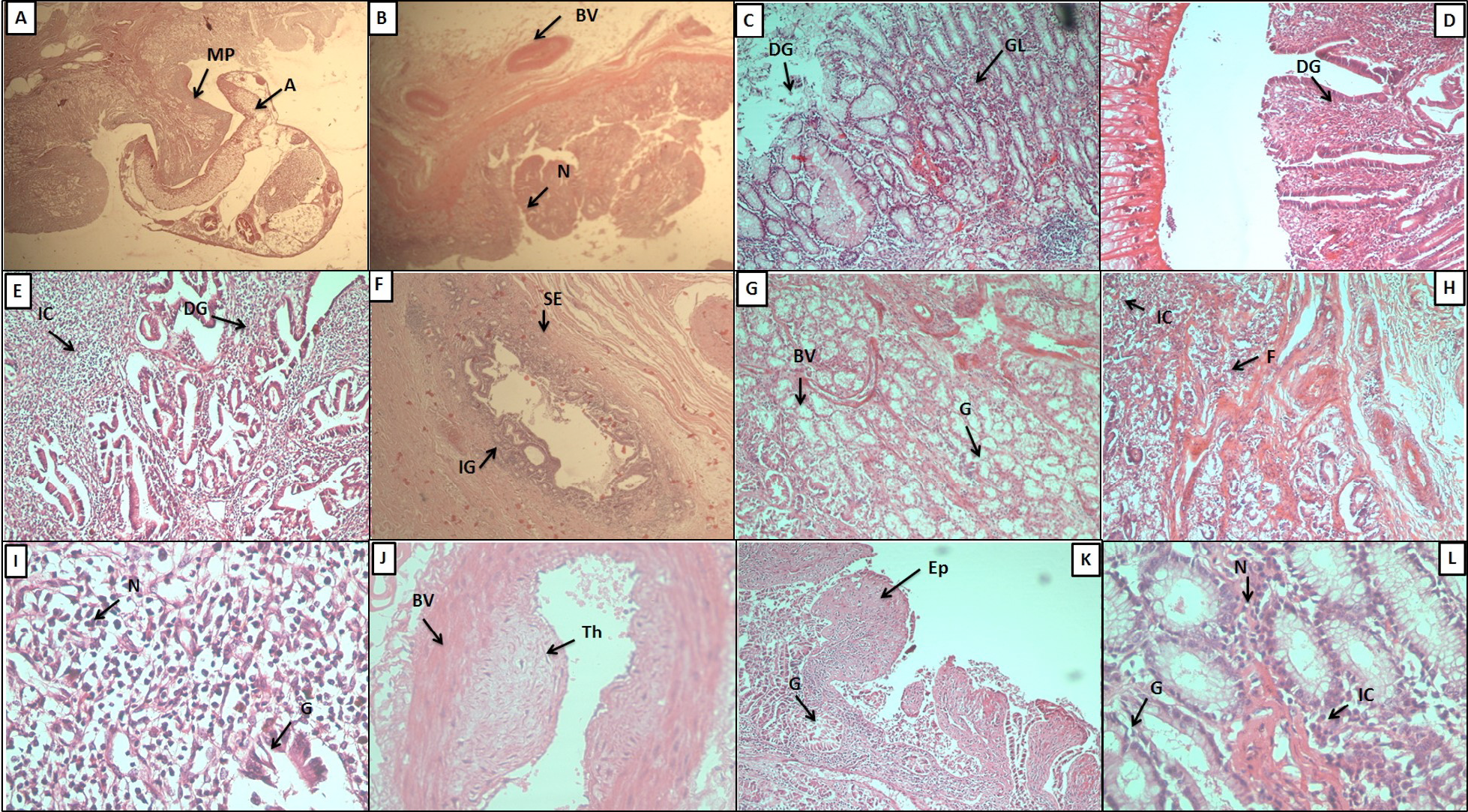
Histopathological study of buffalo bile duct. A: Cross section of the infected bile duct; A, acetabula; MP, mucosal plug. B: mucosal plugs formed due to parasite attachment; BV, blood vessel; N, nodule. C: the glandular mucosa showing extensive glandular hyperplasia; DG, degenerated gland; GC, glandular cells. D: the glandular degeneration and villi like appearance at the site of fluke attachment. E: massive glandular degeneration and inflammation; IC, inflammatory cells. F: glandular infiltration in serosal layer; IG, inflammed glands; SE, serosa. G: sub mucosal layer showing increased glandular hyperplasia; BV, blood vessel; G, gland. H: serosal layer of infected bile duct showing fibrosis; IC, inflammatory cells; F, fibrosis. I: inflammatory cells; N, nucleus; G: gland. J: thick walled blood vessel showing hyperplasia and thrombus formation. K: villi like appearance of hyperplastic mucosa and degeneration of upper epithelial layer; EP, epithelial layers; GL: gland. L: increased nuclear size in infected tissue; N, nucleus; IC, intestinal caeca.