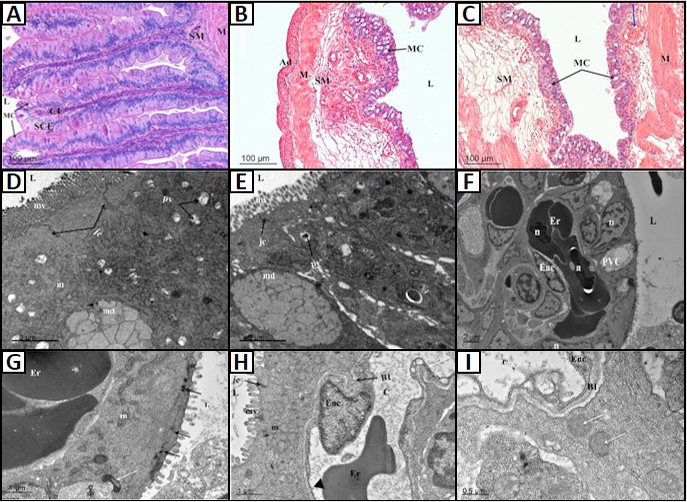
Fig 2
Histological structure and ultrastructure of the intestinal tract of P. dabryanus. A, transverse-section of anterior intestine: simple columnar epithelium, goblet cells in epithelial mucous membrane of anterior intestine, submucosa and muscular layer were shown; B, transverse-section of middle intestine: columnar epithelium and goblet cells in the epithelial mucous membrane of middle intestine, submucosa and muscular layer were shown; C, transverse-section of posterior intestine: columnar epithelium, goblet cells in epithelial mucous membrane of posterior intestine, submucosa and muscular layer were shown. The blue arrow notes the blood vessels; D, showing the mucous epithelial cell of anterior intestine; E, showing the mucous epithelium cell of middle intestine; F, showing the mucous epithelium cell of posterior intestine and blood capillary; G, showing epithelial cell in mucous membrane of posterior intestine adjacent to a capillary. Black arrow notes the electron-dense vesicles; White arrow notes the lamella bodies; H, showing the epithelium in mucous membrane of posterior intestine and endothelial cell of capillary. Black arrowhead notes pore; and White arrow notes pyramidal projection of endothelial cell protruding into the capillary lumen; I, showing thin layers of endothelial cell. White arrows indicate the lamella bodies. Ad, adventitia; BI, basal lamina; C, capillary; CL, central lacteal; Er, erythrocyte; EnC, endothelial cell; jc, junctional complex; L, lumen; M, mucous layer; m, mitochondria; MC, mucous cell; md, mucus droplet; mv , microvillus; n , nucleus; pv, pinocytotic vesicle; PVC, pavement epithelial cell; SCE, simple columnar epithelium; SM, submucosa.