Anti-Stress Activity of Oviductus Ranae in Mice with Acute Stress Based on Network Pharmacology
Zhe Lin1, Yumo Li1, Yuchen Wang1, Yuechen Li1, Ke Pei1, Guangfu Lv2, He Lin1* and Zhun Yu3*
1College of Pharmacy, Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun 130117, China
2Jilin Ginseng Academy, Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun 130117, China
3The Third Affiliated Hospital, Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun 130117, China
* Corresponding author: linhe@ccucm.edu.cn; yuzhun0908@126.com
Fig. 1.
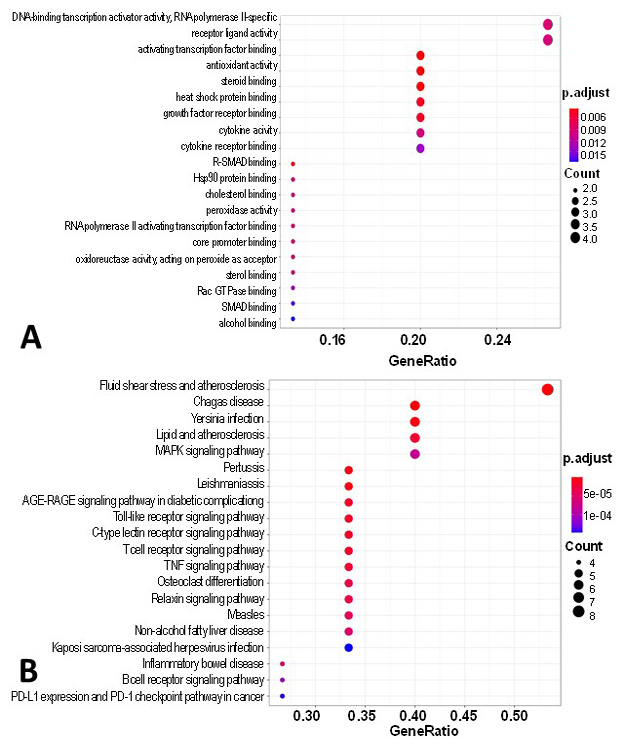
Functional enrichment analysis of the therapeutic targets of OR against stress. (A) The top 20 GO-BP terms; (B) The top 20 KEGG pathway terms.
The circle size represents the count of therapeutic targets enriched in a certain pathway; the associated genes (%) means the percentage of target genes to the background genes of a certain pathway.
Fig. 2.
Effect of OR on the forced swimming endurance test (A) and anoxic tolerance test (B) in mice.
* p <0.05 compared with the control.
Fig. 3.
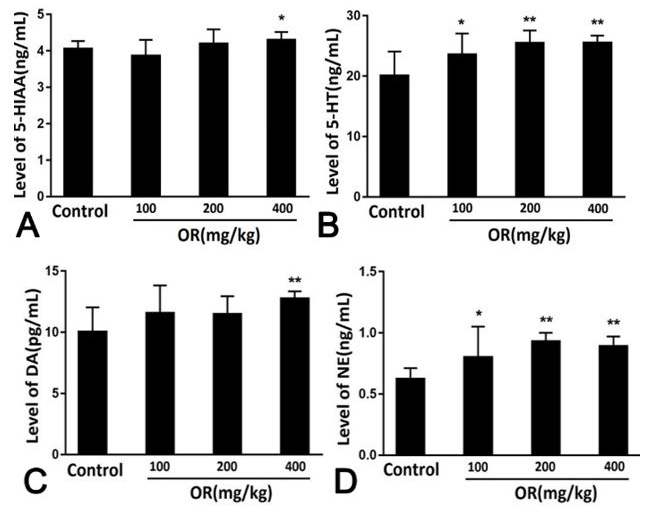
The effect of OR on the changes of monoamine neurotransmitters in brain tissue under stress state.
5-HIAA, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (A); 5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine (B); DA, dopamine (C); NE, norepinephrine (D). * p<0.05 or ** p<0.01 compared with the control.
Fig. 4.
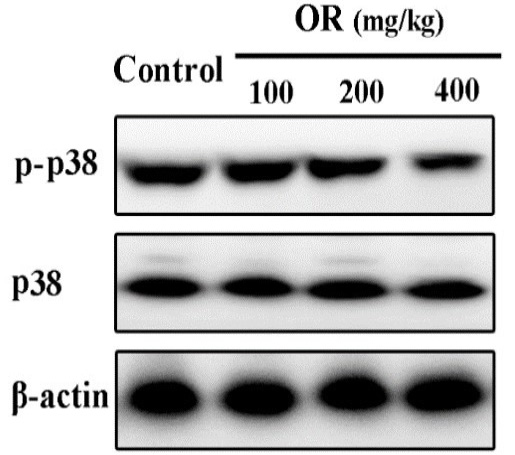
Effects of OR on phosphorylation levels of p38 in the brain tissues by western blot.