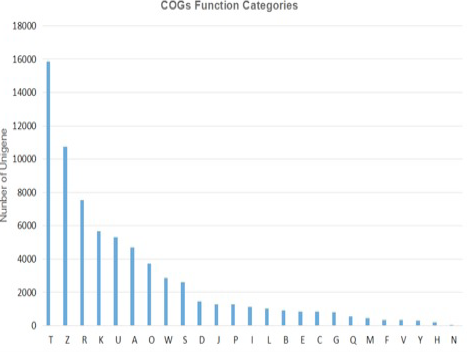
COG functional classification of the final UniGene sequence set generated from the tree shrew hippocampal transcriptome.UniGene classifies the COG functions, compares UniGenes and CDD library by rpstblastn, takes the five best results of E-value < 1e-5 to forecast the classification of COG functions, and map it to different classification of COG. 19305 counts of Unigene were annotated into 25 kinds of COG sorts. The COGs _categories figure indicated the COG sorts distribution of UniGene. T, signal transduction mechanisms: Cytoskeleton: General function prediction only: Transcription; U, Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport; A, RNA processing and modification; O, Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones; W, Extracellular structures: Function unknown: Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning: Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis: Inorganic ion transport and metabolism; I, Lipid transport and metabolism: Replication, recombination and repair: Chromatin structure and dynamics; E, Amino acid transport and metabolism; C, Energy production and conversion; G: Carbohydrate transport and metabolism; Q, Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism; M, Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis; F, Nucleotide transport and metabolism; V, Defense mechanisms; Y, Nuclear structure; H, Coenzyme transport and metabolism; N: Cell motility.