Identification, Molecular Characterization and Expression Pattern Analysis of SoxD Subgroup Genes in Yellow River Carp (Cyprinus carpio)
Identification, Molecular Characterization and Expression Pattern Analysis of SoxD Subgroup Genes in Yellow River Carp (Cyprinus carpio)
RuiHua Zhang, YongFang Jia, TingTing Liang, QianWen Yang, QiYan Du and ZhongJie Chang*
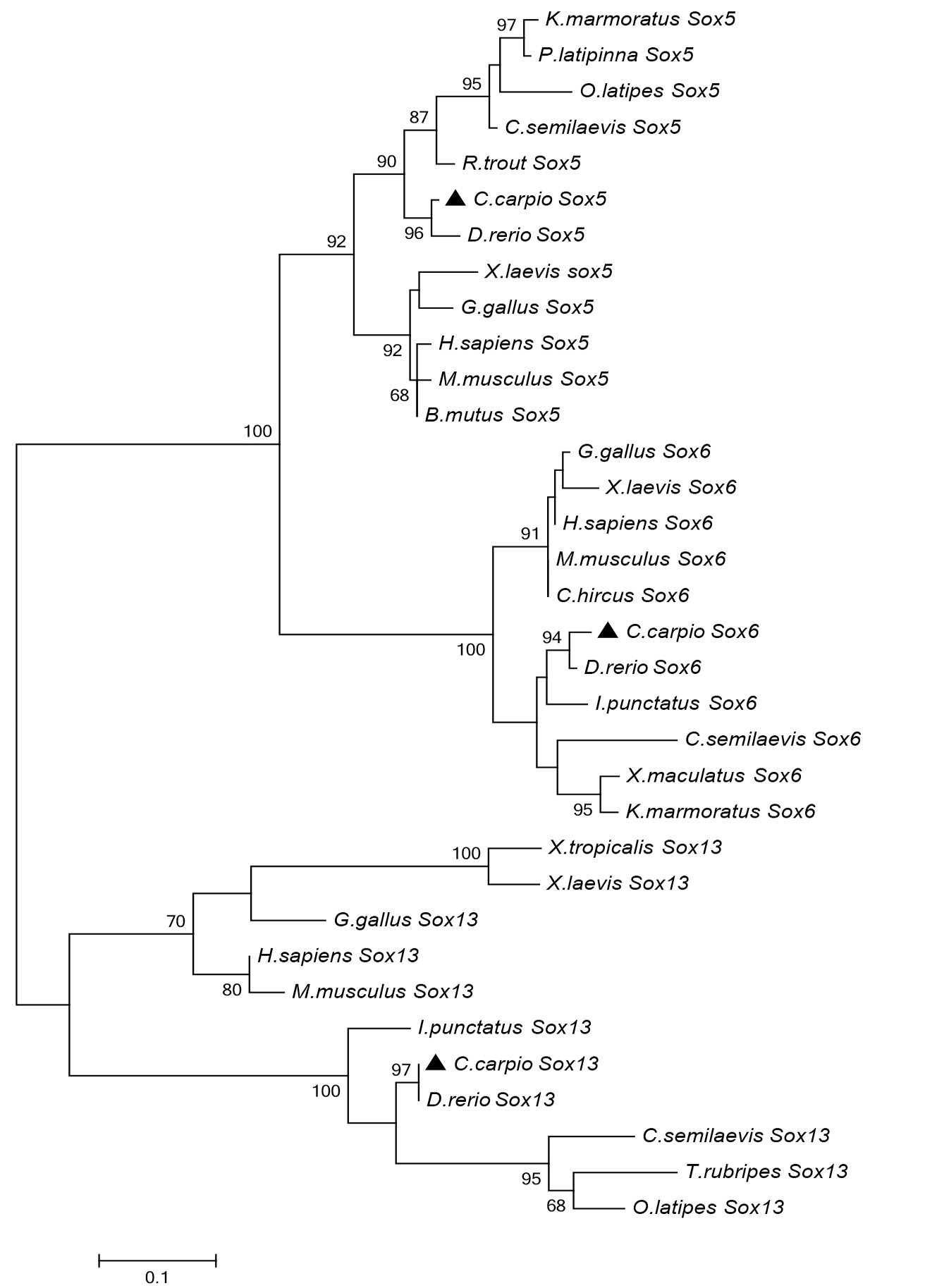
Phylogenetic tree of CcSox5, CcSox6 and CcSox13 in comparison with SoxD proteins in other representative vertebrates using predicted amino acid sequences. The phylogenic tree was constructed by MEGA6 using the Jones–Thornton–Taylor (JTT) model based upon Neighbor-Joining method with 1000 bootstrap replicates. The scale bar is 0.1. The GenBank accession numbers are as follows: Homo sapiens: Sox5, BC060773.1; Sox6, AF309034.1; Sox13, NM_005686.2; Mus musculus: