Cardioprotective Effect of Naringenin against Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Alteration of Apoptotic Signaling Pathway
Cardioprotective Effect of Naringenin against Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Alteration of Apoptotic Signaling Pathway
Tao Ren1, Guiqiu Cao2, Xiao Han3, Feng Tan1, Qiaoli Chen4, Shicheng Yang5 and Haiyan Zhang6*
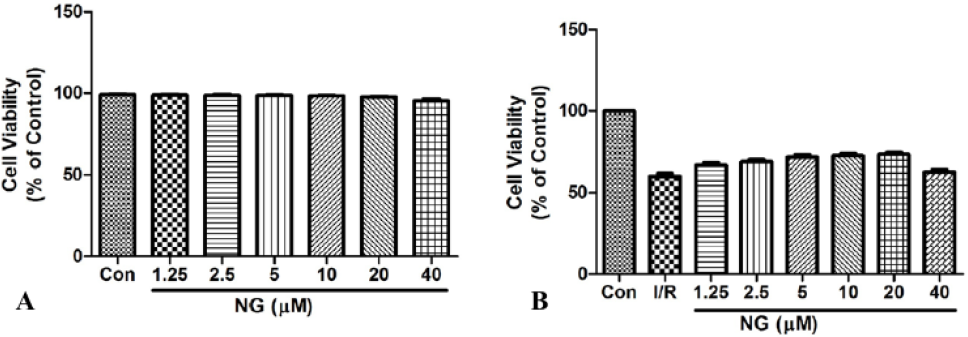
Effect of naringenin on the cell viability by H/R in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. A) H9c2 cells were treated with various concentration of naringenin for 24 h and MTT assay was used for the estimation of cell viability. B) H9c2 cells were treated with for 12 h with naringenin and then exposed to 6h of hypoxia. The data presented as means±SD from three independent experiments.
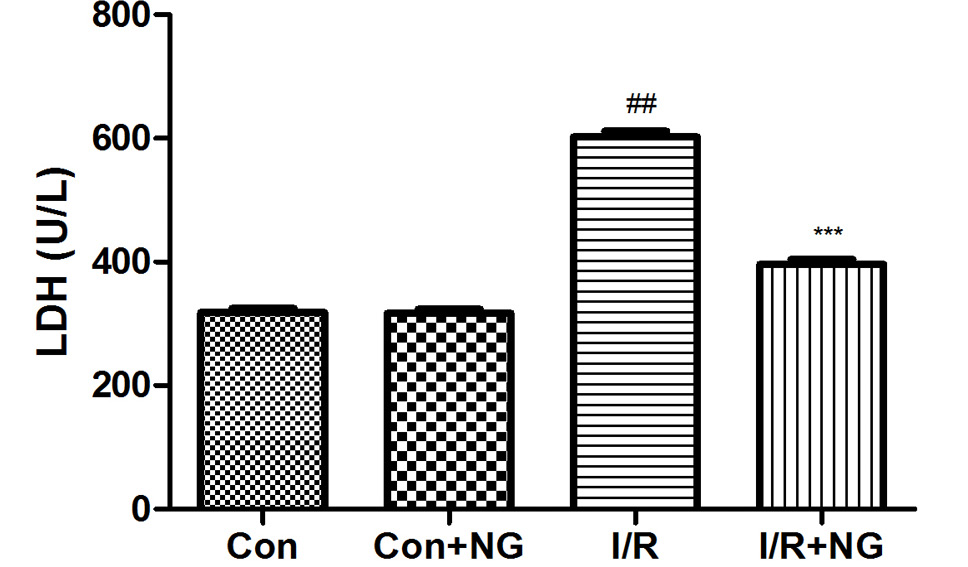
Effect of naringenin on the LDH release by H/R in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. The data presented as means±SD from three independent experiments. ##P < 0.01 versus control group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus H/R group.
