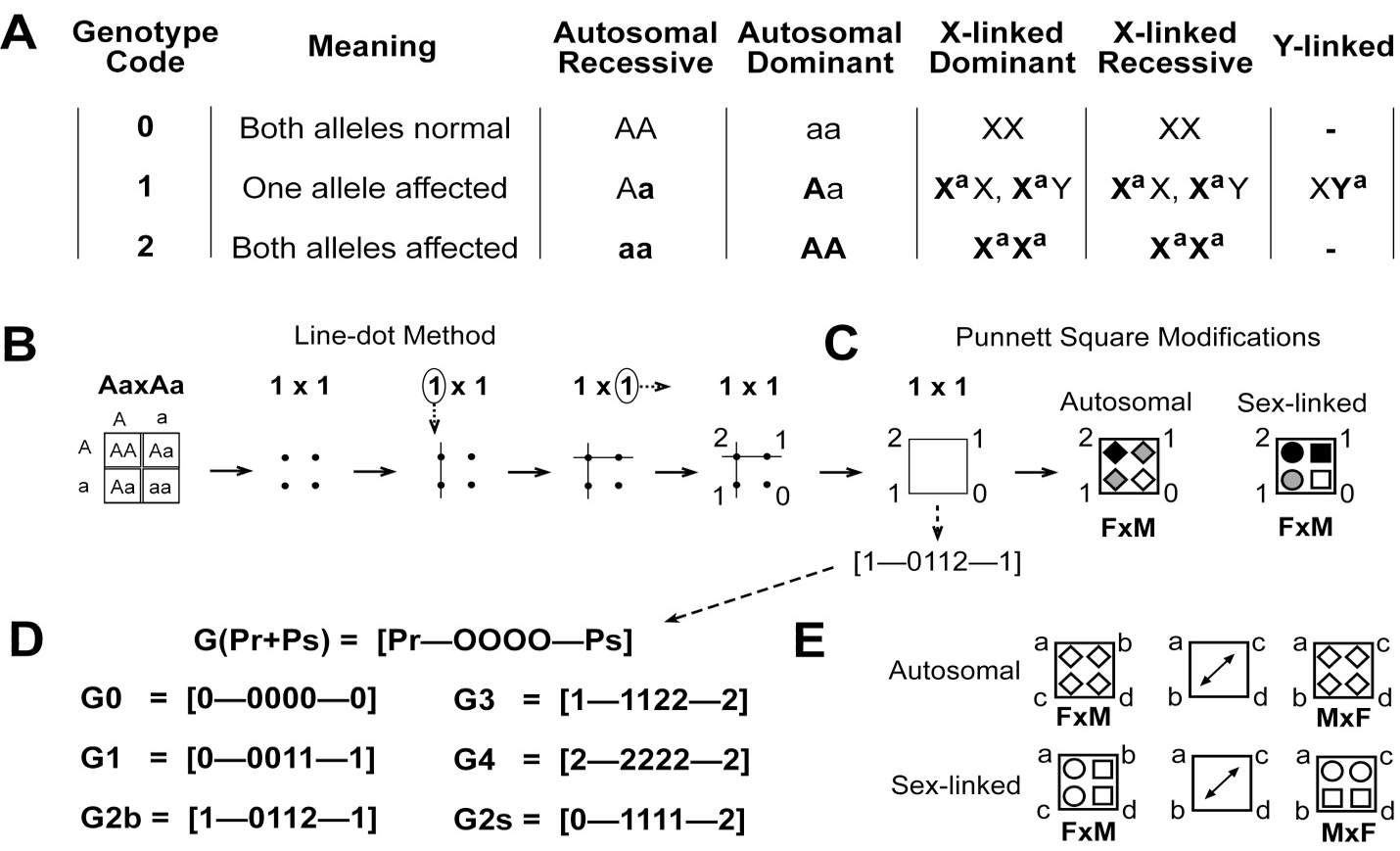
Overview of different approaches used. A, ternary coding for genotypes and their corresponding symbols generally used in literature. Bold symbols are affected alleles; B, line-dot method. Here, dot = 0, one line passing through a dot = 1, two lines passing through a dot = 2; C, Punnett square modifications. Unfilled symbols = normal, filled symbols = affected, light filled symbols = heterozygotes that will be affected for dominant and carrier for recessive conditions; D, ternary coded genotype probability groups. Parents’ genotype codes are on the sides and four offspring codes are in the middle. Group name is based on the total number of affected alleles (Pr and Ps) shared by parents. 2b = total of two affected alleles each allele shared by both parents, 2s = total of two affected alleles which are coming from single parent; E, diagonal shift of genotypes in autosomal and sex-linked outcomes described with diagonal pointing arrow.