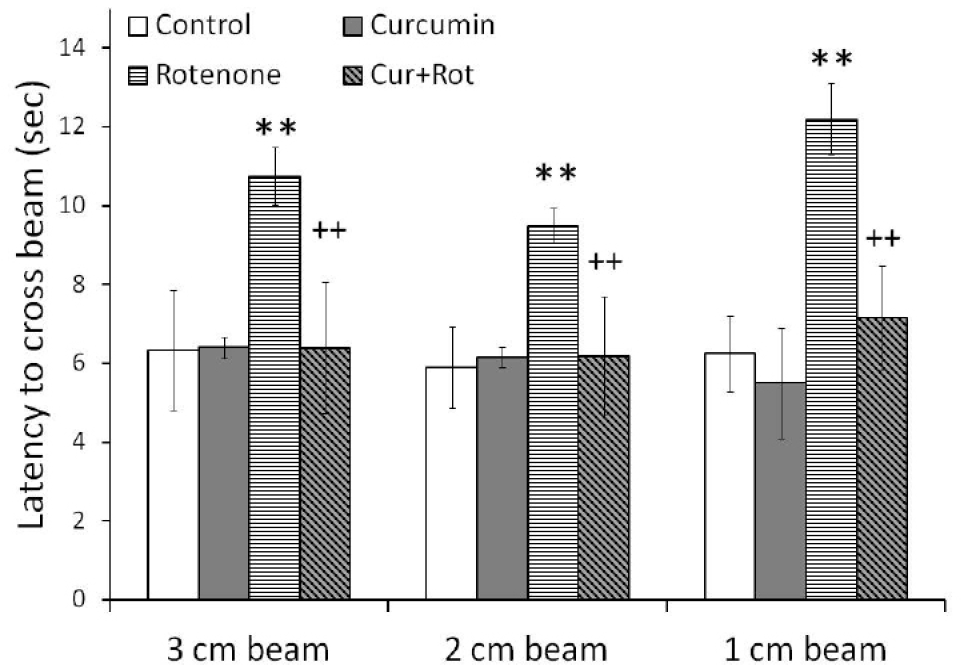
Fig. 7.
Beam test was performed to assess the motor coordination. Subcutaneous injection of rotenone affected the motor coordination and significantly increased the time to cross the beam in all three beams of varying diameters as compared to control rats, confirming the loss of motor skills. Pre-treatment with curcumin significantly normalized the impaired motor activity in Cur+Rot group. Significant differences were obtained by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. **p <0.01 as compared to controls and ++p<0.01 when compared with rotenone injected group (n=6). Values are mean+SD (n=6).