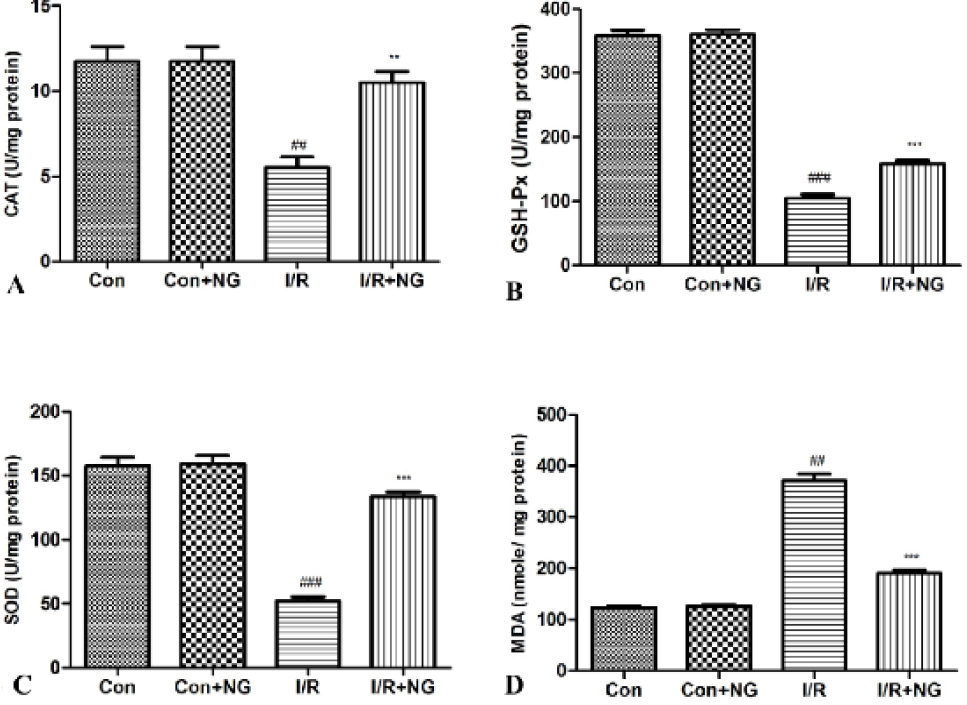
Effect of naringenin on antioxidant parameter of H/R in H9c2 cardiomyocytes cells. A) CAT, B) GSH-Px, C) SOD and D) MDA. The data presented as means±SD from three independent experiments. ##P < 0.01 versus control group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus H/R group.
Effect of naringenin on ROS concentration of H/R in H9c2 cardiomyocytes cells. The data presented as means±SD from three independent experiments. ##P < 0.01 versus control group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus H/R group.