Sox5, AB006330.1; Sox6, U32614.1; Sox13, NM_011439.2; Gallus gallus; Sox5, NM_001004385.1; Sox6, XM_015286512.1; Sox13, XM_004934897.2; Bos taurus: Sox5, NM_001083471.1; Bos mutus: Sox5, XM_005897700.2; Capra hircus: Sox6, :XM_018059599.1; Oryzias latipes: Sox5, NM_001122910.1; Sox13, XM_011475310.1; Xenopus laevis: Sox5, AB682776.1; Sox6, NM_001280658.1; Sox13, NM_001087769.1; Danio rerio: Sox5, NM_001033585.1; Sox6, NM_001123009.1; Xenopus tropicalis: Sox13, XM_012963174.2; Kryptolebias marmoratus: Sox5, XM_017429903.1; Sox6, XM_017441909.1; Poecilia latipinna; Sox5, XM_015049850.1; Cynoglossus semilaevis; Sox5, XM_008315905.2; Sox6, XM_008311513.2; Sox13, XM_017036517.1; Ictalurus punctatus: Sox6, XM_017478071.1; Oncorhynchus mykiss: Sox5, FJ713023.1; Xiphophorus maculatus: Sox6, XM_005805573.1; Ictalurus punctatus: Sox13, XM_017450839.1
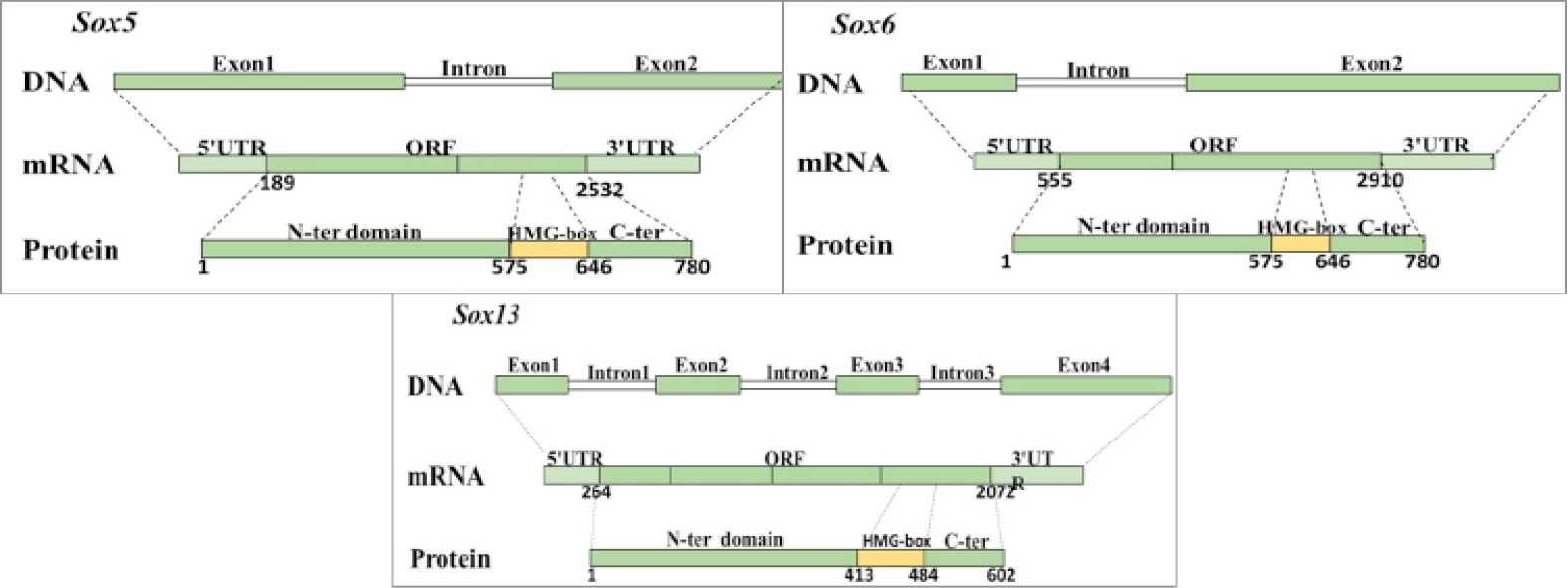
