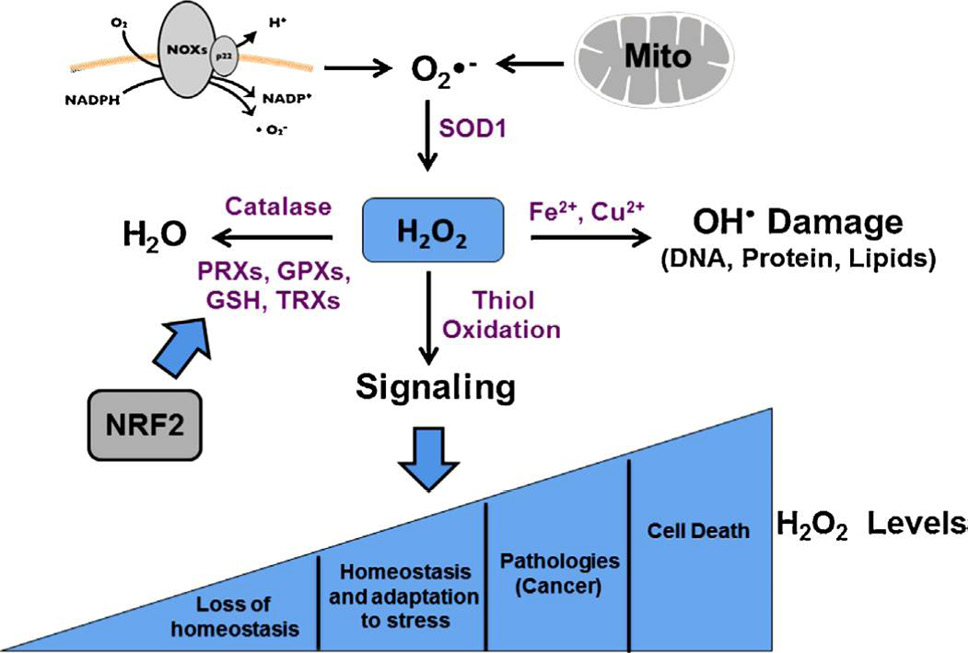
Fig 1
ROS regulation and cellular effects. H2O2 and superoxide (O2_) from mitochondria and cytosolic NADPH oxidases converted to H2O2 by cytosolic SOD1 later on converted to water by catalase, GPXs and PRXs. H2O2 causes damages to DNA, proteins and lipids and cell signaling via OH_ radicals and oxidation of protein‘s thiol. H2O2 at different ranges have different cellular effects; very low range is beneficial to cell ‘s homeostasis and optimum level used to cope with cellular stresses and its level above this range can cause disease (cancer) and very high range leads to cell death.