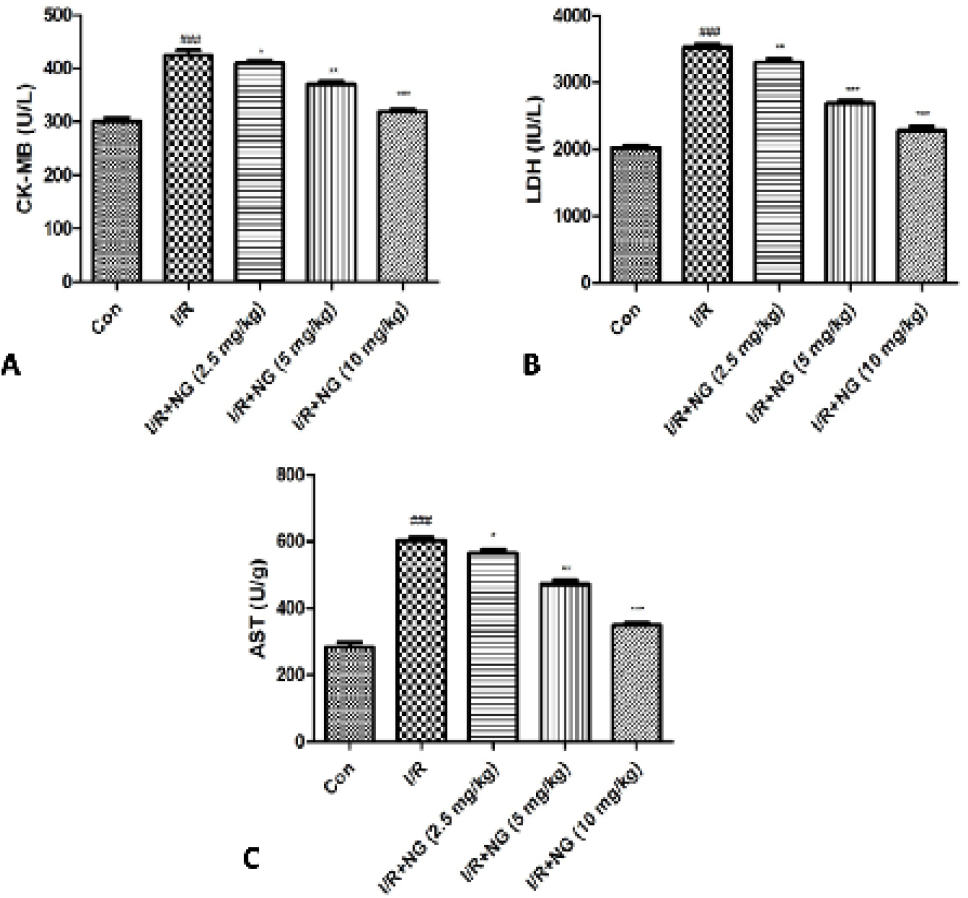
Effect of naringenin on the biochemical parameter of I/R induced mice. A) CK-MB, B) LDH and C) AST. Dennett’s test was used for statistically significance *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001.
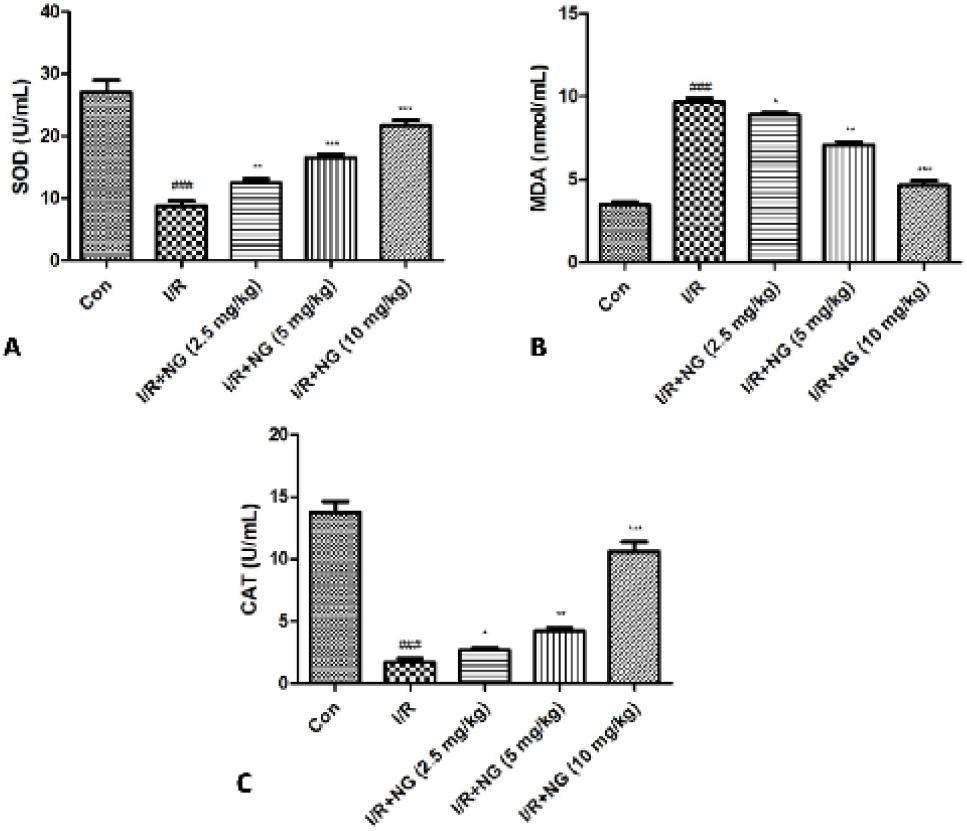
Effect of naringenin on the antioxidant parameters of I/R induced mice. A) SOD, B) CAT and C) MDA. Dennett’s test was used for statistically significance *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001.