Schematic presentation of CcSox5, CcSox6 and CcSox13. The intron (thin box), 5’ and 3’ UTR (light green), and ORF (dark green) encoding the amino acid sequences are shown relative to their lengths in the cDNA sequences obtained. Protein domains are shown relative to their lengths and positions in the amino acid sequences. N-terminal domain (dark green); HMG-box, high mobility group box domain (orange); C-terminal domain (dark green).
Chromosome syntenic relationship of the CcSox5, CcSox6 and CcSox13 genes with their orthologs. Conserved syntenies are shown for chromosomal segments containing Sox5, Sox6 and Sox13. Rectangles represent genes in chromosome/scaffold and arrows represent gene-coding direction. Chr, chromosome.
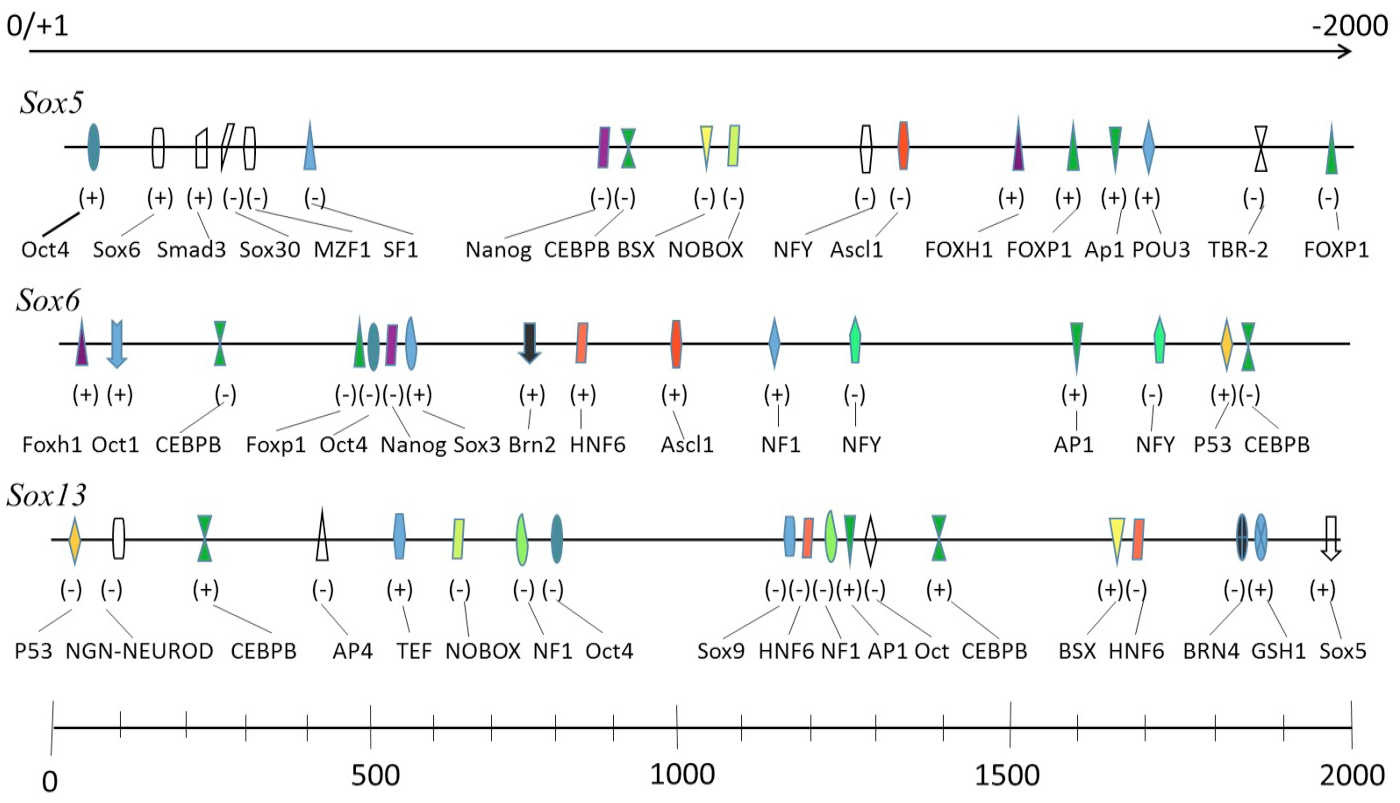
