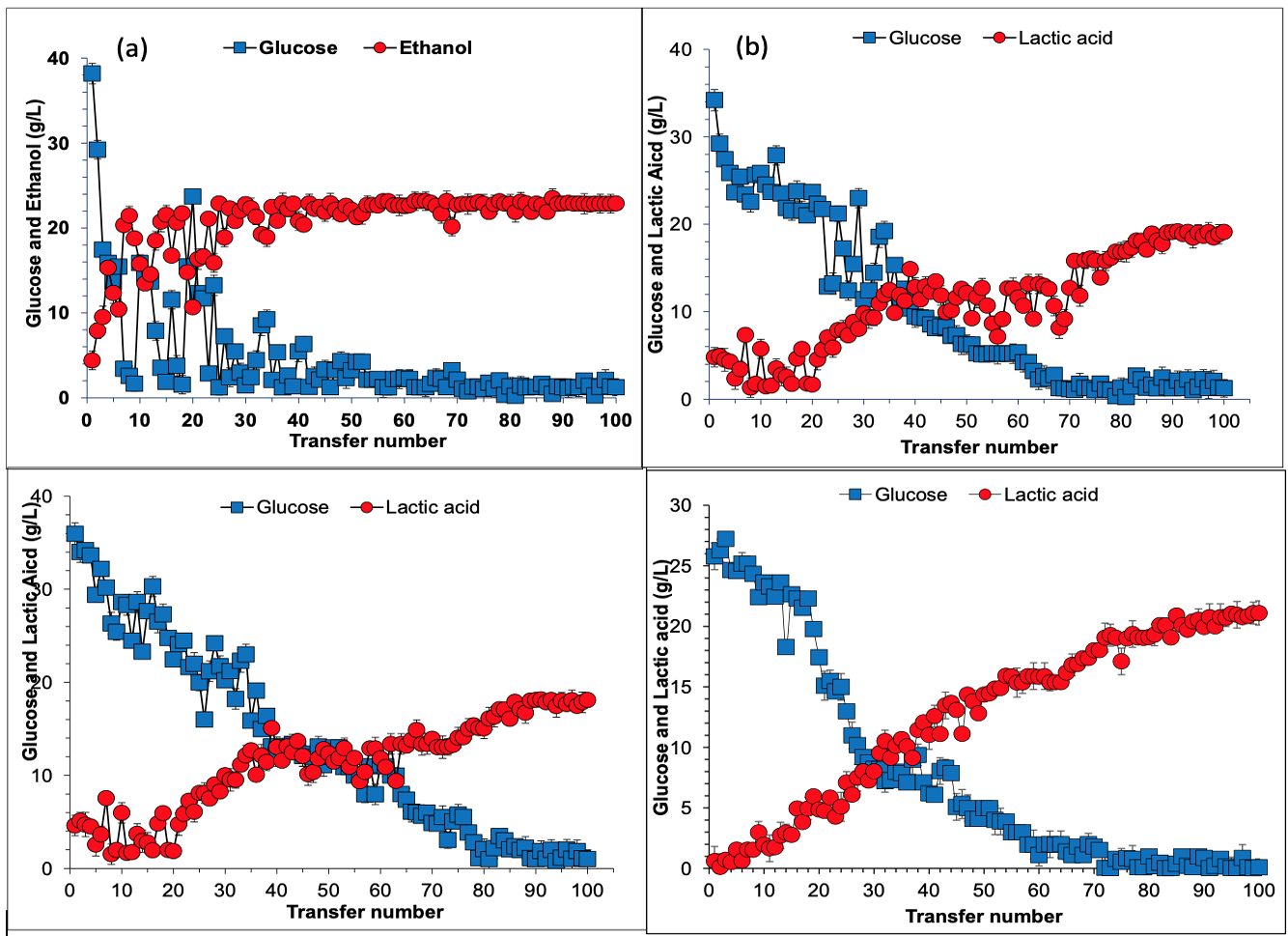
Evolutionary adaptation of ethanol and lactic acid fermenting strains. (a) Long term adaptation of S. cerevisiae Angel using hydrolysate prepared from 15 % w/w freshly pretreated wheat. Conditions: 20 ml wheat straw hydrolysate (100%) supplemented with (g/L) KH2PO4 2, MgSO4 1, NH4 (SO4)2 1, yeast extract 1, 37 °C, pH 5.5 and shaking at 150 rpm. Primarily, S. cerevisiae Angel was inoculated on synthetic medium for activation. In the next step, 10% v/v inoculum was sequentially transferred into fresh 100% wheat straw hydrolysate medium for 100 transfers; each transfer was carried out after 12h of fermentation. (b) Evolutionary adaptation of Pediococcus sp in wheat straw hydrolysate. Conditions: 20 mL of wheat straw hydrolysate (100%) supplemented with tryptone 10.0 g/L, yeast extract 10.0 g/L, MnSO4∙H2O 0.25 g/L, C6H14N2O7 2.0 g/L, MgSO4∙7H2O 0.58 g/L, K2HPO4 2.0 g/L, C6H12O6.∙H2O 22.0 g/L, CH3COONa 5.0 g/L. Strain was activated on MRS medium then 10% v/v of inoculum was transferred to wheat straw hydrolysate for 100 transfers, each transfer was carried out after 12 h of fermentation. (c) Evolutionary adaptation of Lactobacillus sp in wheat straw hydrolysate, where as other conditions were same as mentioned for Pediococcus sp. (d) Evolutionary adaptation of Bacillus coagulans in wheat straw hydrolysate, other conditions were same as mentioned for b.