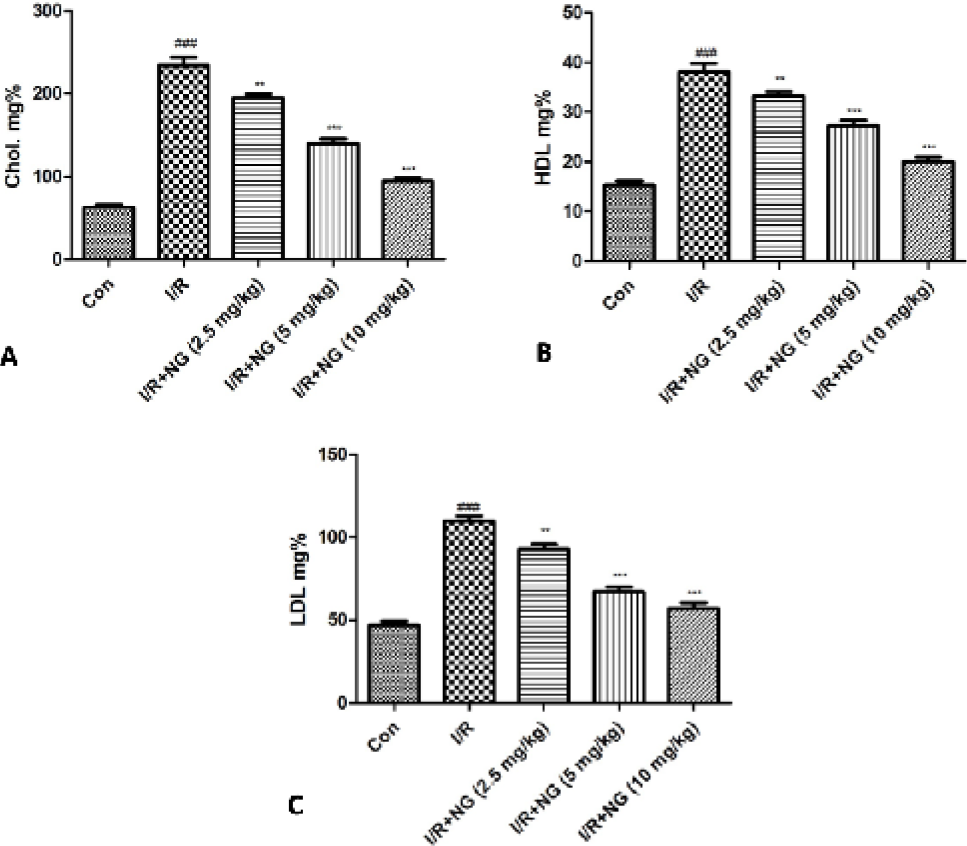
Effect of naringenin on the lipid parameters of I/R induced mice. A) Cholesterol, B) High density lipoprotein and C) Low density lipoprotein. Dennett’s test was used for statistically significance *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001.
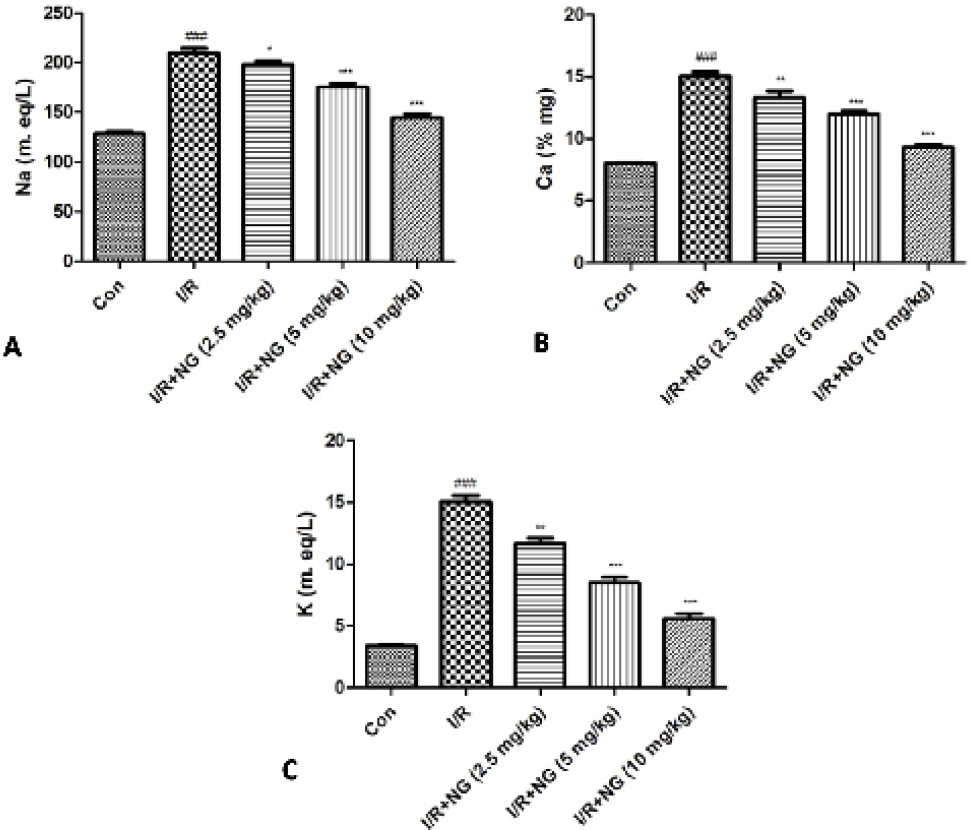
Effect of naringenin on the Na, Ca and K level of I/R induced mice. A) Na, B) Ca