A schematic diagram of putative regulatory motifs in the promoter of CcSox5, CcSox6 and CcSox13. The scale is given above and the full names of the potential TF binding sites are provided at the bottom. Transcriptional initiate site (ATG) is designated as +1. BSX, Brain specific homeobox; BRN4, POU domain transcription factor brain 4; NGN–NEUROD, Neurogenin and NeuroD; Oct4, POU domain, class 5, transcription factor 1; Nanog, Homeobox transcription factor Nanog; FOXP1, Alternative splicing variant of FOXP1, activated in ESCs; AP1, Activator protein 1; CEBPB, CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta; NF-Y, Nuclear factor Y; SF1, Steroidogenic Factor-1.
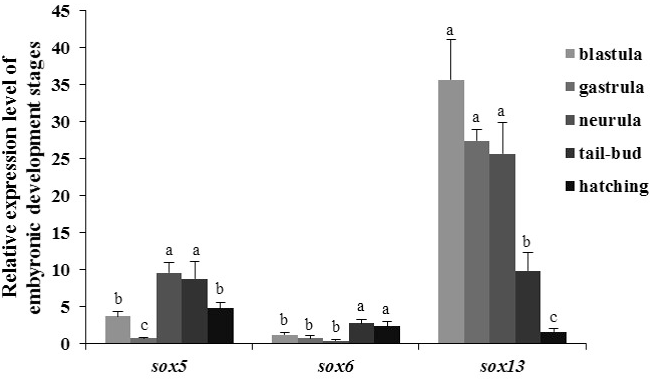
Relative expression of CcSox5, CcSox6 and CcSox13 genes during embryonic development by qRT-PCR analysis. Error bars represent the mean ± SEM (n=6). Significant differences (p < 0.05) exist between any two samples labeled with different single letters.
