Relationship between Human Disturbance and Habitat Use by the Endangered François’ Langur (Trachypithecus francoisi) in Mayanghe Nature Reserve, China
Relationship between Human Disturbance and Habitat Use by the Endangered François’ Langur (Trachypithecus francoisi) in Mayanghe Nature Reserve, China
Jialiang Han1, Guohou Liu1*, Wenke Bai2,3, Qixian Zou4, Ye Cao5, Caiquan Zhou2,3*, and Guy Michael Williams6
Mayanghe Nature Reserve, established to protect the François’ langur in Guizhou, provinces, China.
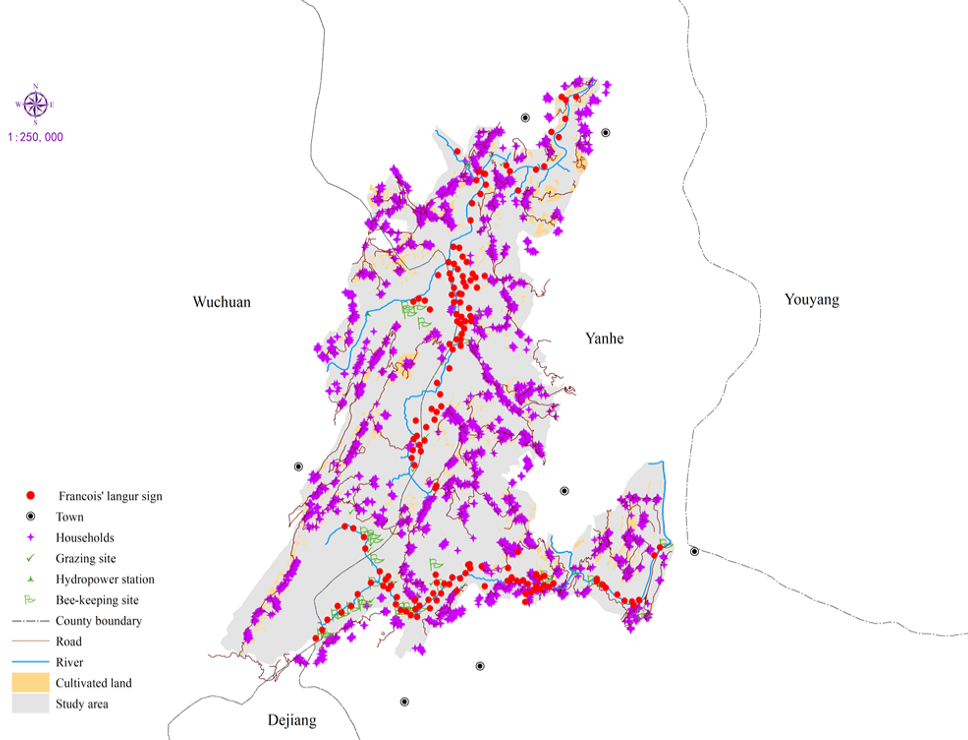
The locations of François’ langur signs and human disturbance in the study area.
Line- and curve-fitting analysis of the relationship between the François’ langur habitat use intensity and distance to households.