and C) K. Dennett’s test was used for statistically significance *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001.
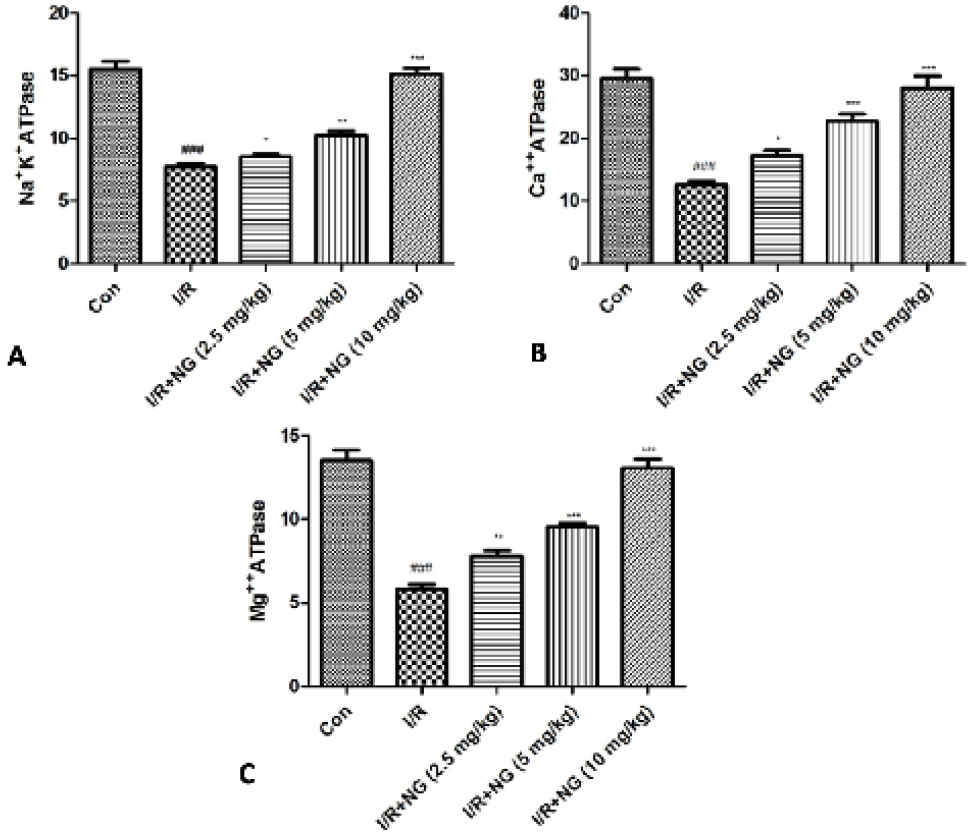
Effect of naringenin on the membrane-bound enzymes of I/R induced mice. A) Mg++ ATPase, B) Na+K+ ATPase and C) Ca++ ATPase. Dennett’s test was used for statistically significance *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001.