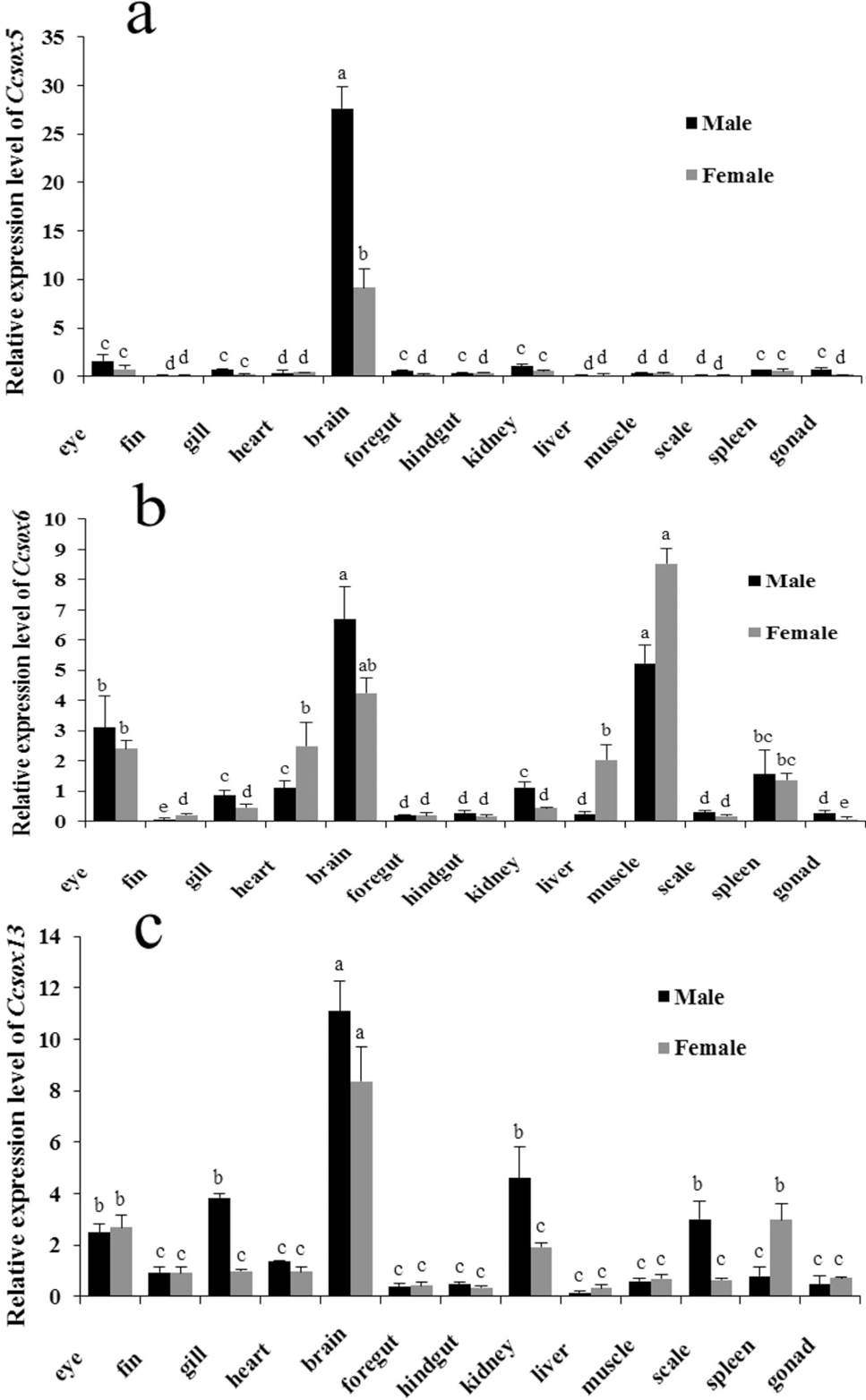
Differential expression of male and female tissues of CcSox5, CcSox6 and CcSox13 genes (a, b, c) by qRT-PCR analysis. Error bars represent the mean ± SEM (n=6). Significant differences (p < 0.05) exist between any two samples labeled with different single letters.
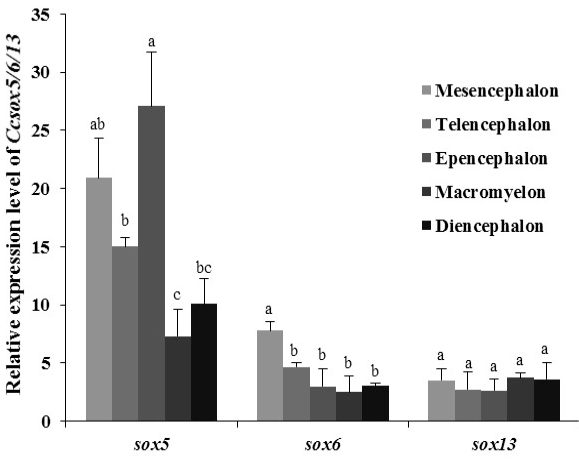
Relative expression of CcSox5, CcSox6 and CcSox13 genes in different parts of the adult brain by qRT-PCR analysis. Error bars represent the mean ± SEM (n=6). Significant differences (p < 0.05) exist between any two samples labeled with different single letter.