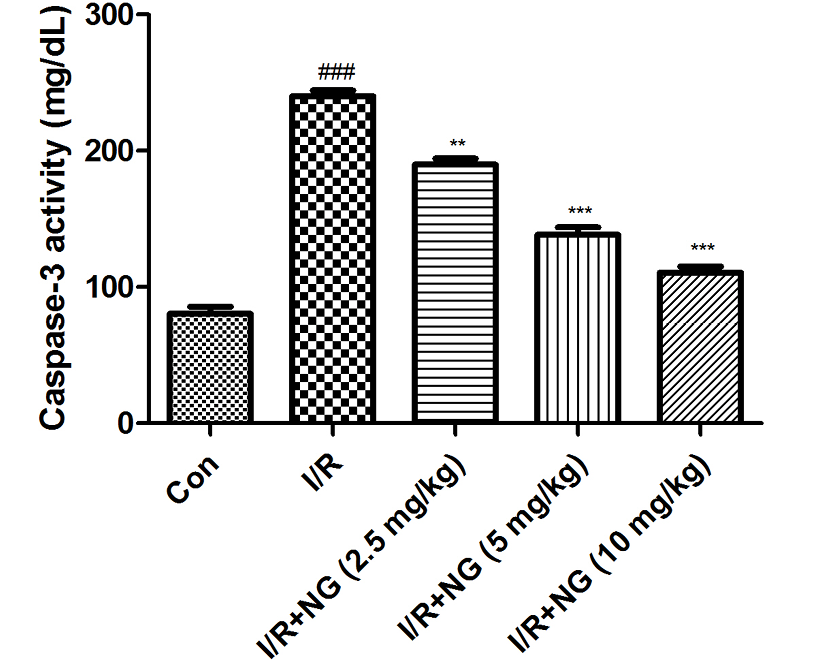
Effect of naringenin on the caspase-3 marker of I/R induced mice. Dennett’s test was used for statistically significance *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001.
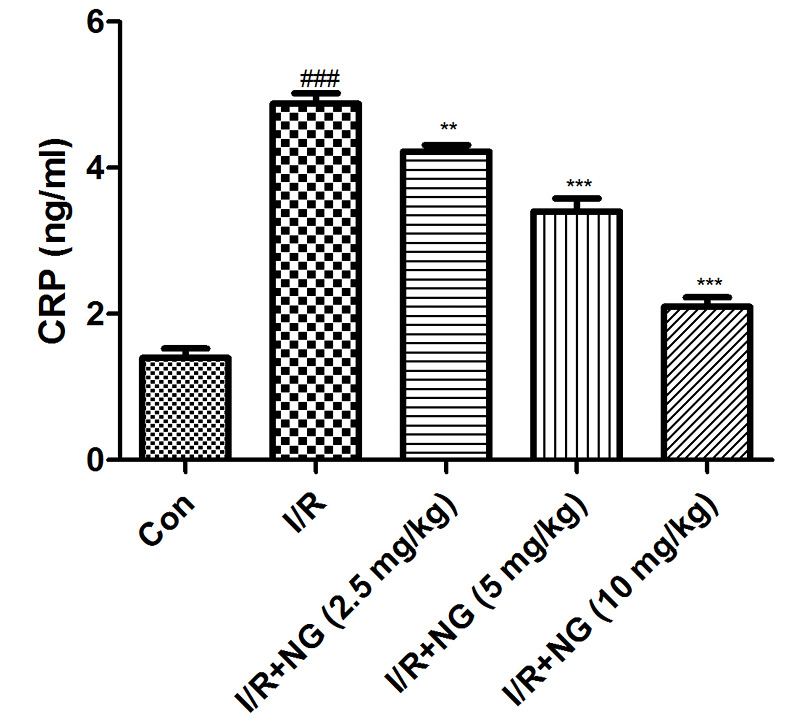
Effect of naringenin on the CPR level of I/R induced mice. Dennett’s test was used for statistically significance *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001.